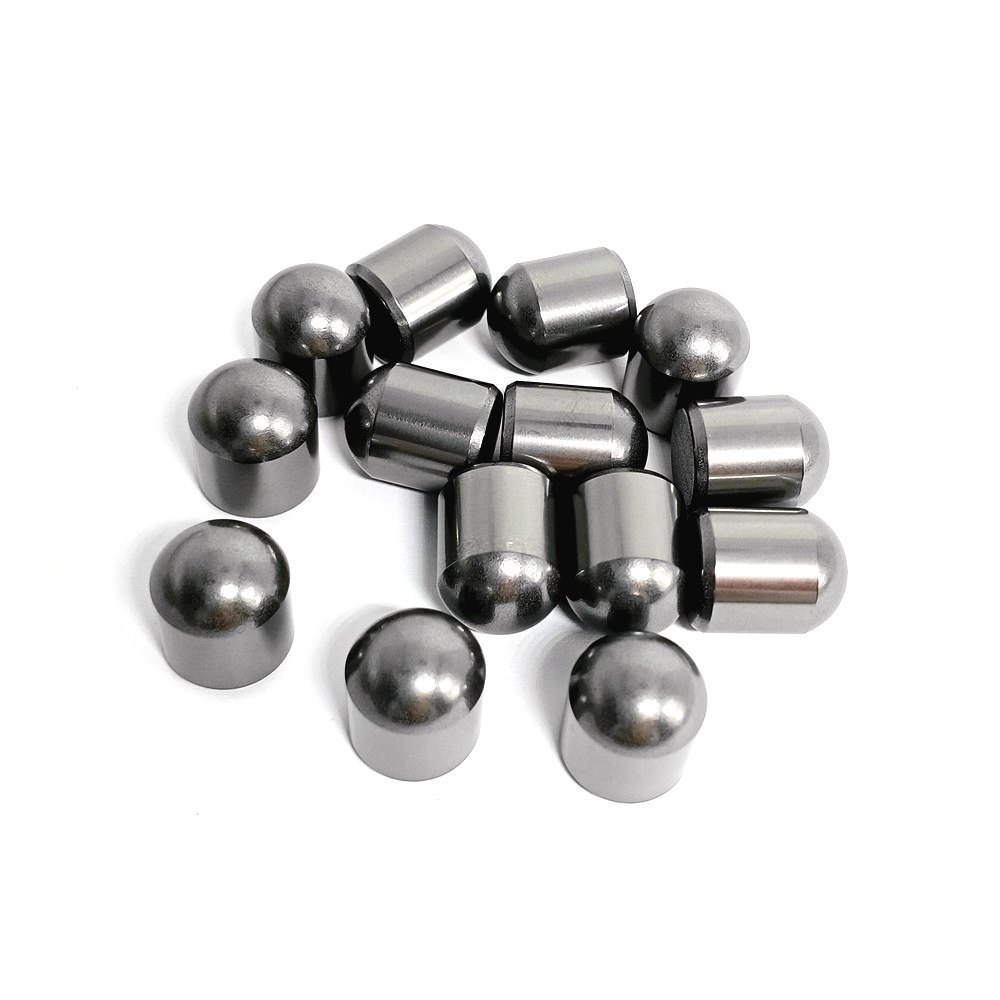
- Carbide button
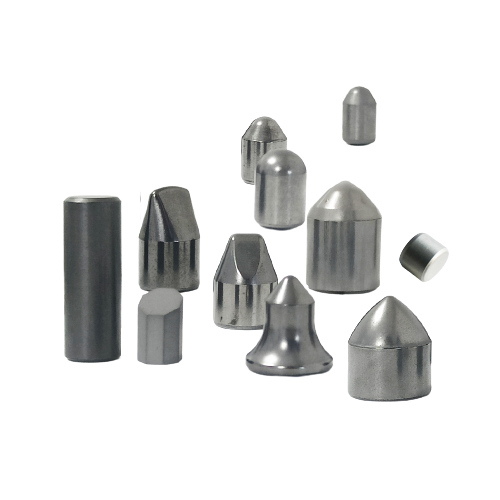

Carbide button
If you would like to learn more about our carbide grades, please click on HERE to browse the grade page.
A comprehensive standard selection of buttons in various dimensions is available in the below tables, but other sizes, tolerances & configurations also available on request.
Contact us if what you need is not shown here.
