真空加圧焼結炉
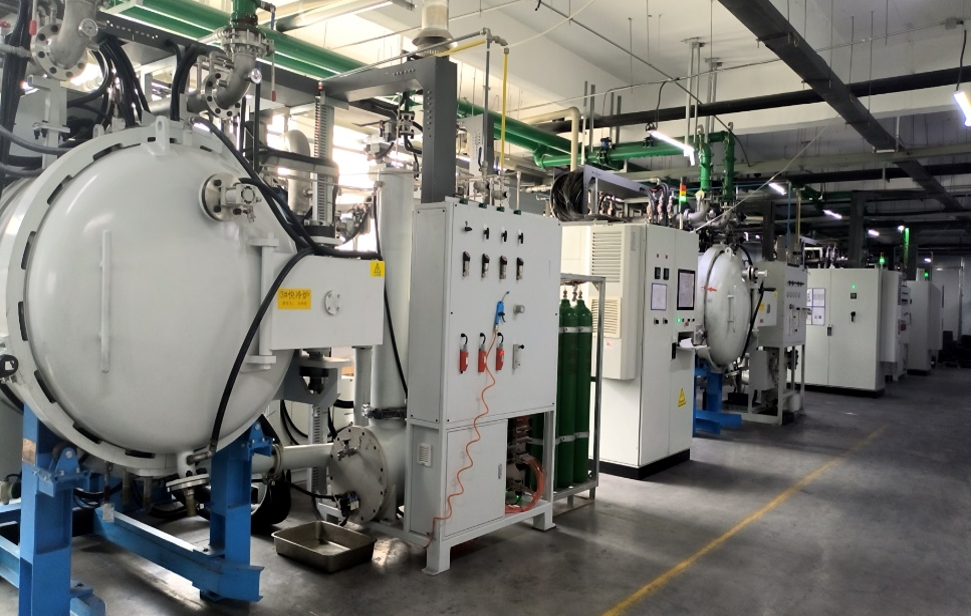

真空加圧焼結炉は、真空またはガス保護雰囲気下、材料の溶融温度以下で、金属またはセラミック材料の粉末を圧密し、熱を加え、場合によっては圧力を加えて部品を製造するための炉です。
多くの材料では、焼結は高温下でのみ行われるため、酸化を防ぐために真空中または保護雰囲気中で行う必要があります。当社の真空焼結炉は、炭化タングステンやその他の金属、セラミックスの高品質焼結に最適です。硬質金属粉 (炭化タングステンなど) は、当社の真空焼結炉 (真空加圧焼結炉) を用いた液相焼結プロセスで処理される好例です。
TRUER焼結炉は硬質金属(超硬合金)またはテクニカルセラミックスの脱脂、真空焼結、およびその後の圧力ガス(最高200 bar)下での静水圧緻密化を組み合わせます。
アプリケーション
脱脂と焼結
- 真空または分圧下で、Ar、N2、H2を使用する。
- 圧力制御モニター付き
- バインダーのモニタリング
- オプションの高圧急速冷却
材料
- 硬質金属(炭化タングステン)
- サーメット
- PM- 特殊合金
- テクニカル・セラミックス
メリット
- 真空および加圧操作の両方で優れた温度均一性
- 省エネ・省ガス設計によるコスト効率
- 強力な高速冷却によるプロセス時間の短縮
- ダブル脱脂システム、高効率、信頼性、長寿命
- スマートな設計、簡単な操作、試運転時間の短縮
- その他のサイズやカスタマイズも可能

技術パラメーター
炉型 3312
| パラメータ | 仕様 |
| 使用可能スペース | 300×300×1250 mm |
| 最大最高温度 | 1600℃ |
| 充電負荷 | 260kgまで |
| 動作圧力 | 0.6 MPa |
| 加熱パワー | 180KW |
| ガス媒体 | Ar, N2 とH2 |
| 急速冷却時間 | 0.6MPaの空炉で1500℃から100℃まで25分間 |
| 温度均一性 | 5℃以下 |
| 熱電対 | デュアルコアタングステンレニウム(WRe5.26) |
炉型 5518
| パラメータ | 仕様 |
| 使用可能スペース | 500×500×1800 mm |
| 最大最高温度 | 2200℃ |
| 充電負荷 | 1500kgまで |
| 動作圧力 | 6 MPa |
| 加熱パワー | 440 KW |
| ガス媒体 | Ar, N2 |
| 冷却時間 | 5.8MPaの空炉で1900℃から100℃まで8時間 |
| 温度均一性 | 5℃以下 |
| 熱電対 | デュアルコアタングステンレニウム(WRe5.26) |

炉型 4416
| 使いやすいスペース: | 400X400X1650mm |
| 最大最高温度 | 1600℃ |
| 充電負荷: | 800kgまで |
| 動作圧力: | 0.6MPa |
| 加熱用パウダー: | 180KW |
| ガス媒体: | Ar、N2、H2 |
| 急速冷却時間: | 0.6MPaの空炉で1500℃から100℃まで25分間 |
| 温度の均一性: | 5℃以下 |
| 熱電対: | デュアルコアタングステンレニウム(WRe5.26) |

炉型 2212
| 使いやすいスペース: | 200X200X1200mm |
| 最大最高温度 | 2200℃ |
| 充電負荷: | 200kgまで |
| 動作圧力: | 6MPa |
| 加熱用パウダー: | 440KW |
| ガス媒体: | Ar、N2、H2 |
| 冷却時間: | 5.8MPaの空炉で1900℃から100℃まで8時間 |
| 温度の均一性: | 5℃以下 |
| 熱電対: | デュアルコアタングステンレニウム(WRe5.26) |

メリット
真空焼結の直後に、50バール(約5MPa)の高圧ガス(通常はアルゴンや窒素などの不活性ガス)を導入する。これにより、有意かつ有益な圧力補助焼結効果が得られる。これは通常、ガス圧焼結または低圧焼結と呼ばれる。HIPとは基本的に異なりますが、単一真空焼結よりも低コストでシンプルなプロセスで優れた効果が得られます。
真空焼結+50 barガス圧の組み合わせの効果:
> さらに高密度化を促進し、残存する相互連結気孔の崩壊または部分的な気孔閉鎖を助け、粒子の再配列と物質移動を促進する。
> 単に気孔率を低下させるよりも、材料の靭性と疲労性能を向上させるのに効果的である。
> 特に特殊合金(黄銅、青銅、高速度鋼、ステンレス鋼など)や、揮発性元素(亜鉛Zn、カドミウムCd、マンガンMn、クロムCrなど)を含む合金の場合。
> 表面品質の向上、元素の揮発を抑制することで、揮発による表面の穴や組成ムラを防ぎ、より滑らかで均一な表面を実現。
> ある程度の保護雰囲気を与え、高温での焼結体の二次酸化や脱炭を防止する(特に鉄系材料)。
