Твердосплавные токарные пластины - невоспетые герои механической обработки. Они помогают нам формировать, вырезать и совершенствовать металл в точные формы, необходимые для бесчисленных применений. Если вы занимаетесь механической обработкой или производством, понимание твердосплавных токарных пластин имеет решающее значение. В этом руководстве мы погрузимся в мир твердосплавных токарных пластин и рассмотрим все, начиная с типов и областей применения и заканчивая выбором подходящей пластины для ваших нужд.
Обзор твердосплавных токарных пластин
Твердосплавные токарные пластины это режущие инструменты, используемые в токарных станках для токарных работ. Они изготавливаются из карбида - соединения углерода и вольфрама, известного своей твердостью и износостойкостью. Эти пластины предназначены для высокоскоростной резки таких прочных материалов, как сталь, нержавеющая сталь, чугун и цветные металлы. Они бывают различных форм, размеров и марок, каждая из которых предназначена для конкретных условий резания и материалов.
Виды твердосплавных токарных пластин
Существует множество типов твердосплавных токарных пластин, каждый из которых подходит для решения различных задач обработки. Ниже приведена подробная таблица с основными типами твердосплавных токарных пластин:
| Тип вставки | Форма | Типичное использование | Преимущества | Недостатки |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Тип C (CNMG, CNMM) | Ромбический | Общий поворот | Универсальные, прочные края | Ограниченный контроль над микросхемами |
| D-тип (DNMG, DNMM) | 55° Ромбический | Отделочные работы | Хорошо подходит для легких порезов | Хрупкие края |
| S-тип (SNMG, SNMM) | Квадрат | Сверхмощное вращение | Прочные режущие кромки | Менее гибкие формы |
| T-тип (TNMG, TNMM) | Треугольник | Черновая и чистовая обработка | Удобство работы с несколькими углами | Края с меньшей прочностью |
| V-образный тип (VNMG, VNMM) | 35° Ромбический | Тонкая отделка | Превосходно подходит для точных разрезов | Хрупкие, менее прочные |
| W-тип (WNMG, WNMM) | Тригон | Черновая обработка в тяжелых условиях | Высокая прочность, универсальность | Сложное формирование микросхем |
| R-тип (RNMG, RNMM) | Круглый | Профилирование, рифление | Самая прочная вставка | Ограниченное удобство использования углов |

Области применения твердосплавных токарных пластин
Твердосплавные токарные пластины используются в различных отраслях промышленности благодаря своей универсальности и долговечности. Вот таблица с подробным описанием их применения:
| Промышленность | Приложение | Тип вставки Рекомендуется |
|---|---|---|
| Автомобильная промышленность | Компоненты двигателя, валы | C-Type, S-Type |
| Аэрокосмическая промышленность | Конструктивные детали, лопатки турбин | V-образный, W-образный |
| Медицинские приборы | Хирургические инструменты, имплантаты | D-тип, V-тип |
| Нефть и газ | Трубная арматура, клапаны | T-Type, S-Type |
| Общее машиностроение | Детали машин, инструменты | C-Type, T-Type |
| Электроника | Корпуса, разъемы | D-тип, R-тип |
| Строительное оборудование | Гидравлические компоненты, рамы | S-Type, W-Type |
Свойства материалов твердосплавных токарных пластин
Понимание свойств материалов твердосплавные токарные пластины имеет решающее значение для выбора подходящего для ваших нужд. Вот подробная таблица этих свойств:
| Недвижимость | Описание |
|---|---|
| Твердость | Высокая твердость, обычно 80-90 HRA |
| Жесткость | Устойчивость к поломкам и сколам |
| Износостойкость | Способность противостоять износу от абразивных материалов |
| Теплопроводность | Высокая, эффективно рассеивает тепло |
| Химическая устойчивость | Устойчивость к окислению и химическим реакциям |
Состав и характеристики твердосплавных токарных пластин
Твердосплавные токарные пластины состоят из нескольких элементов, каждый из которых обусловливает их уникальные характеристики:
| Элемент | Процент (%) | Характеристика |
|---|---|---|
| Вольфрам (W) | 70-80 | Обеспечивает твердость и прочность |
| Углерод (C) | 6-10 | Образует карбидное соединение, повышая твердость |
| Кобальт (Co) | 5-10 | Связывает частицы карбида вольфрама вместе |
| Титан (Ti) | 1-5 | Повышает прочность и износостойкость |
| Тантал (Ta) | 1-3 | Повышает прочность при высоких температурах |
| Ниобий (Nb) | 0.5-2 | Повышает устойчивость к тепловому удару |





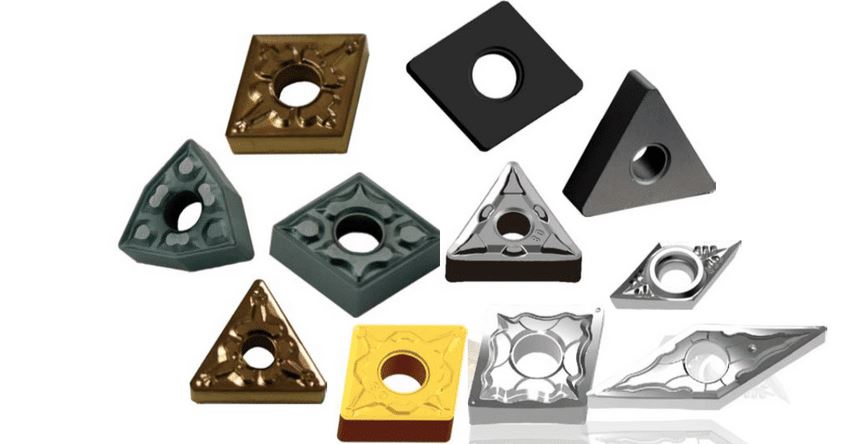
Твердость, прочность и износостойкость
Для эффективной работы твердосплавных токарных пластин необходимо соблюдать баланс между твердостью, прочностью и износостойкостью. Вот сравнительная таблица:
| Недвижимость | Описание |
|---|---|
| Твердость | Обеспечивает способность вставки резать прочные материалы. |
| Прочность | Предотвращает разрушение вставки под высоким давлением. |
| Износостойкость | Продлевает срок службы вставки благодаря устойчивости к износу. |
Технические характеристики, размеры, формы и стандарты
Твердосплавные токарные пластины имеют различные технические характеристики для решения различных задач обработки. Вот таблица с подробным описанием этих характеристик:
| Спецификация | Подробности |
|---|---|
| Размер | Размер режущей кромки варьируется от 1/8″ до 1″ |
| Форма | Ромбический, квадратный, треугольный, круглый, тригонный |
| Стандарты | ISO, ANSI, DIN, JIS |
Поставщики и ценовая политика
Вот список известных поставщиков и их цены на твердосплавные токарные пластины:
| Поставщик | Страна | Диапазон цен (за вставку) |
|---|---|---|
| Kennametal | США | $5 – $30 |
| Sandvik Coromant | Швеция | $8 – $40 |
| Mitsubishi Materials | Япония | $7 – $35 |
| Инструменты Seco | Швеция | $6 – $33 |
| Инструменты Walter | Германия | $9 – $37 |
| Искар | Израиль | $10 – $45 |
| Sumitomo Electric | Япония | $8 – $38 |
| Tungaloy | Япония | $7 – $34 |
| Kyocera | Япония | $6 – $32 |
| Taegutec | Южная Корея | $5 – $30 |
Как правильно выбрать твердосплавные токарные пластины
Правильный выбор твердосплавной токарной пластины может существенно повлиять на эффективность обработки и качество продукции. Вот таблица, которая поможет вам в процессе выбора:
| Критерии | Соображения |
|---|---|
| Тип материала | Выбирайте пластины, подходящие для обрабатываемого материала. |
| Скорость резки | Для высоких скоростей требуются более жесткие и износостойкие пластины. |
| Скорость подачи | Для оптимальной производительности подберите вставку в соответствии с нормой подачи. |
| Глубина среза | Убедитесь, что пластина способна выдержать требуемую глубину реза. |
| Мощность машины | Выбирайте вставки, совместимые с мощностью вашей машины. |
| Требования к отделке | Выбирайте вставки, которые позволяют достичь желаемой чистоты поверхности. |
Сравнение преимуществ и недостатков
Каждый тип твердосплавных токарных пластин имеет свой набор преимуществ и ограничений. Вот сравнительная таблица, которая поможет вам лучше понять их:
| Тип вставки | Преимущества | Ограничения |
|---|---|---|
| C-Type | Универсальные, прочные края | Ограниченный контроль над микросхемами |
| D-тип | Хорошо подходит для легких порезов | Хрупкие края |
| S-Type | Прочные режущие кромки | Менее гибкие формы |
| T-образный | Удобство работы с несколькими углами | Края с меньшей прочностью |
| V-образный | Превосходно подходит для точных разрезов | Хрупкие, менее прочные |
| W-тип | Высокая прочность, универсальность | Сложное формирование микросхем |
| R-Type | Самая прочная вставка | Ограниченное удобство использования углов |
Модели из металлических порошков для твердосплавных токарных пластин
Здесь приведены некоторые конкретные модели металлических порошков, используемых при производстве твердосплавных токарных пластин, а также их описания:
- WC-Co (карбид вольфрама-кобальт):
- Описание: Композитный материал, состоящий из частиц карбида вольфрама, соединенных с кобальтом.
