Carbide plate thickness is an essential factor in various industrial applications, offering exceptional strength, wear resistance, and durability. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a newcomer exploring carbide plates, this guide will delve into every detail, from raw materials to selecting the best supplier. Ready to dive in? Let’s go!
What is Carbide Plate Thickness?
Carbide plates are engineered materials made of tungsten carbide powders combined with a binder metal like cobalt. These plates are widely used across industries like machining, mining, and tool manufacturing. The thickness of a carbide plate significantly impacts its performance, dictating its strength, durability, and suitability for specific applications.

Types of Carbide Plate Thickness
| Type | Thickness Range (mm) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Thin Plates | 0.5 – 1.0 | Precision tools, watches |
| Thin Plates | 1.1 – 3.0 | Cutting tools, wear plates |
| Standard Plates | 3.1 – 10.0 | Mining, industrial tooling |
| Thick Plates | 10.1 – 25.0 | Heavy-duty machinery |
| Ultra-Thick Plates | 25.1 – 50.0+ | Structural reinforcements |
Raw Material and Composition Analysis
Carbide plates are primarily made from tungsten carbide (WC) and a binder metal like cobalt (Co). The mixture typically contains:
- Tungsten Carbide (70%-97%): Provides hardness and wear resistance.
- Cobalt (3%-30%): Acts as a binder, adding toughness and flexibility.
- Other Additives: Titanium carbide (TiC) or tantalum carbide (TaC) for specific properties like corrosion resistance.
This blend ensures carbide plates have the perfect balance of hardness, toughness, and performance longevity.
Applications of Carbide Plate Thickness
| Application | Industry | Benefits of Specific Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Tools | Manufacturing | Precision, wear resistance |
| Dies and Molds | Automotive | Durability under high stress |
| Wear Parts | Mining | Resistance to abrasion and impact |
| Structural Components | Construction | Strength for load-bearing applications |
| Precision Instruments | Aerospace | Minimal deformation, high accuracy |
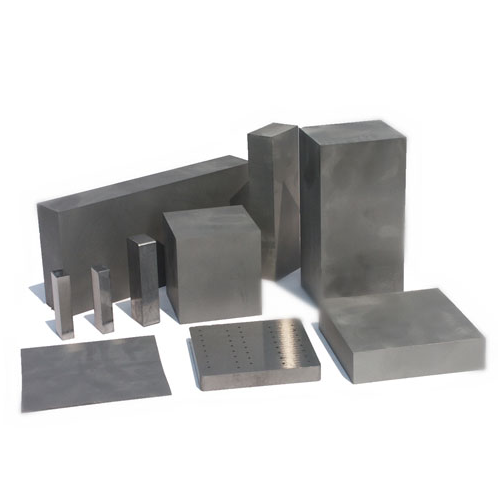





Production Process Flow of Carbide Plate Thickness
Creating carbide plates is a meticulous process that involves several steps:
- Powder Mixing: Tungsten carbide powder is mixed with a binder (cobalt) and other additives.
- Pressing: The powder mixture is compressed into the desired shape and thickness.
- Sintering: The pressed plates are heated at high temperatures to achieve density and strength.
- Surface Finishing: Grinding and polishing improve the plate’s surface for enhanced performance.
- Quality Testing: Plates are tested for hardness, strength, and dimensional accuracy.
Material Properties of Carbide Plate Thickness
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardness | High resistance to deformation |
| Wear Resistance | Exceptional durability against friction |
| Compressive Strength | Handles high pressure and stress loads |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat dissipation |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resistant to chemical attacks |
Composition, Properties, and Characteristics
| Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| WC + Co (High WC) | Extreme hardness | Ideal for wear parts |
| WC + Co (High Co) | Increased toughness | Suitable for heavy impacts |
| WC + TiC/TaC | Corrosion resistance | Great for chemical environments |
| Fine-Grain WC | Enhanced surface finish | Used in precision tooling |
| Coarse-Grain WC | Superior wear resistance | Used in heavy-duty applications |
Hardness, Strength, and Wear Resistance
| Parameter | Range | Relevance to Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRA) | 85 – 93 | Higher thickness often reduces hardness |
| Compressive Strength | 2000 – 4000 MPa | Directly proportional to plate thickness |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Consistent across all thickness ranges |
Specifications, Sizes, Shapes, and Standards
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Standard Sizes | 100×100 mm, 200×200 mm, custom |
| Shapes | Square, rectangular, round |
| Thickness Tolerance | ±0.1 mm |
| Standards | ISO 9001, ASTM, DIN standards |
Choosing Carbide Plate Thickness Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Supplier Reputation | Ensure ISO-certified, high customer ratings |
| Pricing Structure | Based on thickness, composition, and customization |
| Delivery Time | Fast turnaround for standard and custom orders |
| Additional Services | Grinding, polishing, and design support |
Selecting the Right Carbide Plate Thickness
| Criteria | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Application Type | Match thickness to intended use |
| Wear Resistance Needs | Opt for high WC content |
| Impact Resistance | Choose higher Co content |
| Precision Requirements | Use fine-grain carbide plates |
| Budget Constraints | Balance between performance and cost |
Advantages and Limitations of Carbide Plate Thickness
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High hardness and wear resistance | Expensive compared to other materials |
| Long service life | Difficult to machine without special tools |
| Versatile applications | Heavier in thicker sizes |
| Excellent thermal stability | Limited flexibility in certain applications |
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the ideal thickness for cutting tools? | Typically 1.1-3.0 mm, depending on the application. |
| How do I select the best supplier? | Look for certifications, customer reviews, and customization options. |
| Can carbide plates be customized? | Yes, most suppliers offer custom thicknesses, sizes, and shapes. |
| Are thicker plates always better? | Not necessarily; it depends on the application and performance needs. |
| How do I maintain carbide plates? | Clean regularly, avoid harsh chemicals, and ensure proper storage. |


