Introduction: Taming the Beast: Precision Machining of Cast Iron
Cast iron, with its impressive strength and cost-effectiveness, reigns supreme in countless industrial applications. Yet, machining this robust material presents unique challenges due to its abrasive nature and tendency to form hard, discontinuous chips. Enter Type G carbide brazed tips, the specialized tools engineered to conquer the intricacies of cast iron machining, delivering exceptional performance, tool life, and surface finish.
This article delves into the world of Type G carbide brazed tips, exploring their unique characteristics, advantages, and the reasons why they’re the go-to choice for achieving precision and efficiency when machining cast iron components.
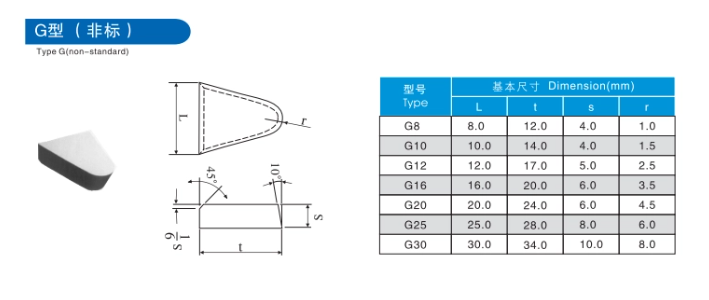
The Cast Iron Challenge: Abrasion, Heat, and Chip Formation
Navigating the Terrain of Tough Machining:
Machining cast iron presents a trifecta of challenges that can quickly degrade conventional cutting tools:
- High Abrasion Resistance: The presence of graphite flakes within the cast iron matrix creates an inherently abrasive material, accelerating tool wear and reducing cutting edge sharpness.
- Heat Generation: The abrasive nature of cast iron generates significant heat during machining, further contributing to tool wear and potentially affecting dimensional accuracy.
- Discontinuous Chip Formation: The brittle nature of cast iron results in the formation of small, discontinuous chips that can become trapped in the cutting zone, leading to increased friction, heat buildup, and potential tool damage.
Type G Carbide Brazed Tips: Engineered for Cast Iron Mastery
The Anatomy of Abrasion Resistance and Chip Control:
Type G carbide brazed tips are specifically designed to address the challenges of cast iron machining, characterized by:
- Tough Carbide Grades: Type G tips employ carbide grades with enhanced toughness and resistance to abrasion, ensuring they can withstand the harsh cutting environment of cast iron.
- Sharp Cutting Edges: Maintaining sharp cutting edges is crucial for efficient chip formation and minimizing heat generation in cast iron machining. Type G tips often feature sharp, positive rake angles to facilitate clean shearing action.
- Chip Control Features: Many Type G tips incorporate chipbreakers or chip control geometries designed to break up the long, stringy chips that cast iron tends to produce. These features promote efficient chip evacuation, reduce heat buildup, and prevent chip welding.
7 Reasons Why Type G Carbide Brazed Tips Excel in Cast Iron Machining
Conquering the Challenges with Confidence:
The specialized design and material properties of Type G carbide brazed tips translate into several key advantages:
- Exceptional Abrasion Resistance: Their tough carbide grades and sharp cutting edges can withstand the high abrasive wear encountered when machining cast iron, significantly extending tool life.
- Efficient Chip Control: The chipbreaker geometries and positive rake angles promote efficient chip formation and evacuation, reducing heat buildup, preventing chip welding, and enhancing surface finish.
- Improved Surface Finish: The combination of sharp cutting edges, efficient chip control, and reduced cutting forces enables Type G tips to achieve surprisingly good surface finishes on cast iron, often eliminating the need for secondary finishing operations.
- Reduced Cutting Forces: The sharp cutting edges and positive rake angles minimize cutting forces, reducing stress on the tool, the machine tool, and the workpiece.
- Increased Productivity: The extended tool life, reduced downtime, and ability to achieve higher cutting speeds and feeds contribute to increased productivity and reduced cycle times.
