Plaquettes en carbure sont les héros méconnus de l'usinage de précision, permettant aux fabricants de créer des pièces de haute qualité dans tous les secteurs. Que vous soyez machiniste, ingénieur ou curieux des outils de coupe métalliques, ce guide démystifiera les plaquettes en carbure. Nous allons explorer leur composition, leurs types, leurs propriétés, leurs applications et bien d'autres choses encore, de manière très détaillée, attrayante et conviviale.
Qu'est-ce qu'une plaquette en carbure ?
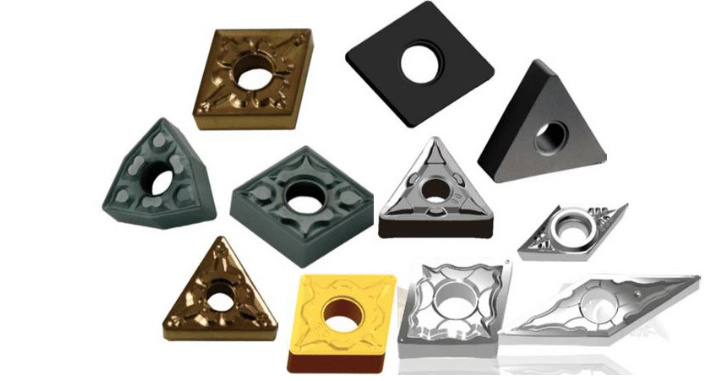
Les plaquettes en carbure sont de petits outils de précision utilisés dans les opérations d'usinage pour couper, façonner et affiner les matériaux. Ces plaquettes, généralement fabriquées à partir de poudre de carbure de tungstène, offrent durabilité et efficacité lors de l'usinage de matériaux durs tels que l'acier, la fonte et les alliages. Il faut les considérer comme les dents acérées sur le bord d'un outil puissant, conçues pour rester aiguisées sous une pression immense.

Types de plaquettes en carbure et leurs utilisations
Les plaquettes en carbure se présentent sous différentes formes, qualités et revêtements pour répondre à des besoins d'usinage spécifiques. Le tableau ci-dessous présente les types de plaquettes en carbure et leurs applications typiques.
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Plaquettes de tournage | Conçus pour la précision des opérations de tournage. Souvent de forme triangulaire, carrée ou en losange. | Opérations de tournage, de contournage et de profilage. |
| Plaquettes de fraisage | Plaquettes utilisées dans les fraises pour enlever efficacement la matière. | Rainurage, surfaçage et finition de surface. |
| Plaquettes de forage | Inserts très résistants qui garantissent la précision du perçage des trous. | Création de trous dans les métaux durs. |
| Inserts brasés | Fixés aux outils, ils offrent d'excellentes performances à moindre coût. | Usinage à usage général. |
| Plaquettes de rainurage | Spécialement conçu pour les opérations de rainurage et de filetage. | Création de rainures, de fentes et de filets. |
| Plaquettes de séparation | Optimisé pour les opérations de tronçonnage avec des coupes nettes. | Séparer les pièces à usiner des matériaux de base. |
| Inserts de filetage | Inserts précis pour créer des filets sur les matériaux. | Filetage intérieur et extérieur. |
| Inserts revêtus | Plaquettes revêtues de TiN, TiCN ou Al2O3 pour une durée de vie prolongée. | Usinage à grande vitesse, applications résistantes à la chaleur. |
| Inserts en céramique | Non carburé mais souvent associé à un usinage spécialisé avec une meilleure résistance à l'usure. | Usinage à haute température de matériaux trempés. |
| Inserts à pointe de diamant | Pointe en diamant polycristallin pour une précision de coupe et une longévité inégalées. | Usinage des matériaux non ferreux et des composites. |
Matières premières et composition des Plaquettes en carbure
Les plaquettes en carbure sont principalement composées de carbure de tungstène, un composé formé de tungstène et de carbone. Voici un aperçu des matières premières et de la composition typiques de ces plaquettes :
| Composant | Rôle | Pourcentage (typique) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbure de tungstène (WC) | Assure la dureté et la résistance à l'usure. | 70-97% |
| Cobalt (Co) | Agit comme un liant pour maintenir les grains de carbure ensemble. | 3-20% |
| Carbure de titane (TiC) | Améliore la résistance à la chaleur et la ténacité. | 0-10% |
| Carbure de tantale (TaC) | Améliore la stabilité à haute température. | 0-5% |
Le mélange exact dépend de l'application prévue de l'insert, de l'équilibre entre la dureté, la ténacité et la résistance à l'usure thermique et mécanique.
Processus de production des plaquettes en carbure
Vous êtes-vous déjà demandé comment sont fabriquées ces petites merveilles ? Le processus est complexe et garantit que chaque insert répond à des normes rigoureuses.
- Préparation de la poudre
Le carbure de tungstène, le cobalt et d'autres additifs sont mélangés en une fine poudre. - Le compactage
La poudre est pressée dans un moule pour former la forme souhaitée de l'insert à l'aide d'une forte pression. - Frittage
Les formes compactées sont chauffées à haute température (environ 1400°C) pour lier les particules et créer un matériau solide et dense. - Meulage et façonnage
Les plaquettes frittées sont rectifiées dans des géométries précises à l'aide d'outils à pointe de diamant. - Revêtement
Selon l'application, les inserts peuvent être revêtus de matériaux tels que le nitrure de titane ou l'oxyde d'aluminium. - Inspection et conditionnement
Chaque insert est soumis à un contrôle de qualité rigoureux afin de garantir la précision des dimensions et des performances avant d'être expédié.





