- Carbide strips
Carbide strips
Carbide strips are commonly used in industrial settings to make tools and equipment that need to to withstand high levels of wear and tear in harsh environments attributed to their exceptional hardness and resistance to abrasion.
We offer a wide range of carbide grades tungsten carbide strips to ensure that our customers can find the right carbide grade to fit their unique requirement. Whether you need tungsten carbide standard strips in stock or customized strips carbide flat bar, we have the perfect solution for you,
A comprehensive standard selection of tungsten carbide strips in various dimensions for each grade is available in the below tables, but other sizes, tolerances & configurations of carbide flat bar also available on request.
Contact us if what you need is not shown here.
Introduction
Carbide strips are flat and rectangular-shaped components made from tungsten carbide and a binder material. They are known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and strength, making them well-suited for various industrial applications.
Carbide strips are commonly used in cutting tools, wear parts, and tooling dies where durability and performance are critical. They offer superior resistance to abrasion, high temperatures, and mechanical stress, allowing them to withstand demanding machining operations.
Composition and Structure
Carbide strips are primarily composed of tungsten carbide particles and a binder material, typically cobalt or nickel. The tungsten carbide particles provide the strips with exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and high strength, while the binder material acts as a matrix that holds the carbide particles together.
The specific composition and ratio of tungsten carbide to binder material can vary depending on the desired properties of the carbide strips and the intended application. Different grades and formulations are available to achieve specific hardness, toughness, and resistance to wear or corrosion.

Exceptional Hardness
Carbide strips exhibit outstanding hardness, providing excellent resistance to wear and abrasion in demanding applications.
Superior Wear Resistance
These strips offer exceptional wear resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance even in high-stress machining operations.
High Strength
Carbide strips possess high strength, allowing them to withstand heavy loads and extreme operating conditions without deformation.
Excellent Thermal Stability
These strips maintain their hardness and strength at elevated temperatures, enabling them to withstand high-speed machining without compromising performance.
Corrosion Resistance
Carbide strips are resistant to corrosion and oxidation, making them suitable for use in harsh and corrosive environments.
Dimensional Stability
These strips exhibit excellent dimensional stability, ensuring consistent performance and accuracy during machining operations.
Low Friction Coefficient
Carbide strips have a low friction coefficient, minimizing energy losses and reducing heat generation during machining.
Versatility
Carbide strips are versatile and find applications in cutting tools, wear parts, tooling dies, and industrial machinery components.
Raw Material Selection
High-quality tungsten carbide powder and a binder material, such as cobalt or nickel, are carefully selected based on the desired properties of the carbide strips.
Mixing
The tungsten carbide powder and binder material are mixed thoroughly to create a homogenous mixture. This ensures even distribution of the carbide particles within the binder matrix.
Compacting
The mixed powder is then compacted under high pressure using specialized equipment, such as a press, to form a green compact with the desired strip shape.
Pre-Sintering
The green compact is pre-sintered at a temperature below the final sintering temperature. Pre-sintering removes any organic binders and provides initial strength to the compacted material.
Sintering
The pre-sintered compact is placed in a high-temperature furnace and subjected to sintering. During sintering, the compact is heated to a specific temperature.
Shaping and Machining
After sintering, the carbide strips are shaped and machined to achieve the desired dimensions, surface finish, and tolerance. This may involve processes such as grinding, milling, or wire cutting.
Surface Treatment (Optional)
Depending on the application requirements, the carbide strips may undergo surface treatment such as coating or polishing to enhance specific properties like wear resistance or surface smoothness.
Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures are implemented to ensure the carbide strips meet the required specifications.
Cutting Tools
Carbide strips are widely used in the manufacturing of cutting tools such as saw blades, milling cutters, and inserts. Their exceptional hardness and wear resistance make them ideal for high-speed cutting operations.
Wear Parts
Carbide strips find applications in wear parts such as punches, dies, and wear plates. They offer superior resistance to abrasion and provide extended service life in applications with high mechanical stress and friction.
Tooling Dies
Carbide strips are commonly used in tooling dies for various industries, including metal stamping, forging, and extrusion. Their high strength and dimensional stability make them suitable for precision forming operations.
Industrial Machinery Components
Carbide strips are utilized in a range of industrial machinery components such as guide rails, bushings, and wear plates. Their excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability contribute to improved performance and extended service life.
Cutting Tools
Carbide strips are widely used in the manufacturing of cutting tools such as saw blades, milling cutters, and inserts. Their exceptional hardness and wear resistance make them ideal for high-speed cutting operations.
