When it comes to industrial tools and wear-resistant parts, carbide plates are among the most versatile and valuable materials. Whether you’re involved in metalworking, woodworking, or the manufacturing of heavy machinery, carbide plates are indispensable. But what exactly are they, and why are they so crucial in various applications?
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about carbide plates. We’ll cover their types, applications, properties, composition, and much more. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of carbide plates and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is a Carbide Plate?
Carbide plates, also known as tungsten carbide plates, are flat, rectangular pieces of material made primarily from tungsten carbide, a hard and durable compound composed of tungsten and carbon atoms. They are used in various industrial applications due to their high wear resistance, hardness, and ability to withstand extreme conditions.
But let’s not stop there—carbide plates are more than just tough; they’re incredibly versatile. Imagine trying to cut through a diamond with a butter knife—sounds impossible, right? That’s the kind of durability and strength carbide plates bring to the table.
Why Are Carbide Plates So Important?
Carbide plates are the unsung heroes in the world of manufacturing. Their importance lies in their ability to handle heavy-duty tasks without breaking a sweat. From machining hard materials to being used as wear parts in machinery, carbide plates are the backbone of many industrial processes.
Think of them as the workhorses of the industrial world—strong, reliable, and built to last. Whether you’re drilling, cutting, or shaping metal, carbide plates ensure that the job gets done with precision and efficiency.
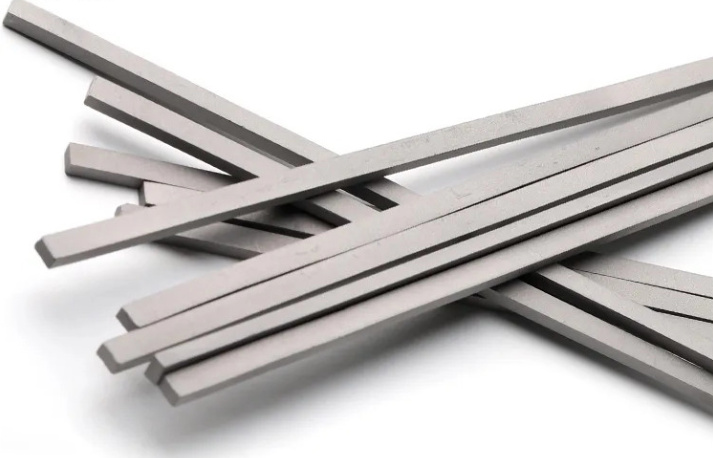

Types of Carbide Plates
Not all carbide plates are created equal. Different types serve different purposes, and understanding these distinctions is key to selecting the right one for your needs.
Sintered Carbide Plates
Sintered carbide plates are made by compressing tungsten carbide powder into a mold and then heating it to a high temperature. This process bonds the particles together, resulting in a dense, durable plate. These plates are often used in applications that require high hardness and wear resistance.
Ground Carbide Plates
Ground carbide plates are sintered plates that have been further processed by grinding. This additional step enhances the plate’s surface finish and dimensional accuracy, making them ideal for precision applications.
Coated Carbide Plates
Coated carbide plates are covered with a layer of another material, such as titanium carbide or aluminum oxide, to enhance their performance in specific applications. The coating can improve wear resistance, reduce friction, or provide additional protection against corrosion.
Cemented Carbide Plates
Cemented carbide plates are a composite material made by binding carbide particles with a metal binder, typically cobalt. This combination provides a good balance of hardness and toughness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Micrograin Carbide Plates
Micrograin carbide plates are made from ultrafine carbide particles. The smaller the grain size, the harder the plate, which makes these plates ideal for cutting tools that require a sharp edge and long-lasting performance.
Carbide Plate for Cold Heading Dies
These plates are specifically designed for use in cold heading dies, where they must withstand the high pressures and stresses involved in shaping metal at room temperature.
Carbide Plate for Stamping Dies
Similar to cold heading dies, stamping dies require materials that can endure high stress and wear. Carbide plates for stamping dies offer excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability.
Carbide Plates for Cutting Tools
Carbide plates are commonly used in the manufacture of cutting tools, such as saw blades, drills, and milling cutters. Their hardness and wear resistance make them ideal for cutting through tough materials.
Carbide Plates for Wear Parts
Wear parts are components that experience constant friction and abrasion, such as bearings, bushings, and liners. Carbide plates are often used in these applications to extend the life of the parts and reduce maintenance costs.
Customized Carbide Plates
For specialized applications, carbide plates can be customized in terms of size, shape, and composition to meet specific requirements. Customization ensures that the plates perform optimally in their intended use.