Introduction
Carbide buttons, also known as carbide inserts or tungsten carbide buttons, are small, durable, and high-performance cutting tools used in various drilling and mining applications. These buttons are typically made from a combination of tungsten carbide particles and a metallic binder, providing exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and strength.
Composition and Structure
Carbide buttons are widely used in industries such as mining, drilling, and construction for their durability and wear resistance. They are typically made from a composite material consisting of a hard carbide layer bonded to a tough steel substrate. The composition and structure of carbide buttons can vary depending on the specific application and manufacturer.

Hardness
Carbide buttons are exceptionally hard materials. Tungsten carbide, which is commonly used in carbide buttons, has a hardness level of approximately 9 on the Mohs scale. This hardness allows carbide buttons to withstand high levels of abrasion, making them well-suited for tasks that involve cutting, drilling, or grinding.
Wear Resistance
Carbide buttons exhibit excellent wear resistance, which means they can withstand repeated friction and abrasion without significant wear or deterioration. This property is particularly important in industries such as mining and drilling, where tools are subjected to harsh and abrasive conditions over extended periods.
Toughness
While carbide is extremely hard, it is also inherently brittle. To enhance toughness and prevent fracturing or chipping, carbide buttons often contain a binder material such as cobalt. The binder acts as a support structure, improving the toughness and resistance to impact or shock loading.
Heat Resistance
Carbide buttons have good heat resistance, allowing them to operate under high-temperature conditions without significant deformation or loss of hardness. This property is crucial in applications involving high-speed drilling or cutting, where the generated heat can be intense.
Corrosion Resistance
Carbide buttons typically have good corrosion resistance, enabling them to withstand exposure to various chemicals, moisture, and harsh environments. This property is advantageous in industries where tools are frequently exposed to corrosive substances or conditions.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Carbide buttons offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, meaning they are lightweight yet possess exceptional strength. This characteristic makes them efficient and effective tools, reducing operator fatigue and allowing for improved productivity.
Versatility
Carbide buttons can be manufactured in different shapes and sizes to suit specific applications. Their versatility allows for customization based on the drilling or cutting requirements, providing enhanced efficiency and precision.
Powder Preparation
Tungsten carbide powder and other necessary materials, such as cobalt powder for the binder phase, are mixed and blended together. The powder mixture is carefully formulated to achieve the desired carbide composition and properties.
Compaction
The powder mixture is placed into a die and compacted under high pressure. This process, known as cold compaction, forms a green compact with the desired shape and dimensions of the carbide button.
Pre-Sintering
The green compact undergoes a pre-sintering or presintering process in a furnace. This step helps in removing the organic binders and lubricants from the compacted material. The pre-sintering is typically carried out at a relatively low temperature, below the melting point of the carbide material.
Sintering
The pre-sintered green compact is then subjected to a high-temperature sintering process. The compact is placed in a furnace and heated to a temperature above the melting point of the carbide material but below the melting point of the binder phase (cobalt). This allows the tungsten carbide particles to bond together while maintaining the integrity of the binder phase.
Shaping and Grinding
After sintering, the carbide material is in a dense and solid form. It is then shaped and ground using precision grinding machines to achieve the final dimensions, shape, and surface finish required for the carbide button.
Brazing or Soldering
In some cases, the carbide button is brazed or soldered onto a steel substrate to form a composite tool. This process involves the use of a filler material that melts at a lower temperature than the carbide material. The button and the substrate are heated, and the filler material is applied to join them together.
Finishing and Quality Control
The finished carbide buttons undergo various finishing processes, such as polishing, cleaning, and coating, to enhance their surface properties and ensure high-quality performance. Additionally, rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the buttons meet the required specifications and performance standards.
Mining and Drilling
Carbide buttons are widely used in mining and drilling operations. They are incorporated into drill bits, downhole tools, and other equipment used for rock drilling, well drilling, and mineral extraction. The hardness and wear resistance of carbide buttons allow them to withstand the harsh conditions of drilling through hard rocks, providing efficient and long-lasting performance.
Construction and Road Building
Carbide buttons are essential in construction and road building activities. They are utilized in tools such as road milling machines, trenching machines, and concrete cutting equipment. The wear resistance of carbide buttons enables them to effectively cut and remove asphalt, concrete, and other tough materials, contributing to efficient construction processes.
Metal Cutting and Machining
Carbide buttons are employed in metal cutting and machining applications. They are utilized in tools such as inserts, end mills, and turning tools used in milling, turning, and machining operations. The hardness and toughness of carbide buttons enable them to withstand the high temperatures and forces generated during metal cutting, resulting in improved cutting efficiency and extended tool life.
