Carbide turning inserts are the unsung heroes of machining. They help us shape, carve, and perfect metal into the precise forms we need for countless applications. If you’re involved in machining or manufacturing, understanding carbide turning inserts is crucial. This guide will dive deep into the world of carbide turning inserts, covering everything from types and applications to selecting the right one for your needs.
Overview of Carbide Turning Inserts
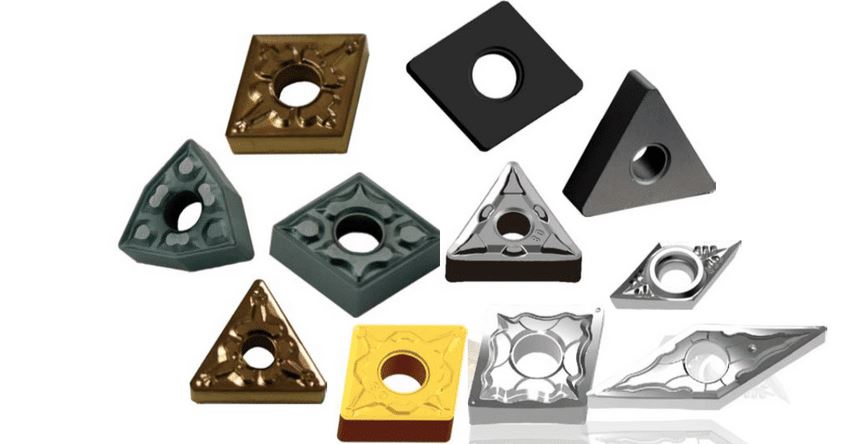
Carbide turning inserts are cutting tools used in lathes for turning operations. They are made from carbide, a compound of carbon and tungsten, known for its hardness and resistance to wear. These inserts are designed to handle the high-speed cutting of tough materials like steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous metals. They come in various shapes, sizes, and grades, each tailored to specific cutting conditions and materials.
Types of Carbide Turning Inserts
There are numerous types of carbide turning inserts, each suited for different machining tasks. Here’s a detailed table summarizing the main types of carbide turning inserts:
| インサート・タイプ | 形状 | Typical Use | メリット | デメリット |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Type (CNMG, CNMM) | ひし形 | 一般旋削 | Versatile, strong edges | Limited chip control |
| D-Type (DNMG, DNMM) | 55° Rhombic | 仕上げ作業 | Good for light cuts | Fragile edges |
| S-Type (SNMG, SNMM) | 正方形 | 頑丈な旋盤加工 | Strong cutting edges | Less flexible in shapes |
| T-Type (TNMG, TNMM) | トライアングル | 荒削りと仕上げ | Multi-corner usability | Lower strength edges |
| V-Type (VNMG, VNMM) | 35° Rhombic | 仕上げ | Excellent for precise cuts | Fragile, less durable |
| W-Type (WNMG, WNMM) | トライゴン | Heavy-duty roughing | High strength, versatile | Complex chip formation |
| R-Type (RNMG, RNMM) | ラウンド | Profiling, grooving | Strongest insert | Limited corner usability |

Applications of Carbide Turning Inserts
Carbide turning inserts are used across various industries due to their versatility and durability. Here’s a table detailing their applications:
| 産業 | 申し込み | Insert Type Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| 自動車 | Engine components, shafts | C-Type, S-Type |
| 航空宇宙 | Structural parts, turbine blades | V-Type, W-Type |
| 医療機器 | 手術器具、インプラント | D-Type, V-Type |
| 石油・ガス | Pipe fittings, valves | T-Type, S-Type |
| 一般エンジニアリング | Machinery parts, tools | C-Type, T-Type |
| エレクトロニクス | Enclosures, connectors | D-Type, R-Type |
| 建設機械 | Hydraulic components, frames | S-Type, W-Type |
Material Properties of Carbide Turning Inserts
の材料特性を理解する。 carbide turning inserts is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific needs. Here’s a detailed table of these properties:
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 硬度 | High hardness, typically 80-90 HRA |
| タフネス | Resistance to breaking and chipping |
| 耐摩耗性 | Ability to withstand wear from abrasive materials |
| 熱伝導率 | High, dissipates heat effectively |
| 化学的安定性 | 酸化や化学反応に強い |
Composition and Characteristics of Carbide Turning Inserts
Carbide turning inserts are composed of several elements, each contributing to their unique characteristics:
| エレメント | パーセント(%) | 特徴 |
|---|---|---|
| タングステン(W) | 70-80 | 硬度と強度を提供 |
| カーボン(C) | 6-10 | Forms the carbide compound, enhancing hardness |
| コバルト | 5-10 | Binds the tungsten carbide particles together |
| チタン(Ti) | 1-5 | Increases toughness and wear resistance |
| タンタル (Ta) | 1-3 | 高温強度の向上 |
| Niobium (Nb) | 0.5-2 | Improves resistance to thermal shock |





