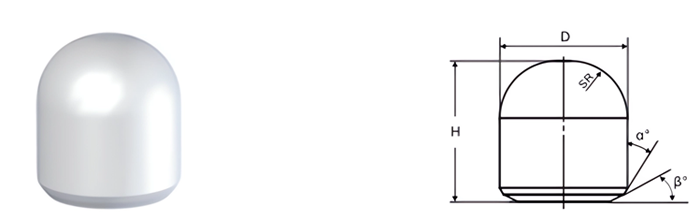
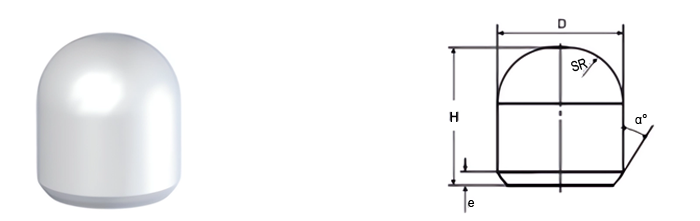
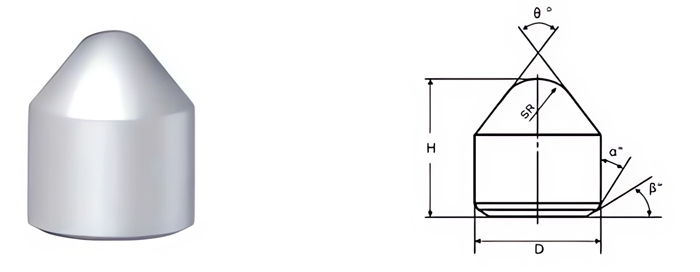
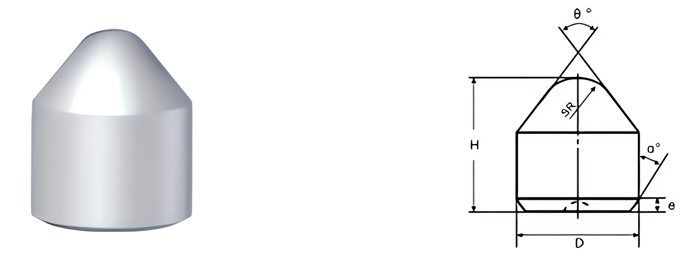
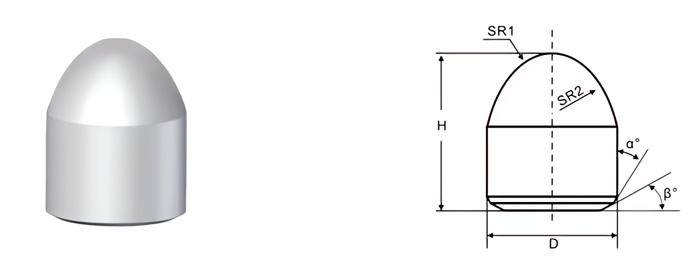
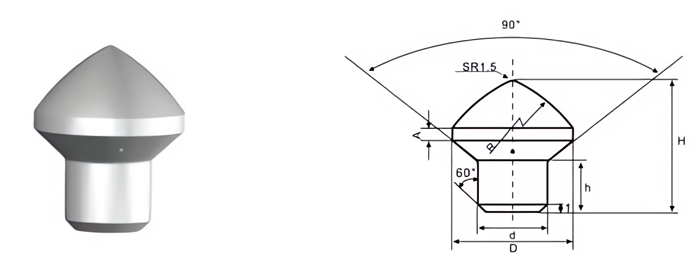
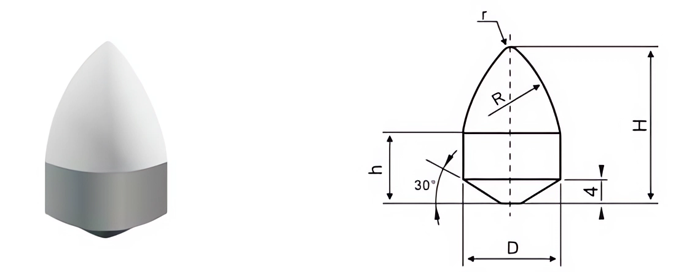
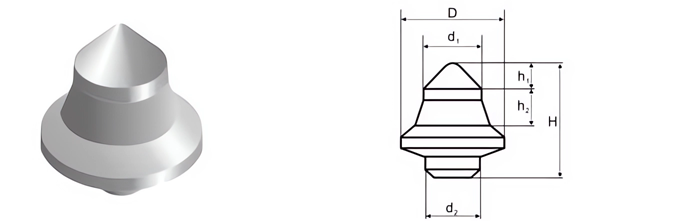
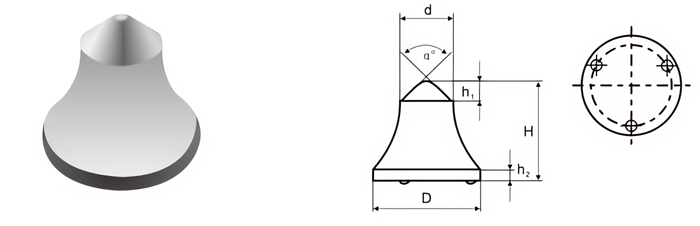
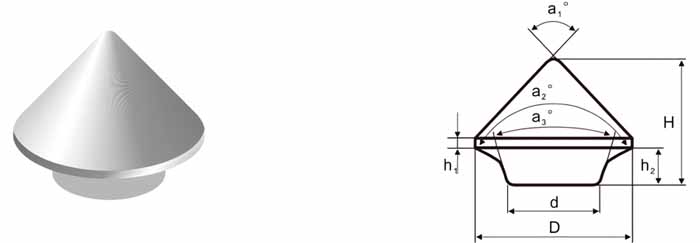
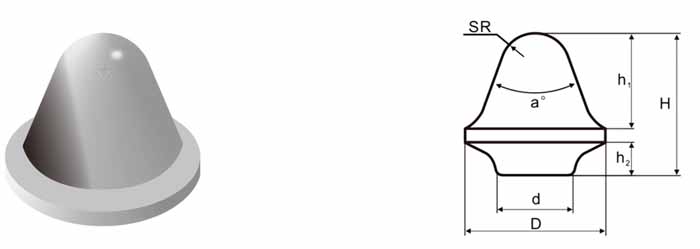
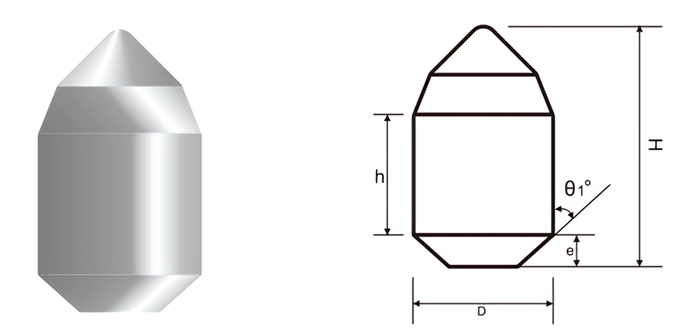
- Cutting Efficiency: Shape and size impact penetration and material removal.