Applications of Carbide Plates
Carbide plates are used in a wide variety of industries, thanks to their durability, hardness, and resistance to wear. Here, we’ll explore some of the most common applications.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Metal Cutting | Carbide plates are used in cutting tools for machining metals. |
| Woodworking | Used in saw blades and router bits for woodworking applications. |
| Mining | Carbide plates are used in mining tools to cut through rock and ore. |
| Construction | Used in construction equipment for cutting and shaping building materials. |
| Aerospace | Carbide plates are used in the manufacture of aerospace components. |
| Automotive | Used in the production of automotive parts that require high wear resistance. |
| Oil and Gas | Carbide plates are used in drilling tools and equipment in the oil and gas industry. |
| Agriculture | Used in agricultural machinery for cutting and tilling soil. |
| Medical Devices | Carbide plates are used in surgical tools and medical devices. |
| Recycling | Used in recycling machinery to cut and shred materials. |
Material Properties of Carbide Plates
Carbide plates are known for their exceptional material properties, which make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Here’s a look at some of the key properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Carbide plates are extremely hard, often ranging from 85 to 95 HRA. |
| Wear Resistance | They offer excellent resistance to wear, even in abrasive environments. |
| Toughness | Despite their hardness, carbide plates have good toughness and can withstand impact. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Some carbide plates are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. |
| Thermal Stability | Carbide plates can withstand high temperatures without losing their properties. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Carbide plates have good electrical conductivity, which can be advantageous in certain applications. |
| Magnetic Properties | Some carbide plates exhibit magnetic properties, which can be useful in specific applications. |
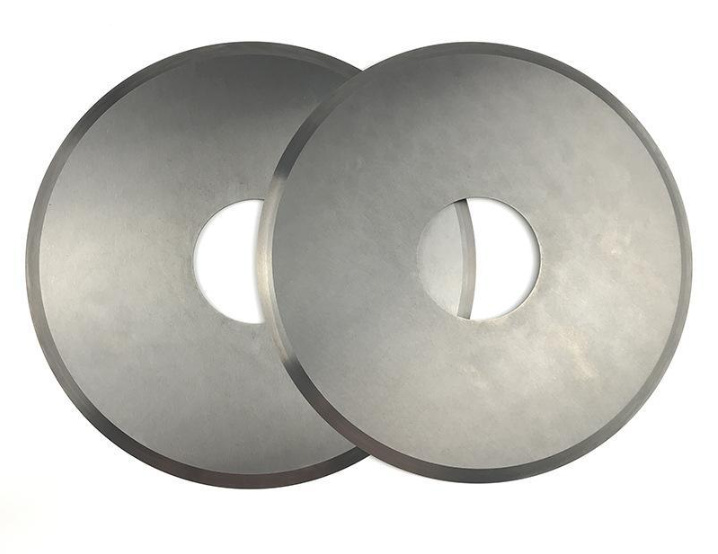
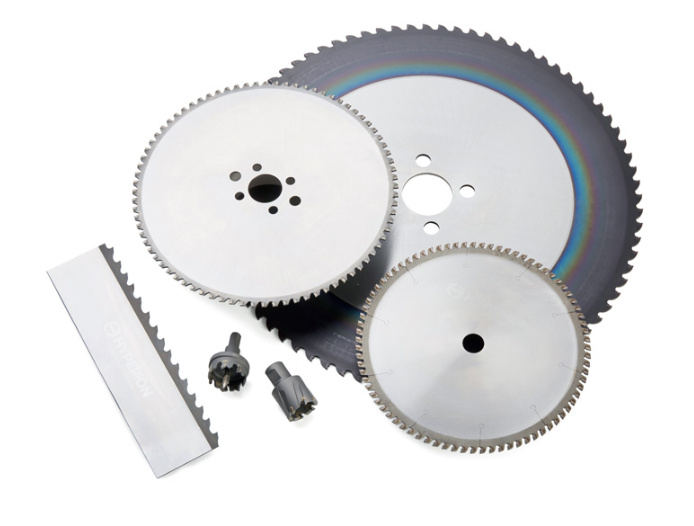
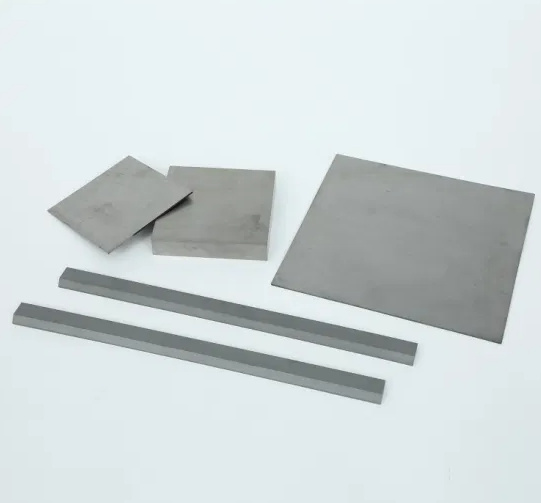





Composition and Characteristics
Carbide plates are primarily composed of tungsten carbide, which is bonded with a metal binder, usually cobalt. The exact composition can vary depending on the desired properties of the plate.
