Introduction
Carbide brazed tips are a key component in the machining industry, offering unparalleled hardness, durability, and cutting efficiency. However, not all carbide brazed tips are created equal. The specific type of carbide used can dramatically affect the tool’s performance, making it essential to understand the differences in properties among the various types. In this blog, we will delve deep into the different types of carbide brazed tips, their unique properties, and how they compare. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to choose the right type for your specific needs.
What Are Carbide Brazed Tips?
Carbide brazed tips are cutting tools made by attaching a piece of carbide to a steel body using a brazing process. This combination leverages the hardness and wear resistance of carbide with the flexibility and toughness of steel, making these tools ideal for various machining operations.
Key Properties of Carbide Brazed Tips
Understanding the key properties that define the performance of carbide brazed tips is essential. Here are the main attributes to consider:
- Hardness: The ability to resist deformation and wear.
- Toughness: The capability to absorb impact and resist chipping.
- Wear Resistance: The ability to withstand abrasive wear.
- Thermal Stability: The ability to maintain performance at high temperatures.
- Corrosion Resistance: The ability to resist chemical attack and oxidation.
Types of Carbide Brazed Tips
1. C1 Grade: General-Purpose
Properties:
- Hardness: Medium
- Toughness: High
- Wear Resistance: Good
- Thermal Stability: Moderate
- Corrosion Resistance: Moderate
Applications:
- General-purpose machining of non-ferrous metals, plastics, and wood.
- Suitable for light to medium-duty operations.
2. C2 Grade: Versatile and Wear-Resistant
Properties:
- Hardness: High
- Toughness: Moderate
- Wear Resistance: Very High
- Thermal Stability: Good
- Corrosion Resistance: Good
Applications:
- Machining of cast iron, non-ferrous metals, and non-metallic materials.
- Ideal for medium-duty operations with a focus on wear resistance.
3. C3 Grade: High Hardness for Precision
Properties:
- Hardness: Very High
- Toughness: Lower than C1 and C2
- Wear Resistance: Excellent
- Thermal Stability: High
- Corrosion Resistance: Moderate
Applications:
- Precision machining of hard and abrasive materials.
- Suitable for finishing operations requiring high surface quality.
4. C4 Grade: Extreme Wear Resistance
Properties:
- Hardness: Extremely High
- Toughness: Low
- Wear Resistance: Superior
- Thermal Stability: Very High
- Corrosion Resistance: Good
Applications:
- Heavy-duty machining of hard alloys, tool steels, and hardened materials.
- Excellent for applications where extreme wear resistance is required.
5. C5 Grade: Balanced Performance
Properties:
- Hardness: High
- Toughness: High
- Wear Resistance: High
- Thermal Stability: Good
- Corrosion Resistance: High
Applications:
- General-purpose machining of a wide range of materials.
- Suitable for both roughing and finishing operations.
6. C6 Grade: High Toughness
Properties:
- Hardness: Moderate
- Toughness: Very High
- Wear Resistance: Good
- Thermal Stability: Moderate
- Corrosion Resistance: Moderate
Applications:
- Machining operations involving interrupted cuts and heavy loads.
- Ideal for roughing operations where toughness is critical.
7. C7 Grade: Thermally Stable
Properties:
- Hardness: High
- Toughness: Moderate
- Wear Resistance: High
- Thermal Stability: Superior
- Corrosion Resistance: Good
Applications:
- High-speed machining and operations generating significant heat.
- Suitable for machining high-temperature alloys and hardened materials.
