Overview of Solid Carbide Inserts
If you’re into metalworking or machining, you’ve likely come across solid carbide inserts. These tiny yet mighty tools are essential for cutting and shaping metals with precision and efficiency. But what exactly makes them so special? Let’s dive into the world of solid carbide inserts, exploring their types, applications, properties, and everything in between.
Solid carbide inserts are renowned for their durability and ability to withstand high temperatures, making them indispensable in various industrial applications. They’re crafted from a composite material that includes fine particles of carbide, usually tungsten, held together by a metallic binder, typically cobalt. This combination results in a tool that’s incredibly hard and wear-resistant.
Types of Solid Carbide Inserts
Carbide inserts come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored for specific tasks. Here’s a detailed table to help you understand the different types of solid carbide inserts:
| Insert Type | Shape | Application | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNMG | Rhomboid | General turning | Versatile, 4 cutting edges |
| TNMG | Triangle | Heavy turning | 6 cutting edges, robust |
| DNMG | Diamond | Precision turning | 4 cutting edges, high precision |
| VNMG | V-shape | Fine finishing | 2 cutting edges, great for finishing |
| SNMG | Square | Roughing | 8 cutting edges, excellent for roughing |
| WNMG | Trigon | Semi-finishing | 6 cutting edges, good balance |
| CCMT | Square | Light turning | Positive rake, low cutting forces |
| DCMT | Diamond | Copy turning | High precision, fine finish |
| TCMT | Triangle | Light finishing | Positive rake, low cutting forces |
| SCMT | Square | General machining | Sturdy, versatile |

Applications of Solid Carbide Inserts
Solid carbide inserts are used in a variety of industries, from automotive to aerospace. Below is a table summarizing their applications:
| Industry | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components | Precision machining of pistons, gears |
| Aerospace | Turbine blades | High-temperature resistance |
| Medical | Surgical instruments | Precise and clean cuts |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling tools | Durable and wear-resistant |
| Electronics | PCB manufacturing | Fine and precise cutting |
| General Engineering | Molds and dies | Versatile and robust |
Material Properties of Solid Carbide Inserts
Understanding the material properties of solid carbide inserts is crucial for selecting the right one for your needs. Here’s a detailed table:
