Dans le monde de l'usinage et des outils de coupe, la géométrie et la conception des outils de coupe sont très importantes. carbure Les pointes brasées jouent un rôle crucial dans la détermination de leur performance de coupe. Ces composants, petits mais incroyablement puissants, sont conçus pour résister à des conditions extrêmes et fournir des coupes précises et efficaces. Ce blog se penche sur les subtilités de la géométrie et de la conception des pointes brasées en carbure, en explorant la façon dont ces facteurs influencent les performances de coupe et les considérations essentielles pour optimiser l'efficacité de l'outil.
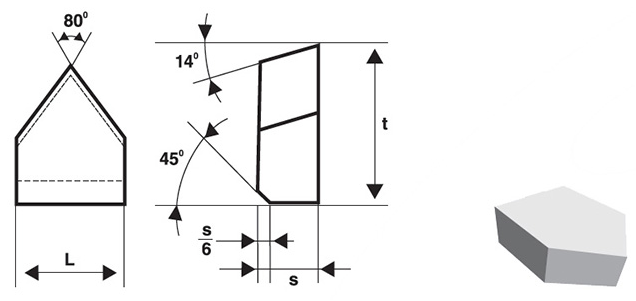
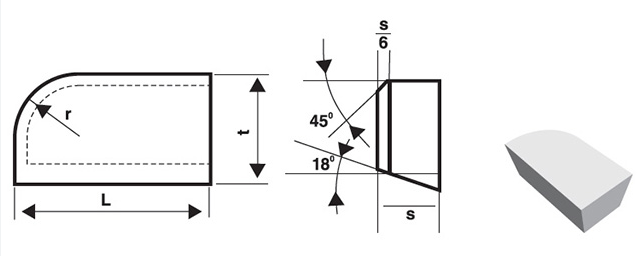
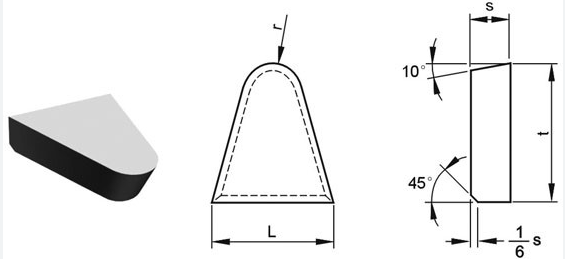
Vue d'ensemble
Les pointes brasées en carbure sont largement utilisées dans diverses industries en raison de leur dureté exceptionnelle et de leur résistance à l'usure. La géométrie et la conception de ces pointes sont méticuleusement élaborées pour améliorer les performances de coupe, réduire l'usure de l'outil et améliorer l'efficacité globale de l'usinage. Il est essentiel de comprendre l'impact de la géométrie et de la conception sur les performances de coupe pour sélectionner les bons outils et obtenir des résultats optimaux dans différentes applications.
Introduction détaillée à la géométrie et à la conception des pointes brasées en carbure
Qu'est-ce que la géométrie des pointes brasées au carbure ?
La géométrie des pointes brasées en carbure se réfère à la forme, aux angles et aux dimensions de l'arête de coupe et des surfaces de la pointe. Les paramètres géométriques clés sont les suivants
- Angle d'inclinaison : L'angle entre l'arête de coupe et la surface de la pièce. Il influence la formation de copeaux et la force de coupe.
- Angle de décharge : L'angle entre le flanc de l'outil et la surface de la pièce, empêchant le frottement et réduisant la friction.
- Angle du bord de coupe : L'angle formé par l'intersection des faces du râteau et du flanc, qui affecte la solidité et la résistance à l'usure de l'outil.
- Rayon de l'angle : L'arête arrondie à la pointe de l'outil, qui a un impact sur la finition de la surface et la durée de vie de l'outil.
Comment la conception influence-t-elle les performances de coupe ?
La conception d'une pointe brasée en carbure englobe sa structure globale, y compris l'emplacement des arêtes de coupe, la répartition du matériau et toutes les caractéristiques supplémentaires telles que les brise-copeaux ou les revêtements. Ces éléments de conception travaillent en harmonie avec la géométrie pour optimiser les performances de coupe. Les principaux aspects de la conception sont les suivants
- Forme de la pointe : Différentes formes (par exemple, carrée, ronde, diamant) sont adaptées à des applications et des matériaux spécifiques.
- Casseurs de puces : Des caractéristiques qui permettent de contrôler le flux des copeaux et d'éviter leur colmatage, améliorant ainsi l'efficacité de la coupe.
- Revêtements : Couches protectrices qui réduisent le frottement, augmentent la résistance à l'usure et prolongent la durée de vie des outils.
Impact de la géométrie et de la conception sur les performances de coupe
La géométrie et la conception des pointes brasées en carbure affectent directement plusieurs aspects critiques de la performance de coupe, notamment :
1. Efficacité de la coupe
- Angle d'inclinaison : Un angle de coupe positif réduit les efforts de coupe et la consommation d'énergie, améliorant ainsi l'efficacité. Toutefois, il peut réduire la résistance de l'outil.
- Angle de décharge : Des angles de dépouille adéquats évitent les frottements et l'accumulation de chaleur, améliorant ainsi l'efficacité de la coupe.
2. Durée de vie de l'outil
- Angle du bord de coupe : Les angles d'arête de coupe plus importants offrent une plus grande solidité et une meilleure résistance à l'usure, prolongeant ainsi la durée de vie de l'outil.
- Rayon de l'angle : Un rayon d'angle plus important répartit les efforts de coupe de manière plus uniforme, ce qui réduit l'usure et prolonge la durée de vie de l'outil.
3. Finition de la surface
- Angles d'inclinaison et de détente : Les angles optimisés permettent des coupes plus douces et de meilleurs états de surface.