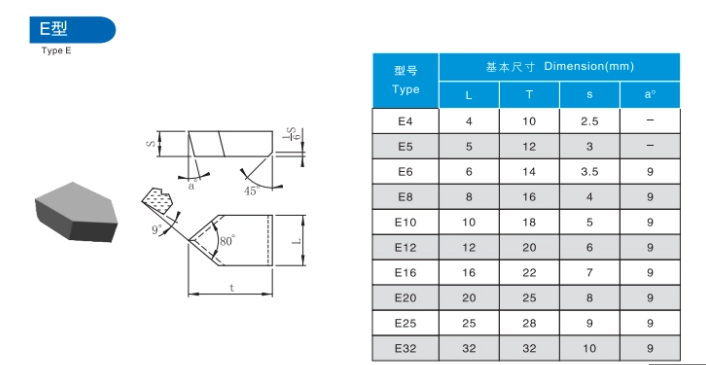
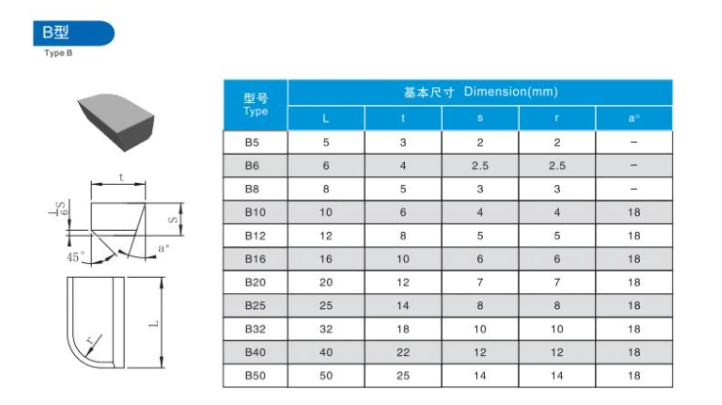
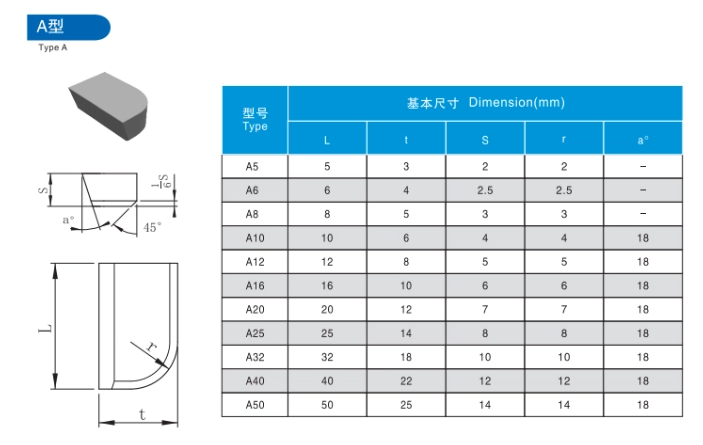
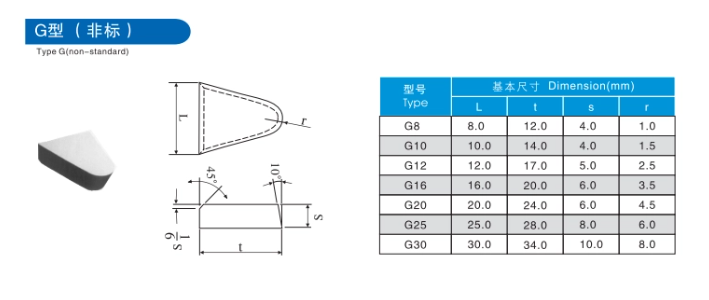
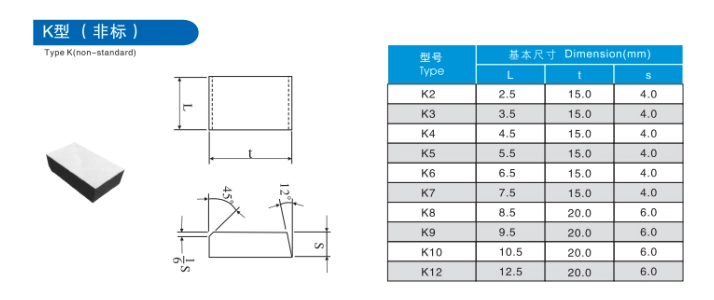
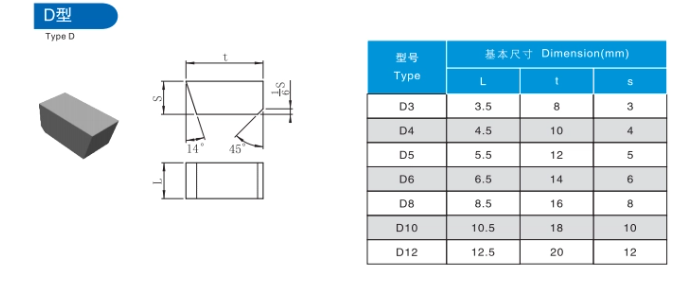
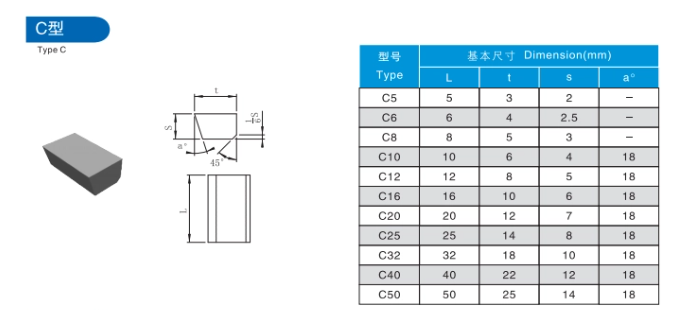
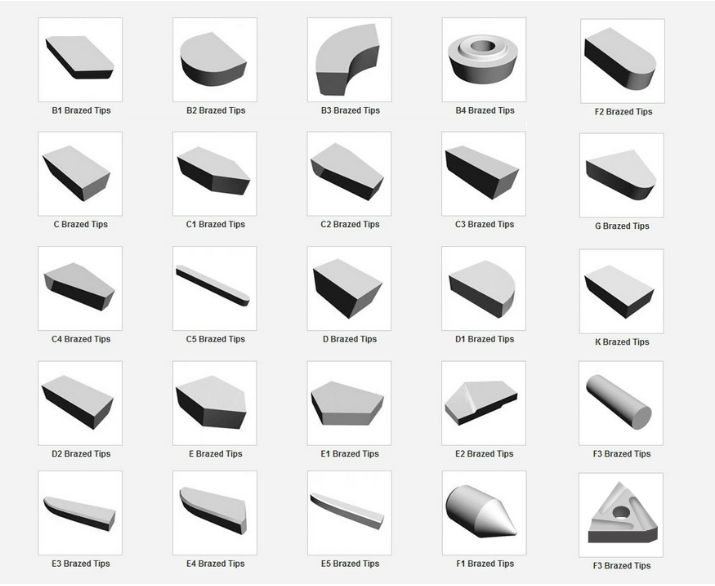
Comparative Analysis of Carbide Brazed Tips
To provide a clearer understanding of how these carbide brazed tips compare, let’s look at a comparative analysis of their key properties:
| Property | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Medium | High | Very High | Extremely High | High | Moderate | High |
| Toughness | High | Moderate | Lower | Low | High | Very High | Moderate |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Very High | Excellent | Superior | High | Good | High |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | Good | High | Very High | Good | Moderate | Superior |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Good | Moderate | Good | High | Moderate | Good |
Table 1: Comparative Analysis of Carbide Brazed Tips
Choosing the Right Carbide Brazed Tip
Selecting the appropriate carbide brazed tip depends on several factors, including the material being machined, the type of operation, and the specific requirements of the application. Here are some guidelines to help you choose the right type:
1. Material Being Machined
- Non-Ferrous Metals and Plastics: C1 or C2 grades are suitable due to their good toughness and wear resistance.
- Cast Iron and Non-Metallic Materials: C2 or C3 grades offer high hardness and wear resistance.
- Hard Alloys and Hardened Materials: C4 or C7 grades provide superior wear resistance and thermal stability.
2. Type of Operation
- Roughing Operations: C5 or C6 grades are ideal for their high toughness and ability to withstand heavy loads.
- Finishing Operations: C3 or C4 grades are preferable for their high hardness and precision.
