When it comes to industrial and machining applications, end chamfered ground carbide rods are a key material. These rods combine advanced metallurgy with precision engineering to provide robust performance in demanding conditions. Let’s dive deep into their specifications, applications, and everything else you need to know. Buckle up—this is going to be both educational and fascinating.
What is an End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rod?
An end chamfered ground carbide rod is a high-performance material designed for cutting, drilling, and machining operations. These rods have chamfered edges, ensuring smoother integration into tooling setups. The ground finish provides dimensional precision, ensuring a perfect fit in various mechanical and industrial applications.

Types of End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rods
| Type | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Chamfered Rods | Feature uniform chamfered ends, suitable for general-purpose tooling. | General machining, industrial tools manufacturing. |
| Straight Coolant Hole Rods | Include holes for coolant flow to reduce heat during machining. | High-speed machining, precision drilling. |
| Helical Coolant Hole Rods | Offer twisted coolant holes for enhanced coolant flow efficiency. | Deep hole drilling, hard material cutting. |
| Micro-Grain Carbide Rods | Made with fine-grain powders for enhanced hardness and wear resistance. | Aerospace, automotive, and high-precision manufacturing. |
| Ultra-Fine Grain Carbide Rods | Use ultra-fine grains for superior strength and toughness. | Cutting hard metals like titanium and Inconel. |
| Coated Carbide Rods | Feature surface coatings like TiN or TiAlN for added wear resistance. | High-temperature operations, extended tool life. |
| Non-Magnetic Carbide Rods | Designed to minimize magnetic interference in specific applications. | Medical tools, electronic component manufacturing. |
| Mixed Grain Carbide Rods | Blend grains of various sizes to optimize performance across strength and hardness. | Versatile machining applications. |
| Impact-Resistant Carbide Rods | Offer enhanced toughness to withstand repeated mechanical impacts. | Hammer drills, high-load industrial equipment. |
| Corrosion-Resistant Carbide Rods | Made with additives for improved chemical resistance. | Oil and gas industries, chemical processing tools. |
Raw Material and Composition Analysis of End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rods
The primary material in these rods is tungsten carbide, a compound made from tungsten and carbon. It’s one of the hardest materials available and is often combined with cobalt or nickel as a binder. The ratio of tungsten carbide to binder significantly affects the rod’s properties.
Typical Composition
| Component | Percentage | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | 85–95% | Provides hardness and wear resistance. |
| Cobalt/Nickel | 5–15% | Acts as a binder for toughness. |
| Additives (e.g., TiC, TaC) | 0–5% | Enhance specific properties like heat or corrosion resistance. |
Applications of End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rods
| Application | Industry | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Cutting Tools | Machining, toolmaking | Provides sharp, durable edges for high-speed cutting. |
| Aerospace Component Manufacturing | Aerospace | Handles high-strength alloys like titanium. |
| Oil and Gas Drilling Equipment | Energy | Withstands extreme pressures and abrasive conditions. |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Healthcare | Enables precision in surgical instruments. |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Automotive | Enhances efficiency in machining engine components. |
| Die and Mold Making | Tool and Die | Ensures smooth finishes for complex molds. |

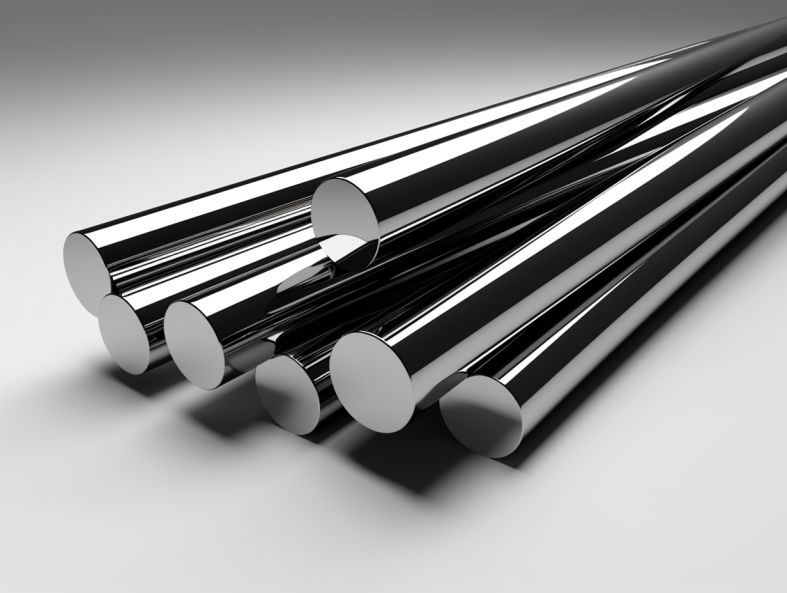


Production Process Flow of End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rods
Producing these rods involves several critical steps to ensure quality and consistency:
- Powder Preparation: Tungsten carbide powder and binders are mixed in precise proportions.
- Pressing: The mixture is pressed into rod-shaped molds.
- Sintering: The pressed rods are sintered at high temperatures to bond the particles.
- Chamfering and Grinding: Edges are chamfered, and surfaces are ground to achieve precision dimensions.
- Quality Inspection: Final products undergo rigorous testing for hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy.
Material Properties of End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rods
| Property | Range | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 85–94 HRA | Determines wear resistance. |
| Density | 14.5–15.1 g/cm³ | Indicates material compactness. |
| Transverse Rupture Strength | 2000–4000 MPa | Reflects toughness under mechanical stress. |
| Thermal Conductivity | 60–100 W/m·K | Shows heat dissipation capability. |
| Magnetic Permeability | <0.2 | Non-magnetic options for sensitive applications. |
Specifications, Sizes, Shapes, and Standards
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Diameter Range | 1–50 mm |
| Length Range | 30–330 mm |
| Shape Options | Round, square, hexagonal. |
| Standards Complied | ISO 9001, DIN 6527, ANSI B212. |
Hardness, Strength, and Wear Resistance of Straight Coolant Hole Carbide Rods
| Attribute | Measurement | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 90–93 HRA | Handles abrasive environments with ease. |
| Strength | 3000–4000 MPa | Resists cracking under load. |
| Wear Resistance | High | Extends lifespan in demanding conditions. |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Supplier | Location | Pricing Range ($/kg) | Specialization |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ Carbide Co. | Germany | 50–70 | High-precision rods with custom specifications. |
| ABC Tungsten Supplies | USA | 60–80 | Ultra-fine grain carbide rods. |
| Global Metals Ltd. | China | 40–65 | Affordable options with consistent quality. |
Selecting the Right End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rod
| Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Application Type | Choose micro-grain rods for precision; straight coolant rods for cooling. |
| Material to Cut | Hard metals require ultra-fine grain carbide. |
| Budget | Consider standard rods for general use, premium for critical tasks. |
Advantages and Limitations of End Chamfered Ground Carbide Rods
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Extremely wear-resistant. | Higher initial cost. |
| Versatility | Suitable for a variety of industries. | Limited flexibility compared to softer materials. |
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the main benefits of carbide rods? | Superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. |
| How do coolant hole designs improve performance? | Enhance heat dissipation and prolong tool life during high-speed cutting. |
| Can these rods cut titanium alloys? | Yes, especially micro-grain and ultra-fine grain carbide rods. |




