In the world of machining and cutting tools, the geometry and design of carbide brazed tips play a crucial role in determining their cutting performance. These small yet incredibly powerful components are engineered to withstand extreme conditions and deliver precise, efficient cuts. This blog delves into the intricacies of carbide brazed tip geometry and design, exploring how these factors influence cutting performance and what considerations are essential for optimizing tool efficiency.
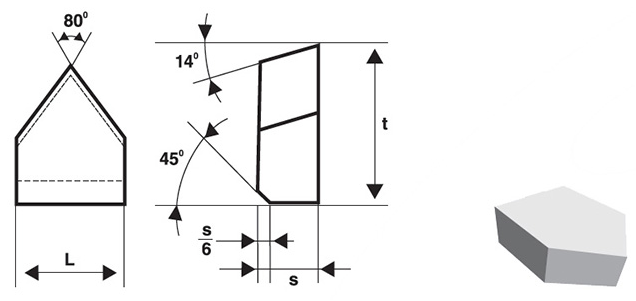
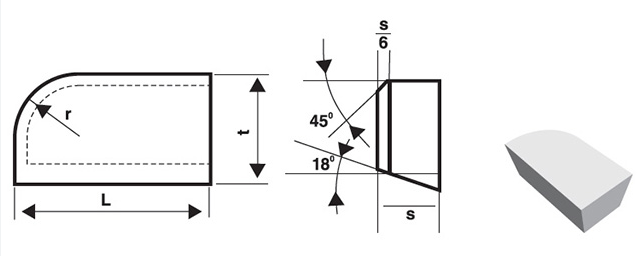
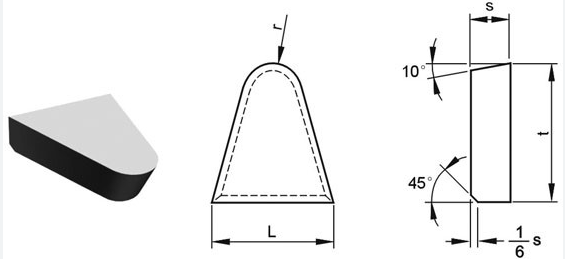
Overview
Carbide brazed tips are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. The geometry and design of these tips are meticulously crafted to enhance cutting performance, reduce tool wear, and improve overall machining efficiency. Understanding the impact of geometry and design on cutting performance is vital for selecting the right tools and achieving optimal results in different applications.
Detailed Introduction to Carbide Brazed Tip Geometry and Design
What is Carbide Brazed Tip Geometry?
Carbide brazed tip geometry refers to the shape, angles, and dimensions of the cutting edge and surfaces of the tip. Key geometric parameters include:
- Rake Angle: The angle between the cutting edge and the workpiece surface. It influences chip formation and cutting force.
- Relief Angle: The angle between the flank of the tool and the workpiece surface, preventing rubbing and reducing friction.
- Cutting Edge Angle: The angle formed by the intersection of the rake and flank faces, affecting the tool’s strength and wear resistance.
- Corner Radius: The rounded edge at the tool’s tip, impacting surface finish and tool life.
How Does Design Influence Cutting Performance?
The design of a carbide brazed tip encompasses its overall structure, including the placement of the cutting edges, the distribution of material, and any additional features such as chip breakers or coatings. These design elements work in harmony with the geometry to optimize cutting performance. Key design aspects include:
- Tip Shape: Different shapes (e.g., square, round, diamond) are suited for specific applications and materials.
- Chip Breakers: Features that help control chip flow and prevent chip clogging, enhancing cutting efficiency.
- Coatings: Protective layers that reduce friction, increase wear resistance, and extend tool life.
Impact of Geometry and Design on Cutting Performance
The geometry and design of carbide brazed tips directly affect several critical aspects of cutting performance, including:
1. Cutting Efficiency
- Rake Angle: A positive rake angle reduces cutting forces and energy consumption, improving efficiency. However, it may reduce tool strength.
- Relief Angle: Adequate relief angles prevent friction and heat buildup, enhancing cutting efficiency.
2. Tool Life
- Cutting Edge Angle: Larger cutting edge angles provide greater strength and wear resistance, extending tool life.
- Corner Radius: A larger corner radius distributes cutting forces more evenly, reducing wear and prolonging tool life.
3. Surface Finish
- Rake and Relief Angles: Optimized angles result in smoother cuts and better surface finishes.
- Corner Radius: A larger radius can improve surface finish but may require higher cutting forces.
4. Chip Control
- Chip Breakers: Properly designed chip breakers help manage chip flow and prevent clogging, maintaining cutting efficiency.