- Interrupted Cuts: C6 grade is suitable due to its very high toughness.
3. Application Requirements
- High-Speed Machining: C7 grade is recommended for its excellent thermal stability.
- Precision Machining: C3 grade offers the necessary hardness and wear resistance for high-quality finishes.
- General-Purpose Use: C1 or C5 grades provide a balance of properties for a wide range of applications.
Advantages of Using the Right Carbide Brazed Tip
Choosing the right carbide brazed tip for your machining operations offers numerous advantages:
- Improved Tool Life: The appropriate carbide grade ensures longer tool life, reducing the frequency of tool changes and maintenance.
- Enhanced Cutting Performance: Optimal hardness and wear resistance result in better cutting performance and higher-quality finishes.
- Increased Productivity: Reduced downtime and maintenance lead to higher productivity and cost savings.
- Versatility: Selecting the appropriate grade allows you to handle a wide range of materials and applications with ease.
- Cost Efficiency: The right grade minimizes tool wear and breakage, leading to lower overall costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of carbide brazed tips and their properties is crucial for optimizing your machining operations. Each type offers a unique combination of hardness, toughness, wear resistance, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for specific applications and materials. By selecting the right carbide brazed tip, you can achieve superior cutting performance, longer tool life, and increased productivity. Whether you are machining non-ferrous metals, hard alloys, or high-temperature materials, there is a carbide brazed tip tailored to meet your needs. Make informed choices and experience the unparalleled benefits of using the right carbide brazed tips in your operations.




