産業用および機械加工用アプリケーションに関して言えば、 端面取り超硬棒 は重要な材料です。これらのロッドは、高度な冶金学と精密工学を組み合わせ、厳しい条件下で堅牢な性能を発揮します。その仕様、用途、その他知っておくべきことを深く掘り下げてみましょう。勉強にもなるし、魅力的な話にもなる。
エンド面取り研磨超硬ロッドとは?
端面取りされた超硬ロッドは、切断、穴あけ、および機械加工作業用に設計された高性能材料です。これらのロッドの端は面取りされており、工具セットアップへのスムーズな統合を保証します。研削仕上げにより寸法精度が向上し、さまざまな機械および産業用途に完璧に適合します。

エンド面取り超硬ロッドの種類
| タイプ | 説明 | 一般的なアプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| 標準面取りロッド | 均一な面取りが施された両端が特徴で、汎用工具に適しています。 | 一般機械加工、産業用工具製造 |
| ストレートクーラントホールロッド | 加工中の熱を抑えるため、クーラントを流す穴を設ける。 | 高速加工、精密穴あけ |
| ヘリカルクーラントホールロッド | ねじれたクーラントホールがクーラントの流れ効率を向上。 | 深穴加工、硬質材料の切断 |
| 微粒超硬棒 | 硬度と耐摩耗性を向上させるため、微粒子パウダーを使用。 | 航空宇宙、自動車、高精度製造。 |
| 超微粒子超硬ロッド | 優れた強度と靭性のために超微粒子を使用。 | チタンやインコネルなどの硬い金属の切断。 |
| コーティング超硬棒 | 耐摩耗性を高めるために、TiNやTiAlNなどの表面コーティングが施されている。 | 高温作業、工具寿命の延長。 |
| 非磁性超硬棒 | 特定の用途における磁気干渉を最小限に抑えるよう設計されています。 | 医療器具、電子部品製造 |
| 混合粒超硬棒 | さまざまなサイズの粒をブレンドすることで、強度と硬度にわたって性能を最適化。 | 多彩な加工アプリケーション |
| 耐衝撃性超硬棒 | 繰り返しの機械的衝撃に耐える強靭性を提供。 | ハンマードリル、高負荷産業機器。 |
| 耐食性超硬棒 | 耐薬品性を向上させる添加剤を使用。 | 石油・ガス産業、化学処理ツール |
の原材料と成分分析 エンド面取り研磨超硬棒
これらのロッドの主材料は 炭化タングステンタングステンと炭素から作られる化合物。最も硬い素材のひとつで、バインダーとしてコバルトやニッケルと組み合わされることが多い。炭化タングステンとバインダーの比率は、ロッドの特性に大きく影響します。
典型的な構成
| コンポーネント | パーセント | 役割 |
|---|---|---|
| 炭化タングステン | 85-95% | 硬度と耐摩耗性を提供する。 |
| コバルト/ニッケル | 5-15% | 強靭さのバインダーとして働く。 |
| 添加物(TiC、TaCなど) | 0-5% | 耐熱性や耐食性など、特定の特性を強化する。 |
エンド面取り超硬ロッドの用途
| 申し込み | 産業 | メリット |
|---|---|---|
| 精密切削工具 | 機械加工、工具製作 | 鋭利で耐久性のある刃先により、高速切断が可能。 |
| 航空宇宙部品製造 | 航空宇宙 | チタンのような高強度合金を扱う。 |
| 石油・ガス掘削装置 | エネルギー | 過酷な圧力や研磨条件にも耐える。 |
| 医療機器製造 | ヘルスケア | 手術器具の精度を高める。 |
| 自動車製造 | 自動車 | エンジン部品の加工効率を高める。 |
| 金型製作 | 金型 | 複雑な金型の滑らかな仕上げを保証します。 |