- Rake Angle: Influences chip formation and flow, impacting overall chip control.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Carbide Brazed Tips
Selecting the right carbide brazed tips involves considering several factors related to geometry and design:
- Material Being Machined: Different materials require specific geometries and designs for optimal cutting performance.
- Cutting Conditions: Factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut influence the choice of tip geometry.
- Machining Application: The type of machining operation (e.g., turning, milling, drilling) dictates the appropriate tip design.
- Tool Holder and Machine Compatibility: Ensuring the carbide brazed tip is compatible with the tool holder and machine specifications.
Comparative Analysis of Carbide Brazed Tip Geometries
The table below highlights the impact of different geometric parameters on cutting performance:
| Geometric Parameter | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Rake Angle | Reduced cutting forces, improved efficiency | Lower tool strength |
| Relief Angle | Reduced friction, enhanced surface finish | Potential for increased tool wear if excessive |
| Cutting Edge Angle | Increased tool strength, extended tool life | Higher cutting forces |
| Corner Radius | Improved surface finish, reduced wear | Higher cutting forces, potential for chatter |
Applications of Carbide Brazed Tips
Carbide brazed tips are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some key applications:
1. Metalworking
- Turning Operations: Precision machining of cylindrical parts.
- Milling Operations: Efficient material removal in milling processes.
- Drilling Operations: High-performance drilling in various materials.
2. Woodworking
- Cutting and Shaping: Precision cutting and shaping of wooden components.
- Routing: High-speed routing for intricate designs and patterns.
3. Automotive Industry
- Engine Component Machining: Precise machining of engine parts for optimal performance.
- Transmission Part Manufacturing: High-precision machining of transmission components.
4. Aerospace Industry
- Aircraft Component Machining: Machining of critical aircraft components with high precision.
- Landing Gear Machining: Durable and precise machining of landing gear parts.
Comparison of Carbide Brazed Tips from Different Suppliers
The table below compares carbide brazed tips from different suppliers based on key parameters:
| Supplier | Location | Price Range (per piece) | Specialties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kennametal | USA | $10 – $50 | High-performance cutting tips, custom geometries |
| Element Six | UK | $12 – $55 | Advanced designs, precision engineering |
| TRUER | China | $8 – $45 | Cost-effective solutions, high-volume production |
| Sumitomo Electric | Japan | $15 – $60 | Innovative designs, superior quality control |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Geometries
The table below outlines the pros and cons of various carbide brazed tip geometries:
| Geometry | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Rake | Reduced cutting forces, improved chip flow | Lower tool strength, potential for chipping |
| Negative Rake | Increased tool strength, suitable for hard materials | Higher cutting forces, increased power consumption |
| Large Corner Radius | Improved surface finish, reduced tool wear | Higher cutting forces, potential for chatter |
| Small Corner Radius | Lower cutting forces, precise cuts | Increased tool wear, potential for poor surface finish |
Related Topics: Advanced Coatings for Carbide Brazed Tips
In addition to geometry and design, advanced coatings play a significant role in enhancing the performance of carbide brazed tips. Coatings such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) provide additional benefits:
- Reduced Friction: Coatings reduce friction between the tool and workpiece, enhancing cutting efficiency.
- Increased Wear Resistance: Coatings protect the tool from wear, extending its life.
- Improved Heat Resistance: Coatings help dissipate heat, preventing thermal damage to the tool.
Why Choose Carbide Brazed Tips for High-Performance Machining
Carbide brazed tips are an excellent choice for high-performance machining due to their superior hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain cutting efficiency under extreme conditions. The combination of optimized geometry and advanced design ensures these tools deliver precise, efficient cuts, making them indispensable in various industries.
FAQ
1. How does the rake angle affect cutting performance?
A: The rake angle influences chip formation and cutting forces. A positive rake angle reduces cutting forces and improves efficiency but may compromise tool strength.
2. What is the importance of the relief angle in carbide brazed tips?
A: The relief angle prevents friction and heat buildup between the tool and workpiece, enhancing cutting efficiency and reducing tool wear.
3. How do chip breakers enhance cutting performance?
A: Chip breakers control chip flow and prevent clogging, maintaining cutting efficiency and reducing the risk of tool damage.
4. What factors should be considered when selecting a corner radius?
A: The corner radius affects surface finish and tool wear. A larger radius improves finish and reduces wear but requires higher cutting forces.
5. How do coatings improve the performance of carbide brazed tips?
A: Coatings reduce friction, increase wear resistance, and improve heat dissipation, enhancing the overall performance and longevity of the tools.
By understanding the impact of geometry and design on the cutting performance of carbide brazed tips, you can make informed decisions when selecting and using these tools. This knowledge will help you achieve optimal machining results, improve efficiency, and extend the life of your cutting tools.