Well Completion and Oil Extraction
Carbide buttons are used in the oil and gas industry for well completion and oil extraction processes. They are utilized in tools such as drill bits, tricone bits, and PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) bits. The wear resistance and heat resistance of carbide buttons make them suitable for drilling through challenging formations, enabling efficient oil and gas extraction.
Mining and Drilling
Carbide buttons are widely used in mining and drilling operations. They are incorporated into drill bits, downhole tools, and other equipment used for rock drilling, well drilling, and mineral extraction. The hardness and wear resistance of carbide buttons allow them to withstand the harsh conditions of drilling through hard rocks, providing efficient and long-lasting performance.
Construction and Road Building
Carbide buttons are essential in construction and road building activities. They are utilized in tools such as road milling machines, trenching machines, and concrete cutting equipment. The wear resistance of carbide buttons enables them to effectively cut and remove asphalt, concrete, and other tough materials, contributing to efficient construction processes.
Metal Cutting and Machining
Carbide buttons are employed in metal cutting and machining applications. They are utilized in tools such as inserts, end mills, and turning tools used in milling, turning, and machining operations. The hardness and toughness of carbide buttons enable them to withstand the high temperatures and forces generated during metal cutting, resulting in improved cutting efficiency and extended tool life.
Well Completion and Oil Extraction
Carbide buttons are used in the oil and gas industry for well completion and oil extraction processes. They are utilized in tools such as drill bits, tricone bits, and PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) bits. The wear resistance and heat resistance of carbide buttons make them suitable for drilling through challenging formations, enabling efficient oil and gas extraction.
Yes, carbide buttons generally have good heat resistance, allowing them to withstand high temperatures without deformation or loss of hardness. They also possess corrosion resistance, enabling them to withstand exposure to chemicals, moisture, and harsh environments.
Carbide buttons find applications in mining, drilling, construction, metal cutting, and oil extraction. They are used in tools such as drill bits, road milling machines, inserts, and turning tools for efficient cutting, drilling, and machining operations.
Yes, carbide buttons can be customized in terms of shape, size, and cutting geometry to suit specific drilling or cutting requirements. This customization allows for enhanced efficiency, precision, and performance in different applications.
While tungsten carbide is extremely hard and wear-resistant, it can experience wear and tear over time. In some cases, depending on the extent of wear, buttons can be refurbished through grinding or other specialized processes. However, if the wear is significant, replacement is often the most cost-effective solution.
- Microstructure Refinement: Forging processes, involving controlled plastic deformation, refine the grain structure of tungsten carbide, enhancing its strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
- Density and Porosity Control: Forging helps eliminate internal voids and porosity, resulting in denser, more durable carbide buttons that can withstand extreme operating conditions.
- Shape Complexity and Precision: Different forging techniques offer varying degrees of flexibility in achieving intricate shapes and precise dimensions, catering to specific application requirements.
- Cutting Efficiency: Shape and size impact penetration and material removal.
- Wear Resistance: Optimized designs reduce wear and prolong tool life.
- Heat Dissipation: Specific geometries enhance thermal management.
- Application Suitability: Tailored designs improve performance in drilling, mining, and construction.
The optimal button type and grade depend on factors like the hardness of the coal seam, the type of mining equipment used, and the desired balance between penetration and wear resistance. Consulting with our technical experts is recommended for personalized guidance.
- Spherical Buttons: For hard rock drilling and mining.
- Conical Buttons: Ideal for percussive drilling and impact resistance.
- Parabolic Buttons: Used in soft to medium-hard rock formations.
- Chisel Buttons: For cutting and breaking applications.
- Flat-top Buttons: For general-purpose and high-abrasion drilling.