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | Provides hardness and wear resistance. |
| Cobalt Binder | Binds the carbide particles together and provides toughness. |
| Titanium Carbide | Sometimes added to improve resistance to oxidation and high-temperature wear. |
| Tantalum Carbide | Added to improve resistance to thermal shock. |
Hardness, Strength, and Wear Resistance
The performance of a carbide plate is often evaluated based on its hardness, strength, and wear resistance. These factors are crucial in determining the plate’s suitability for specific applications.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardness (HRA) | Typically ranges from 85 to 95 HRA. Higher hardness means better wear resistance but lower toughness. |
| Compressive Strength | Can exceed 4000 MPa, allowing carbide plates to withstand high pressures. |
| Wear Resistance | Measured by the volume loss in a standard wear test; carbide plates typically exhibit very low wear rates. |
| Fracture Toughness | Indicates the plate’s ability to resist crack propagation; higher values mean better resistance to cracking. |
Specifications, Sizes, Shapes, and Standards
Carbide plates come in various sizes, shapes, and standards, depending on their intended application. Here’s a breakdown of common specifications:
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard Sizes | Common sizes include 100x100mm, 150x150mm, and 200x200mm. |
| Thickness | Typically ranges from 1mm to 50mm, depending on the application. |
| Shapes | Rectangular, square, and custom shapes are available. |
| Standards | Plates are often manufactured to industry standards such as ISO, ASTM, and DIN. |
| Surface Finish | Available in both polished and unpolished finishes. |
| Tolerance | Dimensional tolerances can be as tight as ±0.01mm. |
| Edge Preparation | Sharp, chamfered, or rounded edges are available depending on the application. |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
The market for carbide plates is vast, with numerous suppliers offering a wide range of products. Here’s a
look at some key suppliers and their pricing:
| Supplier | Location | Product Range | Price Range (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kennametal | USA | Ground, coated, and custom plates | $100 – $250 |
| Sandvik | Sweden | Sintered, ground, and coated plates | $120 – $280 |
| Zhuzhou Cemented Carbide | China | Sintered and ground plates | $80 – $200 |
| Mitsubishi Materials | Japan | High-performance plates | $130 – $300 |
| Sumitomo Electric | Japan | Coated and uncoated plates | $110 – $270 |
| Tungsten Carbide India | India | Custom and standard plates | $90 – $220 |
| Ceratizit | Luxembourg | Wear parts and cutting tool plates | $150 – $320 |
| Hyperion Materials | USA | Precision-ground plates | $140 – $310 |
| Kyocera | Japan | High-toughness plates | $125 – $290 |
| H.C. Starck Tungsten | Germany | Specialty and customized plates | $130 – $300 |
How to Choose the Right Carbide Plate
Selecting the right carbide plate can be daunting, given the wide range of options available. Here are some factors to consider:
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Application | Determine the specific use case—cutting, shaping, wear parts, etc. |
| Material Properties | Consider hardness, toughness, and wear resistance based on the application. |
| Coating | Decide whether a coated plate is necessary for additional wear resistance or corrosion protection. |
| Size and Shape | Ensure the plate meets the dimensional requirements of your application. |
| Supplier Reputation | Consider the supplier’s reputation for quality and reliability. |
| Cost | Balance the cost with the performance requirements. |
| Customization Needs | Determine if you need a custom plate to meet specific requirements. |
| Environmental Conditions | Consider the operating environment—temperature, corrosion, etc. |
Comparing Advantages and Limitations
Carbide plates offer several advantages, but they also have some limitations. Here’s a comparison:
| Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|
| High Wear Resistance | May be more expensive than other materials. |
| Exceptional Hardness | High hardness can lead to brittleness in some applications. |
| Good Thermal Stability | Limited ductility compared to other materials like steel. |
| Long Service Life | Requires specialized equipment for machining and handling. |
| Versatility in Applications | Heavier than some alternatives, which may be a concern in certain applications. |
FAQs
Q: What are carbide plates made of?
A: Carbide plates are primarily made from tungsten carbide, which is bonded with a metal binder, typically cobalt. The exact composition can vary depending on the desired properties of the plate.
Q: What are the main uses of carbide plates?
A: Carbide plates are used in various applications, including metal cutting, woodworking, mining, construction, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Their hardness and wear resistance make them ideal for these demanding tasks.
Q: How do I choose the right carbide plate for my application?
A: To choose the right carbide plate, consider factors such as the specific application, material properties, coating, size, shape, supplier reputation, cost, and environmental conditions.
Q: Are there different types of carbide plates?
A: Yes, there are several types of carbide plates, including sintered, ground, coated, cemented, and micrograin carbide plates, each with unique properties suited for different applications.
Q: What is the typical hardness of a carbide plate?
A: The hardness of a carbide plate typically ranges from 85 to 95 HRA, depending on the specific type and composition.
Q: Can carbide plates be customized?
A: Yes, carbide plates can be customized in terms of size, shape, composition, and other properties to meet specific requirements.
Q: How much do carbide plates cost?
A: The cost of carbide plates varies depending on the type, size, and supplier, but prices typically range from $80 to $320 per kilogram.
Conclusion
Carbide plates are a critical component in a wide range of industrial applications, from cutting tools to wear parts. Their unique combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance makes them indispensable in environments where other materials would quickly fail. By understanding the different types of carbide plates, their properties, and how to select the right one, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity in your application.
Whether you’re machining metals, cutting wood, or manufacturing components for the aerospace industry, carbide plates are the key to success. With the right knowledge and careful selection, you can harness the power of these remarkable materials to achieve superior results in your projects.



