Carbide cutting tools are the backbone of modern machining and manufacturing. Whether you’re crafting aerospace components or automotive parts, these tools deliver precision, durability, and efficiency that rivals other options. But what makes carbide cutting tools stand out? Let’s dive deep into their composition, types, applications, and much more to answer all your questions about these essential tools.
What Are Carbide Cutting Tools?
Carbide cutting tools are made primarily from tungsten carbide, a compound of tungsten and carbon. Known for their extreme hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures, they’re often the go-to tools for cutting hard materials such as steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous alloys.
Types of Carbide Cutting Tools
Here’s a detailed table outlining the various types of carbide cutting tools available:
| Type of Tool | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| End Mills | Tools with cutting edges on their face and side; used for milling applications. | Milling slots, contours, and pockets. |
| Drill Bits | Tools designed to create cylindrical holes in materials. | Drilling holes in metals and alloys. |
| Lathe Inserts | Replaceable tips for lathes, designed to cut various profiles. | Turning operations in lathes. |
| Cutting Blades | Linear tools for cutting wide material sections. | Slicing metals, plastics, and ceramics. |
| Boring Bars | Tools used to enlarge holes or create precise internal diameters. | Internal machining applications. |
| Reamers | Tools designed for finishing and enlarging pre-drilled holes. | Achieving precise hole diameters. |
| Taps and Dies | Tools for creating threads in holes or on rods. | Threading operations. |
| Grooving Tools | Specialized for cutting grooves in materials. | Creating grooves and channels. |
| Carbide Saw Blades | Circular blades with carbide-tipped teeth. | Cutting wood, metal, and composites. |
| Routers | Tools for shaping and hollowing materials, often in woodworking and plastics. | Intricate designs and shaping. |
Raw Material and Composition Analysis of Carbide Cutting Tools
The primary ingredient in carbide cutting tools is tungsten carbide (WC), often bonded with cobalt (Co) to enhance toughness. Here’s a breakdown:
| Raw Material | Percentage | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | 70–95% | Provides hardness and wear resistance. |
| Cobalt Binder | 5–30% | Adds toughness and reduces brittleness. |
| Additives (e.g., TiC) | <5% | Enhances corrosion resistance or hardness. |
Applications of Carbide Cutting Tools
Carbide cutting tools find applications across industries. Here’s an illustrative table for their uses:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Cutting titanium and aluminum components. | High precision and durability under heat stress. |
| Automotive | Machining engine blocks and gears. | Efficiency in mass production. |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing implants and surgical tools. | Accuracy for small, intricate components. |
| Construction | Cutting concrete and composites. | Handles hard, abrasive materials. |
| Woodworking | Shaping furniture and fittings. | Long-lasting performance on dense woods. |
Production Process Flow of Carbide Cutting Tools
Understanding how these tools are made sheds light on their exceptional performance. Here’s an overview of the production process:
- Raw Material Preparation: Mixing tungsten carbide powder with cobalt and other additives.
- Compaction: Pressing the powder mix into a desired shape using molds.
- Sintering: Heating the compacted material in a furnace to bond particles.
- Grinding and Shaping: Precision grinding to achieve exact dimensions.
- Coating: Applying wear-resistant coatings such as TiN or AlTiN for enhanced performance.
- Quality Testing: Checking for hardness, toughness, and accuracy.
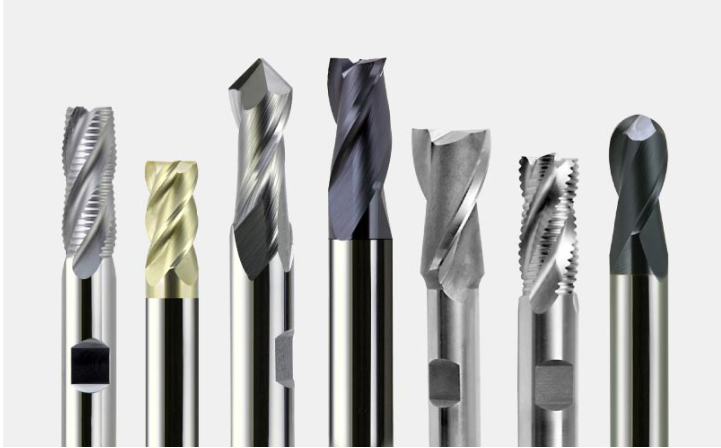





Material Properties of Carbide Cutting Tools
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardness | High resistance to deformation under stress. |
| Toughness | Ability to withstand impact and shock. |
| Wear Resistance | Prolonged lifespan under abrasive conditions. |
| Heat Resistance | Maintains performance at high temperatures. |
Specifications and Standards for Carbide Cutting Tools
| Specification | Range/Details |
|---|---|
| Tool Shapes | Flat, round, triangular, custom. |
| Size Range | From 1 mm to 100 mm cutting diameter. |
| Standards | ISO, ANSI, DIN compliance. |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Supplier | Location | Price Range (Per Tool) |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Carbide Tools | USA | $20–$150 |
| XYZ Machining Solutions | Germany | $25–$200 |
| Tungsten World Co. | China | $10–$100 |
How to Select the Right Carbide Cutting Tool
Choosing the perfect tool depends on various factors. Here’s a guide to help:
| Criteria | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Material | Harder materials require tougher grades. |
| Coating | Choose based on heat and wear resistance. |
| Tool Geometry | Match the shape to the cutting task. |
| Cost | Balance quality with budget. |

Advantages and Limitations of Carbide Cutting Tools
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Extremely durable and wear-resistant. | Higher initial cost than steel tools. |
| Withstands high speeds and temperatures. | Can be brittle under excessive force. |
| Delivers superior cutting precision. | Requires specific handling techniques. |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What makes carbide tools better than steel ones? | They’re harder, more durable, and can handle higher speeds. |
| How do I maintain carbide tools? | Regular cleaning, sharpening, and proper storage. |
| Are carbide tools recyclable? | Yes, they can be recycled to reclaim valuable tungsten. |
| Can carbide tools cut any material? | Almost all, but diamond tools are better for superhard materials. |
Carbide cutting tools are essential in any machining operation where precision, durability, and efficiency are paramount. By understanding their properties, applications, and selection criteria, you’re equipped to make the best choice for your needs. Keep exploring and experimenting—your tools are the foundation of your craft!