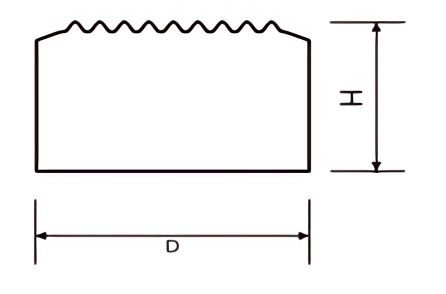
Data
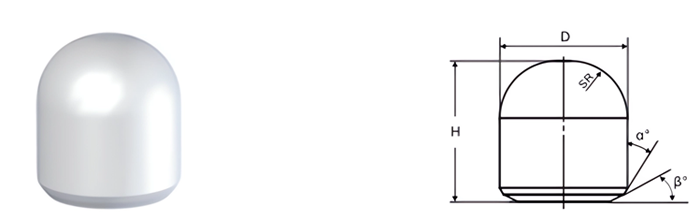
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | SR/mm | α° | β° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBS0625099 | 6.25 | 9.9 | 3.40 | 20 | 26.50 |
| MBS0825122 | 8.25 | 12.2 | 4.40 | 20 | 26.50 |
| MBS0925139 | 9.25 | 13.9 | 5.00 | 20 | 26.50 |
| MBS1025189 | 10.25 | 18.9 | 5.50 | 20 | 27.00 |
| MBS1130190 | 11.30 | 19.0 | 6.00 | 20 | 27.00 |
| MBS1235209 | 12.35 | 20.9 | 6.60 | 20 | 28.00 |
| MBS1235200 | 12.35 | 20.0 | 6.30 | 25 | 24.75 |
| MBS1335199 | 13.35 | 19.9 | 7.00 | 20 | 27.00 |
| MBS1435221 | 14.35 | 22.1 | 7.70 | 20 | 16.00 |
| MBS1435240 | 14.35 | 24.0 | 7.34 | 25 | 25.00 |
| MBS1635249 | 16.35 | 24.9 | 8.80 | 20 | 16.00 |
| MBS1935304 | 19.35 | 30.4 | 9.76 | 20 | 30.00 |
| MBS2165319 | 21.65 | 31.9 | 11.80 | 20 | 30.00 |
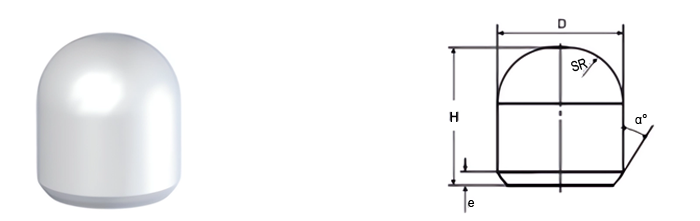
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | SR/mm | e/mm | α° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBS0825100-E15 | 8.25 | 10.0 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 18 |
| MBS0825120-E15 | 8.25 | 12.0 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 18 |
| MBS1825271-E15 | 18.25 | 27.1 | 9.2 | 1.5 | 18 |
| MBS0825122-E07 | 8.25 | 12.2 | 4.4 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS0925149-E07 | 9.25 | 14.9 | 5.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1025130-E07 | 10.25 | 13.0 | 5.5 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1130140-E07 | 11.30 | 14.0 | 6.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1235160-E07 | 12.35 | 16.0 | 6.6 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1335180-E07 | 13.35 | 18.0 | 7.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1335135-E15 | 13.35 | 13.5 | 7.0 | 1.5 | 18 |
| MBS1335199-E15 | 13.35 | 19.9 | 7.0 | 1.5 | 18 |
| MBS1435181-E07 | 14.35 | 18.1 | 7.7 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1435200-E30 | 14.35 | 20.0 | 7.2 | 3.0 | 18 |
| MBS1435150-E17 | 14.35 | 15.0 | 7.5 | 1.7 | 18 |
| MBS1635246-E07 | 16.35 | 24.6 | 8.8 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS1635190-E22 | 16.35 | 19.0 | 8.8 | 2.2 | 18 |
| MBS1635219-E22 | 16.35 | 21.9 | 8.8 | 2.2 | 18 |
| MBS1806250-E20 | 18.06 | 25.0 | 9.0 | 2.0 | 20 |
