Carbide brazed tips are a cornerstone in modern industrial applications, providing exceptional performance in cutting, drilling, and machining processes. If you’ve ever wondered how these tiny but mighty components come to life, their applications, or how to choose the best ones, you’re in the right place. Let’s break this down in an engaging and thoroughly detailed way—without boring jargon!
What is a Carbide Brazed Tip?
Imagine a sharp-edged tool capable of slicing through the toughest metals like a hot knife through butter. That’s essentially what a carbide brazed tip does! It’s a cutting insert made of carbide, bonded to a tool body through brazing. These tips are popular for their unbeatable hardness, wear resistance, and ability to perform in high-heat environments.
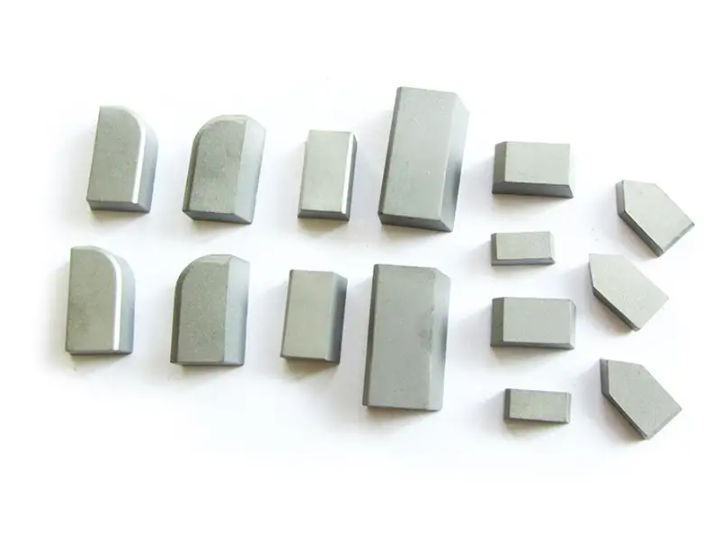

Types of Carbide Brazed Tips
Here’s a categorized table showcasing different types of carbide brazed tips along with their attributes:
| Type | Primary Usage | Typical Materials | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Cutting Tips | Metal and wood cutting | Tungsten carbide | High durability, multi-purpose |
| Turning Tips | Lathes and CNC machines | Cobalt and nickel alloys | Superior heat resistance |
| Drilling Tips | High-precision drilling | Titanium carbide composite | Accurate and smooth performance |
| Milling Tips | Heavy-duty milling operations | Chromium carbide blends | Long life under high-stress use |
| Grooving Tips | Precision grooving applications | Tungsten-titanium carbide | Enhanced chip control and precision |
| Planing Tips | Planing metal surfaces | Fine-grain tungsten carbide | Excellent surface finish |
| Boring Tips | Deep-hole boring | Submicron tungsten carbide | Exceptional rigidity and strength |
| Threading Tips | Thread cutting on materials | Nickel-bonded carbide | Consistent thread profile |
| Wear Resistant Tips | Mining and earthmoving tools | Multi-carbide composite | High impact and abrasion resistance |
| Specialty Tips | Customized applications | Tailored carbide blends | Unique properties as per need |
Raw Materials and Composition Analysis
Carbide brazed tips owe their prowess to the advanced materials used in their manufacture. These materials are finely tuned to meet specific industrial demands. Let’s dive deeper into their raw material composition.
- Tungsten Carbide (WC): The mainstay of carbide tips, offering unparalleled hardness and strength.
- Cobalt (Co): Used as a binder, cobalt holds the carbide grains together, ensuring toughness.
- Nickel (Ni) and Chromium (Cr): Add corrosion resistance and thermal stability.
- Titanium Carbide (TiC): Boosts wear resistance for high-velocity applications.
- Other Additives: Tailored to fine-tune properties like toughness, oxidation resistance, or thermal conductivity.
Applications of Carbide Brazed Tips
The versatility of carbide brazed tips is astounding. Here’s how they excel across industries:
| Industry | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine parts machining, gear cutting | Precision, speed, durability |
| Aerospace | Jet engine components, airframe drilling | High heat and wear resistance |
| Woodworking | Wood shaping, planing, and carving | Smooth cuts and long-lasting edges |
| Mining | Rock drilling, earthmoving tools | Impact and abrasion resistance |
| Oil and Gas | Pipe threading, valve machining | Corrosion and high-temperature handling |
| Metal Fabrication | General machining, lathe operations | Versatility and high finish quality |
| Electronics | PCB drilling and fine component cutting | Micron-level accuracy |