硬度、強度、耐摩耗性
Carbide turning inserts must balance hardness, strength, and wear resistance to perform effectively. Here’s a comparative table:
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 硬度 | Ensures the insert can cut through tough materials. |
| 強さ | Prevents the insert from breaking under high pressure. |
| 耐摩耗性 | Extends the insert’s life by resisting wear and tear. |
仕様、サイズ、形状、規格
Carbide turning inserts come in various specifications to suit different machining tasks. Here’s a table detailing these specifications:
| 仕様 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| サイズ | Ranges from 1/8″ to 1″ in cutting edge size |
| 形状 | Rhombic, square, triangle, round, trigon |
| 規格 | ISO、ANSI、DIN、JIS |
サプライヤーと価格詳細
Here’s a list of notable suppliers and their pricing details for carbide turning inserts:
| サプライヤー | 国名 | 価格帯(1枚あたり) |
|---|---|---|
| ケナメタル | アメリカ | $5 – $30 |
| サンドビック・コロマント | スウェーデン | $8 – $40 |
| 三菱マテリアル | 日本 | $7 – $35 |
| セコ・ツールズ | スウェーデン | $6 – $33 |
| ウォルター・ツールズ | ドイツ | $9 – $37 |
| イスカー | イスラエル | $10 – $45 |
| 住友電工 | 日本 | $8 – $38 |
| タンガロイ | 日本 | $7 – $34 |
| 京セラ | 日本 | $6 – $32 |
| テグテック | 韓国 | $5 – $30 |
How to Select the Right Carbide Turning Inserts
Choosing the right carbide turning insert can significantly impact your machining efficiency and product quality. Here’s a table to guide you through the selection process:
| 基準 | 考察 |
|---|---|
| 素材タイプ | Choose inserts suited for the material you are machining. |
| 切断速度 | Higher speeds require tougher, more wear-resistant inserts. |
| フィード・レート | Match the insert to your feed rate for optimal performance. |
| 切り込み | Ensure the insert can handle your required depth of cut. |
| マシンパワー | Select inserts compatible with your machine’s power capacity. |
| Finish Requirements | Choose inserts that can achieve your desired surface finish. |
利点と限界を比較する
Every type of carbide turning insert has its own set of advantages and limitations. Here’s a comparative table to help you understand them better:
| インサート・タイプ | メリット | 制限事項 |
|---|---|---|
| C-Type | Versatile, strong edges | Limited chip control |
| D-Type | Good for light cuts | Fragile edges |
| S-Type | Strong cutting edges | Less flexible in shapes |
| T-Type | Multi-corner usability | Lower strength edges |
| V-Type | Excellent for precise cuts | Fragile, less durable |
| W-Type | High strength, versatile | Complex chip formation |
| R-Type | Strongest insert | Limited corner usability |
Metal Powder Models for Carbide Turning Inserts
Here are some specific metal powder models used in the production of carbide turning inserts, along with their descriptions:
- WC-Co(炭化タングステン-コバルト):
- 説明: A composite material made of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt.
- 特徴: High hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
- TiC(炭化チタン):
- 説明: A carbide compound of titanium and carbon.
- 特徴: Excellent wear resistance and chemical stability.
- TaC(炭化タンタル):
- 説明: A refractory carbide of tantalum and carbon.
- 特徴: High melting point, strength, and hardness.
- NbC(炭化ニオブ):
- 説明: A hard refractory metal carbide.
- 特徴: High hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance.
- VC(炭化バナジウム):
- 説明: A carbide of vanadium and carbon.
- 特徴: Enhances toughness and wear resistance.
- CrC (Chromium Carbide):
- 説明: A compound of chromium and carbon.
- 特徴: High hardness and corrosion resistance.
- Mo2C (炭化モリブデン):
- 説明: A carbide compound of molybdenum.
- 特徴: Good hardness and thermal stability.
- WC-TiC-TaC (Composite Carbide):
- 説明: A combination of tungsten carbide, titanium carbide, and tantalum carbide.
- 特徴: Superior wear resistance and toughness.
- ZrC(炭化ジルコニウム):
- 説明: A carbide of zirconium.
- 特徴: High hardness and thermal conductivity.
- HfC(炭化ハフニウム):
- 説明: A refractory carbide of hafnium.
- 特徴: Exceptional hardness and high melting point.

よくあるご質問
What are carbide turning inserts made of?
Carbide turning inserts are primarily made from tungsten carbide, cobalt, and other elements like titanium, tantalum, and niobium.
なぜ超硬チップは機械加工に好まれるのか?
They are preferred for their hardness, wear resistance, and ability to handle high-speed cutting.
How do I choose the right carbide turning insert?
Consider the material type, cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut, machine power, and finish requirements.
What are the main types of carbide turning inserts?
The main types include C-Type, D-Type, S-Type, T-Type, V-Type, W-Type, and R-Type.
Can carbide turning inserts be reused?
Yes, they can be indexed or rotated to use multiple cutting edges.
What is the lifespan of a carbide turning insert?
It depends on the material being machined and the cutting conditions but typically ranges from several hours to days of continuous use.
Are carbide turning inserts standardized?
Yes, they adhere to international standards such as ISO, ANSI, DIN, and JIS.
What industries use carbide turning inserts?
They are used in automotive, aerospace, medical devices, oil and gas, general engineering, electronics, and construction equipment industries.
How do carbide turning inserts affect machining performance?
They enhance machining performance by providing precise cuts, reducing downtime, and improving surface finishes.
What are some top brands for carbide turning inserts?
Top brands include Kennametal, Sandvik Coromant, Mitsubishi Materials, Seco Tools, Walter Tools, and Iscar.
結論
Carbide turning inserts are indispensable tools in modern machining, offering unparalleled performance in terms of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. Understanding the various types, applications, and selection criteria can help you choose the right insert for your specific needs, enhancing productivity and ensuring high-quality results in your machining operations.