| MBS1700280-E20 | 17.00 | 28.0 | 8.9 | 2.0 | 18 |
| MBS2045300-E07 | 20.45 | 30.0 | 11.5 | 0.7 | 30 |
| MBS2245300-E07 | 22.45 | 30.0 | 12.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
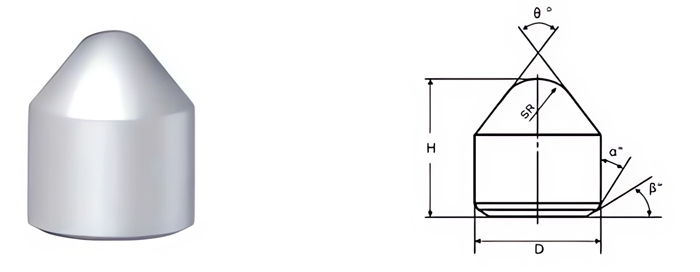
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | SR/mm | θ° | α° | β° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC0825122-700 | 8.25 | 12.2 | 3.0 | 70.0 | 20 | 27.0 |
| MBC0925133-700 | 9.25 | 13.3 | 3.0 | 70.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC0925149-550 | 9.25 | 14.9 | 3.0 | 55.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC1025162-700 | 10.25 | 16.2 | 4.0 | 70.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC1025162-520 | 10.25 | 16.2 | 4.0 | 52.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC1130159-520 | 11.30 | 15.9 | 4.0 | 52.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC1130174-600 | 11.30 | 17.4 | 4.0 | 60.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC1130180-550 | 11.30 | 18.0 | 4.0 | 55.0 | 20 | 26.5 |
| MBC1235179-550 | 12.35 | 17.9 | 4.8 | 55.0 | 20 | 28.0 |
| MBC1235180-550 | 12.35 | 18.0 | 4.0 | 55.0 | 20 | 27.0 |
| MBC1235189-700 | 12.35 | 18.9 | 4.8 | 70.0 | 20 | 28.0 |
| MBC1435219-550 | 14.35 | 21.9 | 5.0 | 55.0 | 20 | 14.5 |
| MBC1435239-670 | 14.35 | 23.9 | 3.0 | 67.0 | 20 | 15.5 |
| MBC1435200-715 | 14.35 | 20.0 | 5.0 | 71.5 | 30 | 15.5 |
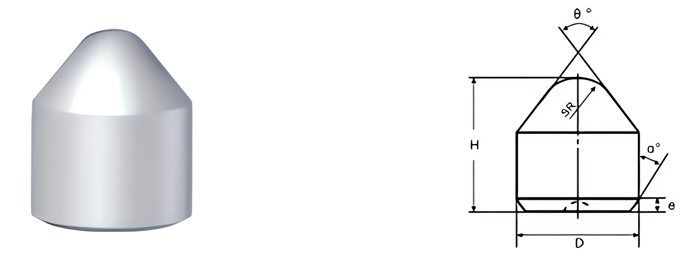
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | SR/mm | θ° | α° | e/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC0725110-700-E07 | 7.25 | 11.0 | 2.8 | 70 | 30 | 0.7 |
| MBC0825120-700-E15 | 8.25 | 12.0 | 3.0 | 70 | 18 | 1.5 |
| MBC0825120-700-E07 | 8.25 | 12.0 | 3.0 | 70 | 30 | 0.7 |
| MBC0925140-700-E07 | 9.25 | 14.0 | 3.0 | 70 | 30 | 0.7 |
| MBC1025180-720-E12 | 10.25 | 18.0 | 2.7 | 72 | 60 | 1.2 |
| MBC1235189-700-E07 | 12.35 | 18.9 | 4.8 | 70 | 30 | 0.7 |
| MBC1235220-520-E10 | 12.35 | 22.0 | 2.0 | 52 | 45 | 1.0 |
| MBC1335199-700-E07 | 13.35 | 19.9 | 4.8 | 70 | 30 | 0.7 |
| MBC1435160-560-E20 | 14.35 | 16.0 | 5.7 | 56 | 18 | 2.0 |
| MBC1435220-710-E15 | 14.35 | 22.0 | 5.0 | 71 | 18 | 1.5 |
| MBC1435201-520-E10 | 14.35 | 20.1 | 5.0 | 52 | 45 | 1.0 |
| MBC1825250-550-E12 | 18.25 | 25.0 | 6.0 | 55 | 20 | 1.2 |
| MBC1935260-420-E21 | 19.35 | 26.0 | 7.5 | 42 | 18 | 2.1 |