| Property | Description | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Resistance to deformation | 90-94 HRA |
| Toughness | Resistance to fracture | High |
| Wear Resistance | Resistance to abrasion | Excellent |
| Thermal Conductivity | Ability to conduct heat | 70-100 W/m.K |
| Density | Mass per unit volume | 14.0-15.5 g/cm³ |
Composition and Characteristics
The composition and characteristics of solid carbide inserts are critical for their performance. Here’s a table summarizing these aspects:
| Element | Percentage | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide (WC) | 70-97% | Provides hardness |
| Cobalt (Co) | 3-30% | Acts as a binder |
| Titanium Carbide (TiC) | 0-25% | Increases toughness |
| Tantalum Carbide (TaC) | 0-15% | Enhances wear resistance |
| Niobium Carbide (NbC) | 0-15% | Improves thermal stability |
Hardness, Strength, and Wear Resistance
Carbide inserts need to balance hardness, strength, and wear resistance. Here’s a comparative table:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Resistance to indentation | 90-94 HRA |
| Compressive Strength | Resistance to compression | 5000-7000 MPa |
| Wear Resistance | Resistance to material loss | Excellent |
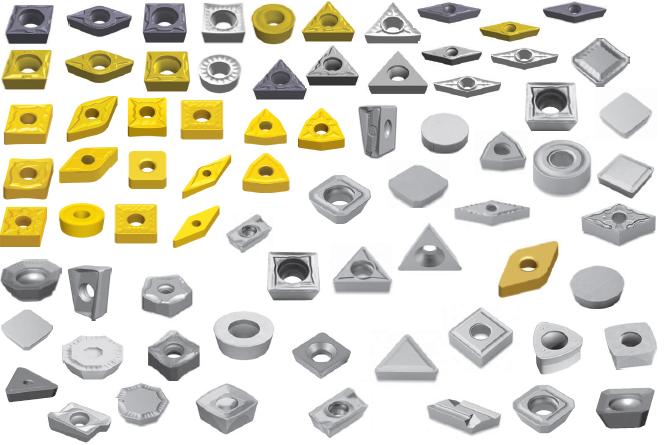
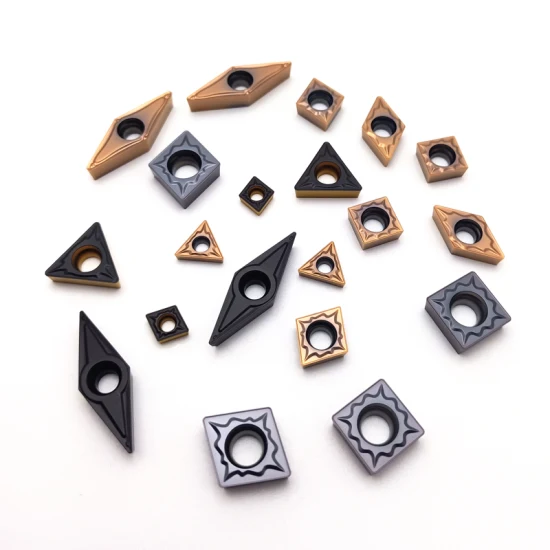
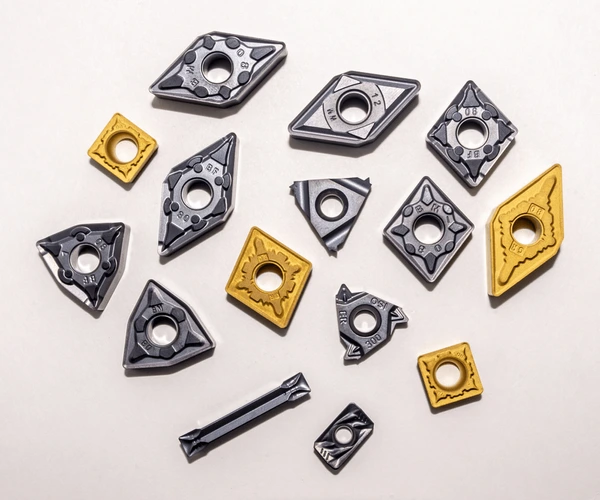
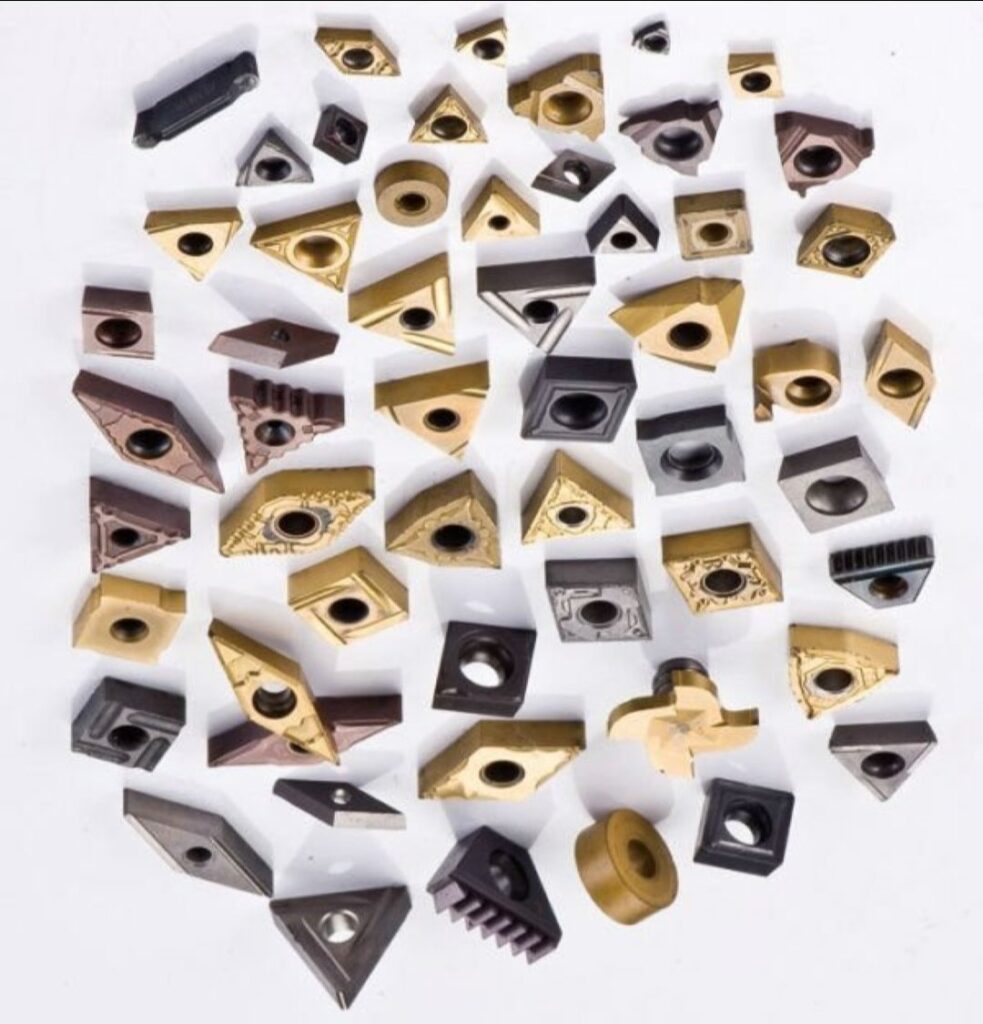





Specifications, Sizes, Shapes, and Standards
The specifications of solid carbide inserts can vary widely. Here’s a detailed table to guide you:
| Specification | Size | Shape | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO Inserts | Various | Various | ISO 1832 |
| ANSI Inserts | Various | Various | ANSI B212 |
| DIN Inserts | Various | Various | DIN 4987 |
| JIS Inserts | Various | Various | JIS B 4130 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
When it comes to purchasing solid carbide inserts, knowing the suppliers and pricing can help you make an informed decision. Here’s a table with details:
| Supplier | Location | Price Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandvik Coromant | Global | $10-$50 per insert | High quality |
| Kennametal | Global | $15-$60 per insert | Durable |
| Mitsubishi Materials | Global | $12-$55 per insert | Reliable |
| Seco Tools | Global | $10-$50 per insert | Versatile |
| Walter AG | Global | $14-$58 per insert | Precision |
Selecting the Right Solid Carbide Inserts