- Cost-Effectiveness in Demanding Applications: The enhanced tool life and improved productivity offered by Type G tips translate into significant cost savings, especially in high-volume cast iron machining operations.
- Versatility in Cast Iron Machining: Type G tips are suitable for a wide range of cast iron machining operations, including roughing, finishing, turning, milling, drilling, and boring.
Applications of Type G Carbide Brazed Tips
Where Precision and Efficiency Meet in Cast Iron Machining:
Type G carbide brazed tips are the go-to choice for a wide range of cast iron machining applications:
- Automotive Industry: Machining engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission cases, and other components where cast iron’s strength and cost-effectiveness are highly valued.
- Heavy Equipment Manufacturing: Producing gears, housings, and other critical components for construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and mining equipment.
- Pump and Valve Manufacturing: Creating intricate features and smooth surfaces on pump housings, valve bodies, and other components where fluid flow and pressure containment are critical.
Choosing the Right Type G Carbide Brazed Tip: Factors to Consider
Optimizing Tool Selection for Cast Iron Mastery:
Selecting the optimal Type G carbide brazed tip involves carefully considering several factors:
- Type of Cast Iron: Different grades of cast iron exhibit varying levels of hardness, strength, and machinability, influencing the choice of carbide grade and coating.
- Machining Operation: The specific machining operation, such as roughing, finishing, turning, milling, drilling, or boring, influences the choice of tip geometry, size, and chipbreaker design.
- Cutting Conditions: The desired cutting speeds, feeds, depths of cut, and the presence of interrupted cuts influence tip selection.
- Machine Tool Capability: The rigidity and power of the machine tool can impact the achievable cutting parameters and the selection of the appropriate tip size and geometry.
Type G Carbide Brazed Tip Selection: A Simplified Guide
To assist in the selection process, here’s a table summarizing typical applications and considerations for different Type G tip geometries:
| Type G Tip Geometry | Typical Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Round Insert with Chipbreaker | General-purpose turning, facing, and boring | Provides good chip control and a balance of sharpness and strength |
| Square Insert with Chipbreaker | Milling, shoulder milling, and slotting | Offers a strong cutting edge and good chip evacuation for interrupted cuts |
| Triangular Insert with Positive Rake | Plunge milling, ramping, and chamfering | Provides a strong cutting edge for aggressive cutting and plunging operations |
Frequently Asked Questions about Type G Carbide Brazed Tips
Q1: Can Type G carbide brazed tips be used for machining materials other than cast iron?
A1: While specifically designed for cast iron, Type G tips can be used to machine other materials, particularly those with similar properties, such as ductile iron and compacted graphite iron. However, their performance may vary depending on the specific material and cutting conditions.
Q2: What are the signs of wear on a Type G carbide brazed tip?
A2: Common wear signs include flank wear on the cutting edge, crater wear on the rake face, and chipping or rounding of the cutting edge. In cast iron machining, wear can manifest as a deterioration of surface finish, increased cutting forces, or changes in chip formation.
Q3: How can I maximize tool life when machining cast iron with a Type G carbide brazed tip?
A3: Key factors include selecting the appropriate tip geometry and grade for the application, optimizing cutting parameters (considering the cast iron grade and the machine tool’s capabilities), ensuring proper cutting fluid application, and maintaining a rigid machine setup.
Q4: What is the role of chipbreakers in Type G carbide brazed tips?
A4: Chipbreakers are designed to break up the long, stringy chips that cast iron tends to produce, promoting efficient chip evacuation, reducing heat buildup, and preventing chip welding, which can damage both the tool and the workpiece.
Q5: When would I choose a round insert versus a square insert Type G tip for cast iron machining?
A5: Round inserts with chipbreakers are often preferred for general-purpose turning, facing, and boring operations on cast iron, while square inserts with chipbreakers are better suited for milling, shoulder milling, and slotting operations where interrupted cuts are common.