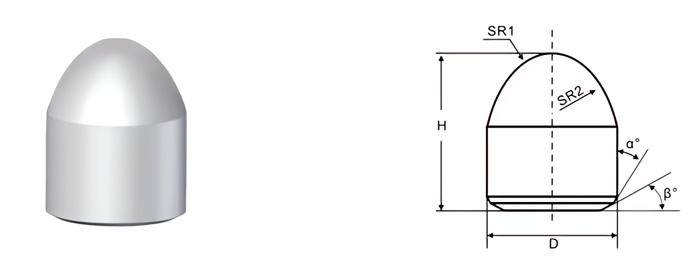
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | SR1/mm | SR2/mm | α° | β° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBP1235219 | 12.35 | 21.9 | 3.0 | 16.0 | 20 | 27 |
| MBP1235226 | 12.35 | 22.6 | 4.6 | 13.3 | 25 | 25 |
| MBP1235230 | 12.35 | 23.0 | 3.0 | 12.0 | 25 | 25 |
| MBP1435267 | 14.35 | 26.7 | 5.3 | 15.4 | 25 | 25 |
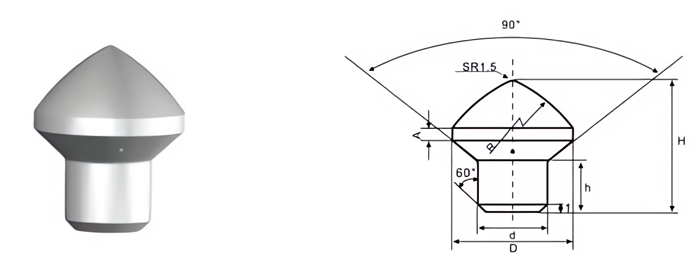
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | d/mm | h/mm | R/mm | r/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMB-M-1200220-1000 | 12.00 | 22.0 | 10.00 | 8.0 | 30 | 1.5 |
| CMB-M-2000250-1200 | 20.00 | 25.0 | 12.00 | 10.0 | 35 | 1.5 |
| CMB-M-2000270-1200 | 20.00 | 27.0 | 12.00 | 10.5 | 35 | 4.0 |
| CMB-M-2200280-1400 | 22.00 | 28.0 | 14.00 | 12.0 | 40 | 1.5 |
| CMB-M-2492342-1725 | 24.92 | 34.2 | 17.25 | 11.8 | 40 | 2.0 |
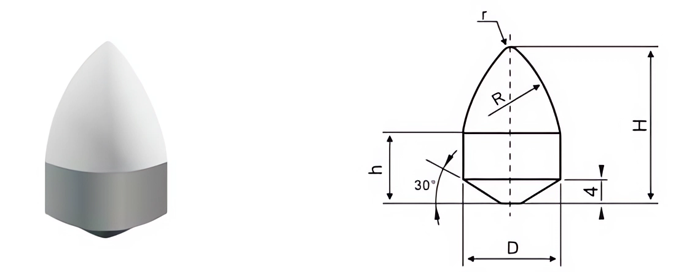
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | h/mm | R/mm | r/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMB-C-1700265-12 | 17.00 | 26.50 | 12 | 26 | 1.75 |
| CMB-C-1700265-15 | 17.00 | 26.50 | 15 | 26 | 1.75 |
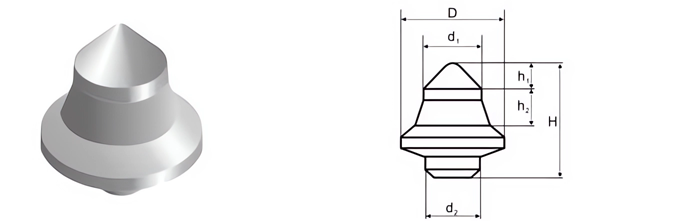
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | h1/mm | h2/mm | d1/mm | d2/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-RB-18002015 | 18.00 | 20.15 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 10 | 9.50 |
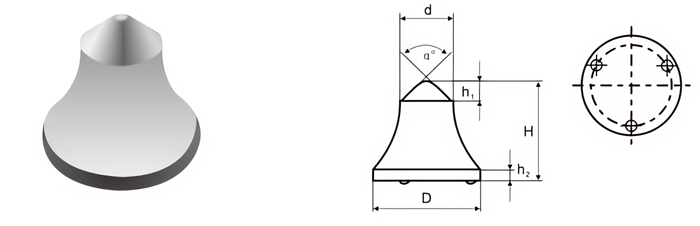
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | d/mm | h1/mm | h2/mm | α° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-RB-16071508 | 16.07 | 15.08 | 8.0 | 3.00 | 1.8 | 92 |
| CB-RB-18751776 | 18.75 | 17.76 | 9.5 | 3.75 | 1.5 | 82 |
| CB-RB-17861716 | 17.86 | 17.16 | 9.6 | 3.84 | 1.6 | 82 |
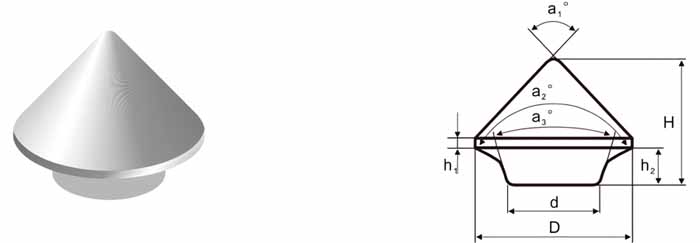
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | d/mm | h1/mm | h2/mm | α1° | α2° | α3° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-RB-15001100 | 15.0 | 11.0 | 8.8 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 95 | 126 | 30 |
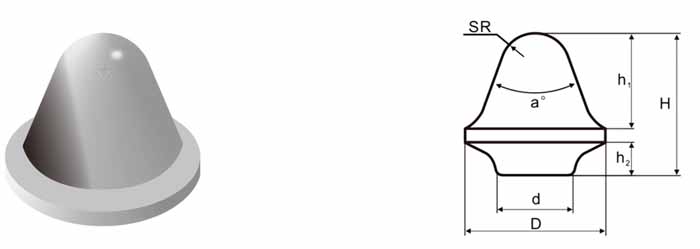
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | d/mm | h1/mm | h2/mm | SR/mm | α° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-RB-16401660 | 16.4 | 16.6 | 8.8 | 11.3 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 40 |