Wear Parts
Carbide strips find applications in wear parts such as punches, dies, and wear plates. They offer superior resistance to abrasion and provide extended service life in applications with high mechanical stress and friction.
Tooling Dies
Carbide strips are commonly used in tooling dies for various industries, including metal stamping, forging, and extrusion. Their high strength and dimensional stability make them suitable for precision forming operations.
Industrial Machinery Components
Carbide strips are utilized in a range of industrial machinery components such as guide rails, bushings, and wear plates. Their excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability contribute to improved performance and extended service life.
Carbide strips are flat and rectangular components made from tungsten carbide and a binder material. They are known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and strength.
Carbide strips offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and strength compared to other materials. They provide extended service life, withstand high temperatures, and perform well under abrasive conditions.
Tungsten carbide strips are thin, flat pieces of cemented carbide, a composite material renowned for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Their secret lies in the unique blend of:
- Tungsten Carbide: This powerhouse ingredient, composed of tungsten and carbon atoms bonded in a tightly packed structure, boasts a hardness approaching that of diamond.
- Cobalt Binder: Acting as a metallic glue, cobalt binds the tungsten carbide particles together, providing the necessary toughness and impact resistance.
Yes, carbide strips can be customized to meet specific requirements, including dimensions, shapes, and surface treatments, based on the application needs.
Carbide strips are primarily used for:
- Cutting Tools: Including woodworking and metalworking tools.
- Wear Parts: In machinery and equipment.
- Mining and Construction Tools: Such as drill bits and cutting edges.
- Precision Machining: For high-durability components.
Carbide punch strips are elongated bars made from tungsten carbide, designed to be used in punching and stamping operations. Tungsten carbide is a composite material composed of tungsten and carbon, often bonded with a metal binder like cobalt or nickel. These strips are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for applications that require precise and repetitive punching.
Carbide grades are classified based on their composition and application. Key types include:
- Cemented Carbide: General-purpose, used in cutting tools.
- Micrograin Carbide: For high precision and fine finishes.
- Ultrafine/ Submicron Carbide: Superior hardness and wear resistance.
- Coated Carbide: Enhanced performance with coatings like TiN or DLC.
The edge geometry of a carbide strip directly impacts its cutting efficiency, durability, and resistance to chipping. Sharper edges provide cleaner cuts and higher precision but are more prone to chipping. Rounded edges offer greater durability and strength, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
The thickness and width determine the strip’s rigidity, flexibility, and heat dissipation. Thicker and wider strips are more rigid and can withstand higher loads, ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Thinner strips offer more flexibility for intricate shapes, and wider strips dissipate heat more effectively, reducing the risk of thermal damage.
The choice depends on the specific requirements of your application, such as the material being punched, the operating conditions, and the desired tool life. Consulting with a knowledgeable supplier can help you select the appropriate type.

Data
Carbide Strips Description
Carbide strips find applications in industries such as metalworking, woodworking, mining, and construction. They are utilized in applications like planer knives, shear blades, wear plates, and punches, among others.
With their exceptional material properties and precise manufacturing, carbide strips deliver extended service life, improved productivity, and cost efficiency in various industrial processes. Their hardness, wear resistance, and strength make them indispensable components for high-performance cutting and wear-resistant applications.
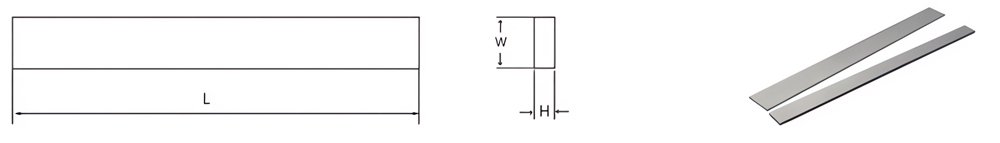
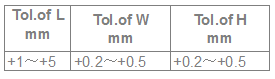
| Part No. | L/mm | W/mm | H/mm | Grade (click here) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK330020 | 330 | 2 | 2-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330040 | 330 | 4 | 2-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330060 | 330 | 6 | 2-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330080 | 330 | 8 | 2-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330100 | 330 | 10 | 2-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330120 | 330 | 12 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330150 | 330 | 15 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330180 | 330 | 18 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330200 | 330 | 20 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330220 | 330 | 22 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330240 | 330 | 24 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
| SK330260 | 330 | 26 | 3-5 | TS710, TS610, TU412, TU409, TU406, TN209, TS715 |
- Contact
Our team is ready to provide support
Truer Carbide is committed to providing efficient solutions to problems. Each team member has the expertise and experience to quickly understand and meet your needs.