Production Process Flow of Carbide Brazed Tips
Ever wondered how carbide brazed tips are made? It’s a meticulous process involving advanced technology and precise engineering. Here’s the production journey:
- Powder Preparation: Tungsten, cobalt, and other powders are blended into the desired composition.
- Compaction: The powder is compressed into the desired shape.
- Sintering: The compacted tips are heated at high temperatures to achieve desired density and hardness.
- Grinding: Precise grinding to achieve sharp edges and specified dimensions.
- Brazing: The tip is attached to the tool body using a brazing process that uses high-temperature alloy fillers.
- Inspection and Testing: Rigorous quality control ensures top-notch performance.
- Packaging: Finally, the tips are packed for shipment and storage.
Material Properties of Carbide Brazed Tips
| Property | Value Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 89–94 HRA | Determines wear resistance |
| Flexural Strength | 1500–3000 MPa | Indicates resistance to bending under stress |
| Density | 14.5–15.5 g/cm³ | Affects tool balance and weight |
| Thermal Conductivity | 75–125 W/mK | Ensures heat dissipation during machining |
| Elastic Modulus | 450–700 GPa | Shows stiffness and rigidity |
| Fracture Toughness | 9–13 MPa·m¹/² | Indicates resistance to crack propagation |
Key Characteristics: Composition and Features
| Element | Percentage (%) | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | 85–90 | Provides the cutting edge with unmatched hardness |
| Cobalt | 8–12 | Binds the carbide grains and adds toughness |
| Titanium Carbide | 0–3 | Boosts wear resistance |
| Chromium | 0–1 | Increases corrosion resistance |
Performance Parameters: Hardness, Strength, and Wear Resistance
| Parameter | Grade A | Grade B | Grade C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRA) | 92 | 90 | 88 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | 2500 | 2200 | 2000 |
| Wear Resistance (mm³) | High | Medium | Low |
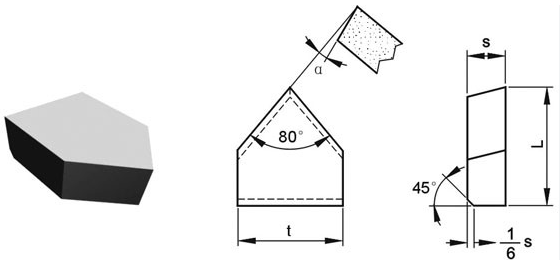
Specifications, Sizes, Shapes, and Standards
| Specification | Available Range | Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Tip Dimensions | 10–50 mm (L), 2–10 mm (T) | ISO 513, ANSI B212.1 |
| Shapes | Round, Square, Triangular | ISO 1832 |
| Tolerance | ±0.02 mm | DIN 69881 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Supplier Name | Region | Price Range (per unit) | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ Carbide Inc. | North America | $2.00–$5.00 | 2–3 weeks |
| Global Tool Parts | Europe | $1.50–$4.50 | 1–2 weeks |
| Precision Hard Metals | Asia | $1.00–$3.50 | 2–4 weeks |
Selecting the Right Carbide Brazed Tip
| Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Material to Be Cut | Hard metals vs. softer materials like wood |
| Tip Geometry | Shape and angles for the intended application |
| Operating Conditions | High heat, speed, or abrasive environments |
| Budget | Cost versus performance trade-off |
| Supplier Reputation | Consistency and quality assurance |

Advantages and Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Extreme hardness and wear resistance | Higher initial cost |
| Versatility across industries | Brittle in extreme impact situations |
| Long tool life and reduced downtime | Requires precise handling |
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What makes carbide brazed tips so effective? | Their combination of hardness, toughness, and heat resistance. |
| Can carbide tips be reused? | They can be reground, but performance may degrade after multiple uses. |
| How do I choose the best tip for my project? | Consider the material, shape, and specific application requirements. |
| Are carbide tips expensive? | While they have a higher upfront cost, their durability provides long-term savings. |