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | h/mm | e/mm | SR | θ1° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-RD-24003200 | 24.0 | 32.0 | 19.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
| CB-RD-22002800 | 22.0 | 28.0 | 14.4 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 45 |
| CB-RD-19002800 | 19.0 | 28.0 | 17.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 45 |
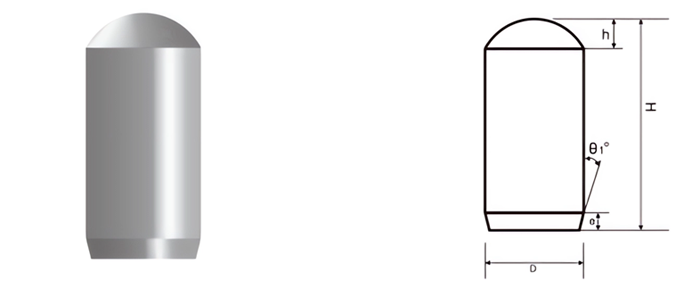
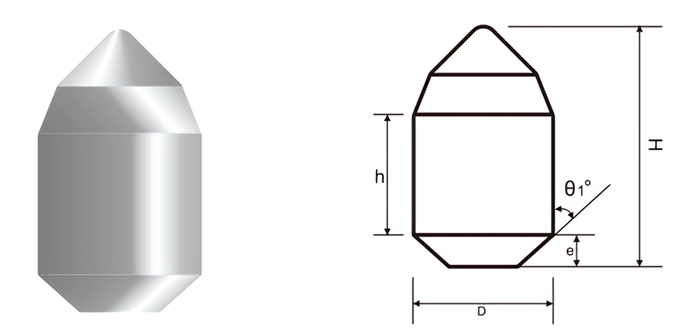
| Part No. | D/mm | H/mm | h/mm | e/mm | SR/mm | θ1° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-R-15903500 | 15.9 | 35.0 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
| CB-R-15904500 | 15.9 | 45.0 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
| CB-R-15905000 | 15.9 | 50.0 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
| CB-R-21903500 | 21.9 | 35.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
| CB-R-21904500 | 21.9 | 45.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
| CB-R-21907000 | 21.9 | 70.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 45 |
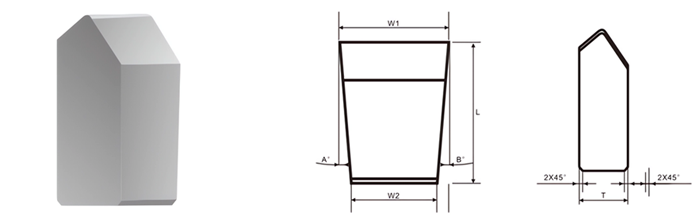
| Part No. | L/mm | T/mm | W1/mm | W2/mm | A° | B° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-TBM-1 | 70 | 25 | 51.82 | 41.73 | 5.61 | 2.70 |
| CB-TBM-2 | 70 | 25 | 53.73 | 46.95 | 2.80 | 2.80 |
| CB-TBM-3 | 70 | 25 | 41.73 | 51.82 | 2.70 | 5.61 |
| CB-TBM-4 | 70 | 25 | 59.49 | 42.17 | 3.00 | 11.20 |
| CB-TBM-5 | 70 | 25 | 59.49 | 42.17 | 11.20 | 3.00 |
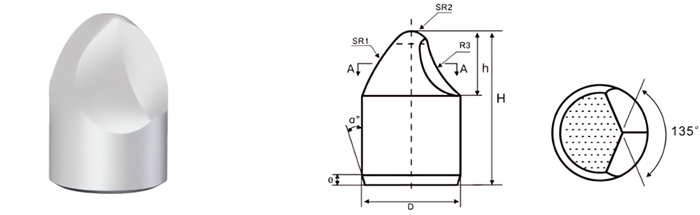
| Part No. | D mm |
H mm |
h mm |
SR1 mm |
SR2 mm |
R3 | e | α° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFB-P-14352000 | 14.35 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 12.0 | 2.0 | 14.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
| OFB-P-16352100 | 16.35 | 21.0 | 10.0 | 14.0 | 2.5 | 16.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
| OFB-P-16352500 | 16.35 | 25.0 | 12.5 | 16.0 | 2.5 | 18.0 | 0.7 | 30 |
| Type | D/mm | H/mm |
|---|---|---|
| PDC-M-I | 8.0-10.0 | 3.0-11.0 |
| PDC-M-II | 10.0-12.0 | 3.0-11.0 |
| PDC-M-III | 14.0-15.0 | 3.0-16.0 |
| Type | D/mm | H/mm |
|---|---|---|
| PDC-OF-I | 14.0-15.0 | 3.0-16.0 |
| PDC-OF-II | 17.3-17.7 | 8.0-19.0 |