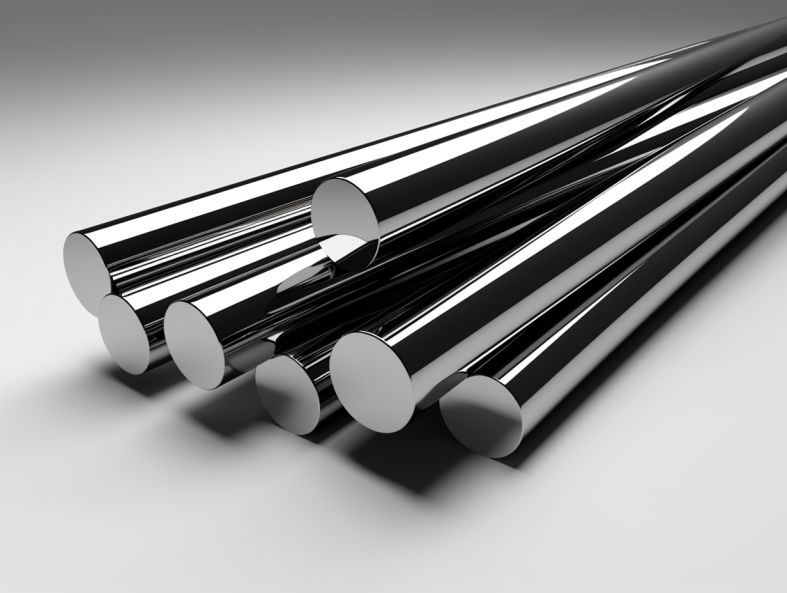


超硬棒鋼端面取り加工工程フロー
これらのロッドを製造するには、品質と一貫性を確保するためにいくつかの重要な工程がある:
- パウダーの調製: 炭化タングステン粉末とバインダーは正確な割合で混合される。
- プレスする: この混合物を棒状の型に押し込む。
- 焼結: プレスされたロッドは、粒子を結合させるために高温で焼結される。
- 面取りと研磨: エッジは面取りされ、表面は精密な寸法を得るために研磨される。
- 品質検査: 最終製品は、硬度、耐摩耗性、寸法精度について厳しい検査を受ける。
端面取り超硬棒の材料特性
| プロパティ | レンジ | 意義 |
|---|---|---|
| 硬度 | 85-94 HRA | 耐摩耗性を決定する。 |
| 密度 | 14.5-15.1 g/cm³ | 素材のコンパクトさを示す。 |
| 横方向の破断強度 | 2000-4000 MPa | 機械的応力下での靭性を反映する。 |
| 熱伝導率 | 60-100 W/m-K | 放熱能力を示す。 |
| 透磁率 | <0.2 | 繊細な用途のための非磁性オプション。 |
仕様、サイズ、形状、規格
| 仕様 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 直径範囲 | 1-50 mm |
| 長さの範囲 | 30-330 mm |
| 形状オプション | 丸、四角、六角形。 |
| 準拠規格 | ISO 9001、DIN 6527、ANSI B212。 |
超硬ストレートクーラントホールの硬さ、強度、耐摩耗性
| 属性 | 測定 | パフォーマンス・ベネフィット |
|---|---|---|
| 硬度 | 90-93 HRA | 研磨環境にも容易に対応。 |
| 強さ | 3000-4000 MPa | 負荷がかかっても割れにくい。 |
| 耐摩耗性 | 高い | 過酷な条件下でも長寿命。 |
サプライヤーと価格詳細
| サプライヤー | 所在地 | 価格帯 ($/kg) | 専門性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ超硬株式会社 | ドイツ | 50-70 | カスタム仕様の高精度ロッド。 |
| ABCタングステン | アメリカ | 60-80 | 超微粒子カーバイドロッド。 |
| グローバル・メタルズ社 | 中国 | 40-65 | 手頃な価格で安定した品質のオプション。 |
正しい選択 エンド面取り研磨超硬棒
| ファクター | 推薦 |
|---|---|
| アプリケーション・タイプ | 精密さにはマイクロ・グレイン・ロッドを、冷却にはストレート・クーラント・ロッドをお選びください。 |
| カットする素材 | 硬い金属には超微粒子カーバイドが必要です。 |
| 予算 | 一般的な使用にはスタンダード・ロッド、重要な作業にはプレミアム・ロッドを。 |
エンド面取り超硬ロッドの利点と限界
| アスペクト | メリット | 制限事項 |
|---|---|---|
| 耐久性 | 極めて耐摩耗性が高い。 | イニシャルコストが高い。 |
| 汎用性 | 様々な産業に適している。 | 柔らかい素材に比べて柔軟性に欠ける。 |
よくあるご質問
| 質問 | 回答 |
|---|---|
| 超硬ロッドの主な利点は何ですか? | 優れた硬度、耐摩耗性、熱安定性。 |
| クーラントホールの設計はどのように性能を向上させるのか? | 高速切削時の放熱性を高め、工具寿命を延ばす。 |
| このロッドでチタン合金を切断できますか? | そう、特に極小粒と超極細粒の超硬ロッドだ。 |