- Характеристики: Высокая твердость, прочность и износостойкость.
- TiC (карбид титана):
- Описание: Карбидное соединение титана и углерода.
- Характеристики: Отличная износостойкость и химическая стабильность.
- TaC (карбид тантала):
- Описание: Тугоплавкий карбид тантала и углерода.
- Характеристики: Высокая температура плавления, прочность и твердость.
- NbC (карбид ниобия):
- Описание: Твердый карбид тугоплавкого металла.
- Характеристики: Высокая твердость, теплопроводность и химическая стойкость.
- VC (карбид ванадия):
- Описание: Карбид ванадия и углерода.
- Характеристики: Повышает прочность и износостойкость.
- CrC (карбид хрома):
- Описание: Соединение хрома и углерода.
- Характеристики: Высокая твердость и коррозионная стойкость.
- Mo2C (карбид молибдена):
- Описание: Карбидное соединение молибдена.
- Характеристики: Хорошая твердость и термическая стабильность.
- WC-TiC-TaC (композитный карбид):
- Описание: Сочетание карбида вольфрама, карбида титана и карбида тантала.
- Характеристики: Превосходная износостойкость и прочность.
- ZrC (карбид циркония):
- Описание: Карбид циркония.
- Характеристики: Высокая твердость и теплопроводность.
- HfC (карбид гафния):
- Описание: Тугоплавкий карбид гафния.
- Характеристики: Исключительная твердость и высокая температура плавления.

Вопросы и ответы
Из чего изготавливаются твердосплавные токарные пластины?
Твердосплавные токарные пластины изготавливаются в основном из карбида вольфрама, кобальта и других элементов, таких как титан, тантал и ниобий.
Почему твердосплавные пластины предпочтительны при обработке?
Их предпочитают за твердость, износостойкость и способность выдерживать высокоскоростную резку.
Как правильно выбрать твердосплавную токарную пластину?
Учитывайте тип материала, скорость резки, скорость подачи, глубину реза, мощность станка и требования к чистоте обработки.
Каковы основные типы твердосплавных токарных пластин?
Основные типы: C-Type, D-Type, S-Type, T-Type, V-Type, W-Type и R-Type.
Можно ли повторно использовать твердосплавные токарные пластины?
Да, их можно индексировать или поворачивать, чтобы использовать несколько режущих кромок.
Каков срок службы твердосплавной токарной пластины?
Оно зависит от обрабатываемого материала и условий резки, но обычно составляет от нескольких часов до нескольких дней непрерывной работы.
Стандартизованы ли твердосплавные токарные пластины?
Да, они придерживаются международных стандартов, таких как ISO, ANSI, DIN и JIS.
В каких отраслях промышленности используются твердосплавные токарные пластины?
Они используются в автомобильной, аэрокосмической, медицинской, нефтегазовой, общетехнической, электронной и строительной промышленности.
Как твердосплавные токарные пластины влияют на производительность обработки?
Они повышают производительность обработки, обеспечивая точность резания, сокращая время простоя и улучшая качество обработки поверхности.
Назовите лучшие бренды твердосплавных токарных пластин?
Среди ведущих брендов - Kennametal, Sandvik Coromant, Mitsubishi Materials, Seco Tools, Walter Tools и Iscar.
Заключение
Твердосплавные токарные пластины - незаменимый инструмент в современной обработке, обеспечивающий непревзойденные характеристики по твердости, прочности и износостойкости. Понимание различных типов, областей применения и критериев выбора поможет вам выбрать подходящую пластину для ваших конкретных нужд, повышая производительность и обеспечивая высокое качество обработки.