| PDC-OF-III | 20.4-20.7 | 8.0-19.0 |
| PDC-OF-IV | 25.0-27.0 | 8.0-15.0 |
Grades for Carbide Buttons of Mining and Construction
| Grade | ISO Code | Grain Size | Density {g/cm³} | Hardness {HRA} | TRS {N/mm} | Application Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade for Mining, Coal Mining and Construction | ||||||
| TM28 | K20 | Medium | 15.00 | 90.3 | 2800 | Exellent balance of impact & wear resistance. suitable for cemented carbide buttons of DTH bits and threaded drilling bits. |
| TM28N | K20 | Medium | 15.00 | 90.0 | 2850 | |
| TM25 | K20 | Medium | 15.00 | 90.2 | 2500 | |
| TC26 | K20 | Coarse | 14.90 | 89.2 | 2600 | |
| TC24 | K30 | Coarse | 14.70 | 88.5 | 2400 | Mainly used for carbide buttons of tricone bits and inserts of other dirlling bits. |
| TC26 | K30 | Coarse | 14.50 | 88.0 | 2600 | |
| TC27 | K40 | Coarse | 14.45 | 87.0 | 2700 | Suitable for carbide inserts of heavy-duty rock drilling tools, also for tricone bits. |
| TEC28 | K30 | Extra-coarse | 14.50 | 87.0 | 2800 | Extra-coarse grain size, with high impact resistance, special for mining, road milling and pile foundation. |
| TEC30A | K40 | Extra-coarse | 14.40 | 86.5 | 3000 | |
| TEC30N | K40 | Extra-coarse | 14.35 | 86.3 | 3000 | |
| TEC30B | K40 | Extra-coarse | 14.30 | 86.2 | 3000 | |
| TEC26N | K30 | Extra-coarse | 14.90 | 86.5 | 2600 | |
| TEC28N | K30 | Extra-coarse | 14.70 | 86.0 | 2800 | |
| Grade for Oil field and PDC | ||||||
| YG8 | K30 | Medium | 14.75 | 90.0 | 2400 | Good wear resistance, suitable for diameter-keeping & serrated inserts. |
| YG11C | K40 | Coarse | 14.40 | 88.0 | 2600 | Good impact resistance, suitable for midium-hard or soft rock application. |
| YG13C | K40 | Coarse | 14.20 | 87.0 | 2600 | |
| TM28NB | K50 | Medium | 14.20 | 87.5 | 2800 | Good impact and wear resistance, suitable for composite with PDC and PCBN. |
| YG13 | K40 | Medium | 14.20 | 87.5 | 2800 | |
| YG16 | K50 | Medium | 13.90 | 87.0 | 2900 | Super impact resistance, suitable for composite with diamond excavation in oil field |
| TM30 | K50 | Medium | 13.90 | 86.5 | 3000 | |
- Contact
Our team is ready to provide support
Truer Carbide is committed to providing efficient solutions to problems. Each team member has the expertise and experience to quickly understand and meet your needs.