Applications de la Plaquettes en carbure
Les plaquettes en carbure sont indispensables dans de nombreuses industries. Voici un tableau présentant leurs applications :
| L'industrie | Application | Exemples de tâches |
|---|---|---|
| Automobile | Usinage de précision de pièces de moteur. | Vilebrequins, arbres à cames, engrenages. |
| Aérospatiale | Usinage de matériaux légers et résistants à la chaleur. | Composants d'aéronefs, pales de turbines. |
| Fabrication | Travail général des métaux et fabrication. | Outils, moules et machines industrielles. |
| Pétrole et gaz | Usinage de matériaux résistants à la corrosion dans des environnements difficiles. | Vannes, pipelines, équipements de forage. |
| Médical | Création d'instruments médicaux de haute précision. | Implants, outils chirurgicaux. |
Propriétés des matériaux des plaquettes en carbure
Les plaquettes en carbure doivent concilier dureté, ténacité et résistance à l'usure. Voici un aperçu des propriétés de ces matériaux :
| Propriété | Description | Valeur typique |
|---|---|---|
| Dureté | Résistance à la déformation. | 1 500-2 200 HV |
| Résistance à la compression | Capacité à supporter des charges de compression. | 4 000 MPa |
| Résistance à la rupture | Capacité à résister à la propagation des fissures. | 8-14 MPa-m½ |
| Densité | Masse par unité de volume. | 13-15 g/cm³ |
| Conductivité thermique | Capacité à conduire la chaleur. | 70-100 W/mK |
Comment choisir la bonne plaquette en carbure
Le choix de la bonne plaquette peut sembler insurmontable, mais il s'agit avant tout d'équilibrer vos besoins en matière d'usinage. Tenez compte des facteurs suivants :
| Facteur | Description | Exemple de sélection |
|---|---|---|
| Type de matériau | Que faites-vous ? De l'acier, de l'aluminium ou autre chose ? | Acier : Inserts revêtus. |
| Type d'opération | Vous tournez, fraisez, percez ou filetez ? | Filetage : Inserts de filetage. |
| Vitesse et vitesse d'avance | Les vitesses élevées nécessitent des plaquettes durables avec des revêtements résistants à la chaleur. | Haute vitesse : revêtement TiAlN. |
| Durée de vie de l'outil | Privilégier la longévité ou la rentabilité ? | Durée de vie de l'outil plus longue : Cermet. |
Avantages et limites de la Plaquettes en carbure
| Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|
| Dureté et résistance à l'usure exceptionnelles. | Peut être fragile en cas d'impact important. |
| Polyvalent pour divers matériaux et applications. | Coût initial plus élevé que celui des outils en acier rapide. |
| Amélioration de la précision et de l'état de surface. | Nécessite des conditions d'usinage spécifiques. |

Fournisseurs et prix des plaquettes en carbure
| Fournisseur | Localisation | Prix (par encart) |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik Coromant | Mondial | $10-$50 |
| Kennametal | Mondial | $8-$40 |
| Matériaux Mitsubishi | Japon | $12-$45 |
| Iscar | Israël | $15-$60 |
| Outils Seco | Suède | $10-$55 |
FAQ
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| Quels sont les matériaux que les plaquettes en carbure peuvent couper ? | Ils sont idéaux pour l'usinage de métaux tels que l'acier, l'acier inoxydable, la fonte et les alliages non ferreux. |
| Quelle est la durée de vie des plaquettes en carbure ? | La durée de vie varie en fonction de l'utilisation, mais les plaquettes de haute qualité durent généralement plus longtemps que les outils HSS en raison de leur résistance supérieure à l'usure. |
| Les plaquettes en carbure peuvent-elles être réaffûtées ? | Non, ils sont jetables. Au lieu de réaffûter, vous remplacez la plaquette. |
| Quels sont les revêtements disponibles pour les plaquettes en carbure ? | Les revêtements les plus courants sont le TiN (nitrure de titane), le TiCN (carbonitrure de titane) et l'Al2O3 (oxyde d'aluminium), qui améliorent la résistance à l'usure et la dissipation de la chaleur. |