Choosing the right carbide insert can be tricky. Here’s a table to help you make the best choice:
| Criteria | Considerations | Recommended Inserts |
|---|---|---|
| Material Hardness | Harder materials require tougher inserts | CNMG, TNMG |
| Surface Finish | For fine finishes, use inserts with positive rake angles | VNMG, DCMT |
| Cutting Speed | High-speed operations need inserts with high wear resistance | CNMG, SNMG |
| Machine Type | Ensure compatibility with your machine tool | CCMT, TCMT |
| Application | Specific tasks require specific insert shapes | DNMG, WNMG |
Advantages and Limitations of Solid Carbide Inserts
Solid carbide inserts have their pros and cons. Here’s a comparative table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle, prone to chipping |
| Temperature | High thermal stability | Can be costly |
| Versatility | Suitable for various materials | Requires precise handling |
| Life Span | Long-lasting compared to HSS | Initial cost is higher |

FAQ
What are solid carbide inserts made of Composition?
Solid carbide inserts are primarily made of tungsten carbide, cobalt, and sometimes other carbides like titanium, tantalum, or niobium.
How do I choose the right carbide insert?
Consider factors like the material you’re cutting, the required surface finish, cutting speed, and your machine type. Refer to our selection table for detailed guidance.
Why are carbide inserts so expensive?
The high cost is due to the materials used (like tungsten and cobalt) and the precision manufacturing processes involved.
Can carbide inserts be reused?
Yes, carbide inserts can often be indexed (rotated) to use multiple cutting edges before they need to be replaced.
What are the common shapes of carbide inserts?
Common shapes include square, triangle, rhomboid, diamond, and V-shape, each suited for specific applications.
How do carbide inserts improve machining efficiency?
They provide precise, clean cuts, withstand high temperatures, and have longer tool life, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Conclusion
Solid carbide inserts are a cornerstone of modern machining, offering unmatched durability, precision, and versatility. From their composition to their applications across various industries, understanding these tools can significantly impact your machining processes. With the right selection and application, carbide inserts can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. So next time you’re gearing up for a project, remember the tiny tool that packs a powerful punch – the solid carbide insert.