- Wear Resistance: Optimized designs reduce wear and prolong tool life.
- Heat Dissipation: Specific geometries enhance thermal management.
- Application Suitability: Tailored designs improve performance in drilling, mining, and construction.
The optimal button type and grade depend on factors like the hardness of the coal seam, the type of mining equipment used, and the desired balance between penetration and wear resistance. Consulting with our technical experts is recommended for personalized guidance.
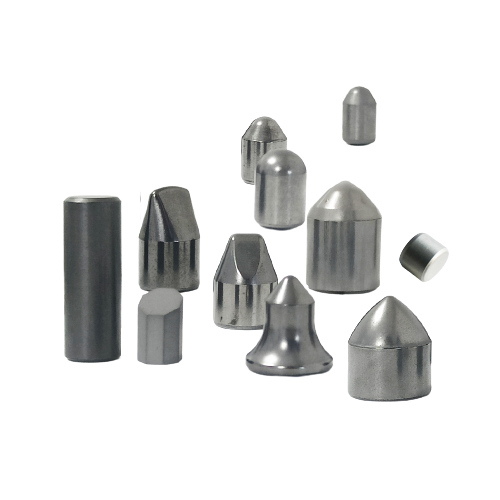
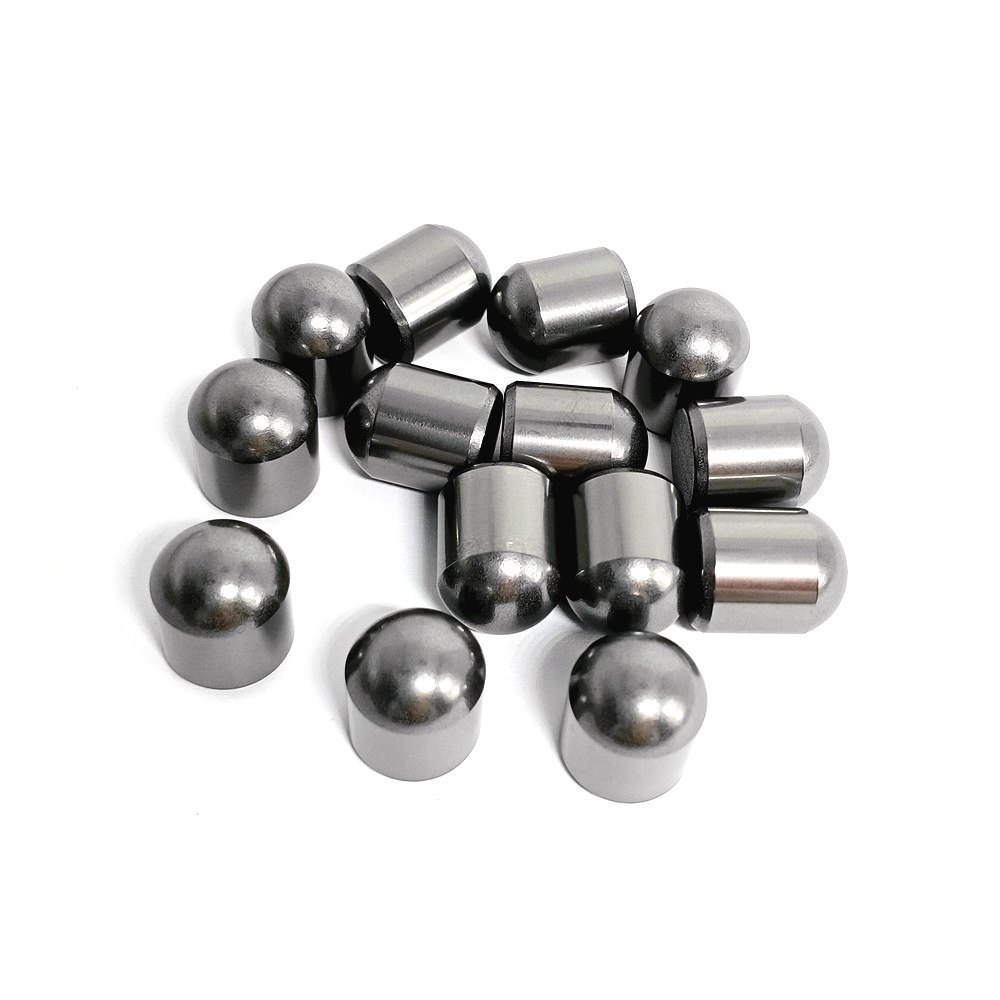
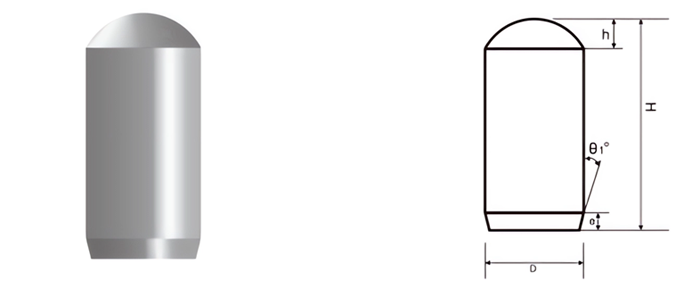
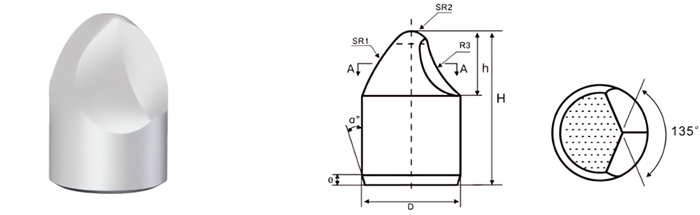
- Spherical Buttons: For hard rock drilling and mining.
- Conical Buttons: Ideal for percussive drilling and impact resistance.
- Parabolic Buttons: Used in soft to medium-hard rock formations.
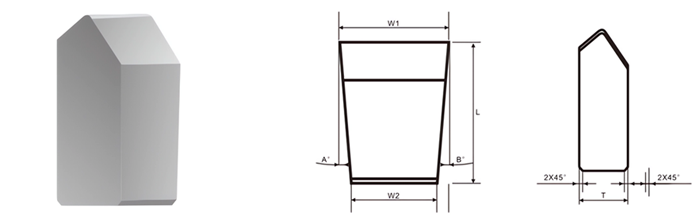
- Chisel Buttons: For cutting and breaking applications.
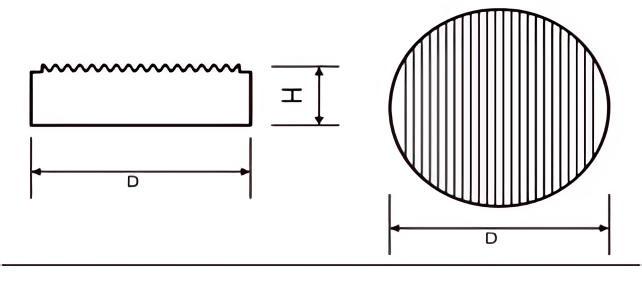
- Flat-top Buttons: For general-purpose and high-abrasion drilling.