- Rayon de l'angle : Un rayon plus grand peut améliorer la finition de la surface mais peut nécessiter des forces de coupe plus élevées.
4. Contrôle des puces
- Casseurs de puces : Des broyeurs de copeaux bien conçus permettent de gérer le flux de copeaux et d'éviter le colmatage, ce qui préserve l'efficacité de la coupe.
- Angle d'inclinaison : Influence la formation et l'écoulement des copeaux, ce qui a un impact sur le contrôle global des copeaux.
Facteurs à prendre en compte lors du choix des pointes brasées au carbure
La sélection des pointes brasées en carbure appropriées implique la prise en compte de plusieurs facteurs liés à la géométrie et à la conception :
- Matériau usiné : Les différents matériaux nécessitent des géométries et des conceptions spécifiques pour une performance de coupe optimale.
- Conditions de coupe : Des facteurs tels que la vitesse de coupe, l'avance et la profondeur de coupe influencent le choix de la géométrie de la pointe.
- Usinage Application : Le type d'opération d'usinage (par exemple, tournage, fraisage, perçage) dicte la conception appropriée de la pointe.
- Compatibilité entre le porte-outil et la machine : S'assurer que l'embout brasé au carbure est compatible avec le porte-outil et les spécifications de la machine.
Analyse comparative des géométries de pointes brasées au carbure
Le tableau ci-dessous met en évidence l'impact des différents paramètres géométriques sur les performances de coupe :
| Paramètre géométrique | Impact positif | Impact négatif |
|---|---|---|
| Angle d'inclinaison | Réduction des efforts de coupe, amélioration de l'efficacité | Résistance inférieure de l'outil |
| Angle de décharge | Réduction du frottement, amélioration de l'état de surface | Risque d'usure accrue de l'outil en cas d'excès |
| Angle du bord de coupe | Résistance accrue de l'outil, durée de vie prolongée | Forces de coupe plus élevées |
| Rayon de l'angle | Amélioration de l'état de surface, réduction de l'usure | Forces de coupe plus élevées, risque de broutage |
Applications des pointes brasées au carbure
Les pointes brasées en carbure sont utilisées dans un large éventail d'applications dans diverses industries. Voici quelques applications clés :
1. Travail des métaux
- Opérations de tournage : Usinage de précision de pièces cylindriques.
- Opérations de broyage : Efficacité de l'enlèvement de matière dans les processus de fraisage.
- Opérations de forage : Perçage de haute performance dans divers matériaux.
2. Travail du bois
- Coupe et mise en forme : Découpe et façonnage de précision de pièces en bois.
- Routage : Routage à grande vitesse pour les dessins et motifs complexes.
3. Industrie automobile
- Usinage de composants de moteurs : Usinage précis des pièces du moteur pour des performances optimales.
- Fabrication de pièces de transmission : Usinage de haute précision de composants de transmission.
4. Industrie aérospatiale
- Usinage de composants d'aéronefs : Usinage de composants critiques d'aéronefs avec une grande précision.
- Usinage des trains d'atterrissage : Usinage durable et précis des pièces de trains d'atterrissage.
Comparaison des pointes brasées en carbure de différents fournisseurs
Le tableau ci-dessous compare les pointes brasées en carbure de différents fournisseurs en fonction de paramètres clés :
| Fournisseur | Localisation | Fourchette de prix (par pièce) | Spécialités |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kennametal | ÉTATS-UNIS | $10 – $50 | Pointes de coupe haute performance, géométries personnalisées |
| Élément six | ROYAUME-UNI | $12 – $55 | Conceptions avancées, ingénierie de précision |
| TRUER | Chine | $8 – $45 | Solutions rentables, production en grande quantité |
| Sumitomo Electric | Japon | $15 – $60 | Conceptions innovantes, contrôle de qualité supérieur |
Avantages et inconvénients des différentes géométries
Le tableau ci-dessous présente les avantages et les inconvénients des différentes géométries de pointes brasées au carbure :
| Géométrie | Avantages | Inconvénients |
|---|---|---|
| Râteau positif | Réduction des efforts de coupe, amélioration du flux des copeaux | Résistance moindre de l'outil, risque d'écaillage |
| Râteau négatif | Résistance accrue de l'outil, adapté aux matériaux durs | Forces de coupe plus élevées, consommation d'énergie accrue |
| Grand rayon d'angle | Amélioration de l'état de surface, réduction de l'usure de l'outil | Forces de coupe plus élevées, risque de broutage |
| Petit rayon d'angle | Forces de coupe réduites, coupes précises | Augmentation de l'usure de l'outil, possibilité d'un mauvais état de surface |
Sujets connexes : Revêtements avancés pour pointes brasées au carbure
Outre la géométrie et la conception, les revêtements avancés jouent un rôle important dans l'amélioration des performances des pointes brasées au carbure. Les revêtements tels que le nitrure de titane (TiN), le carbonitrure de titane (TiCN) et le nitrure de titane et d'aluminium (AlTiN) offrent des avantages supplémentaires :
- Réduction du frottement : Les revêtements réduisent la friction entre l'outil et la pièce à usiner, améliorant ainsi l'efficacité de la coupe.
- Résistance accrue à l'usure : Les revêtements protègent l'outil de l'usure et prolongent sa durée de vie.
- Résistance à la chaleur améliorée : Les revêtements aident à dissiper la chaleur, évitant ainsi tout dommage thermique à l'outil.
Pourquoi choisir des pointes brasées au carbure pour l'usinage haute performance ?
Les pointes brasées en carbure constituent un excellent choix pour l'usinage de haute performance en raison de leur dureté supérieure, de leur résistance à l'usure et de leur capacité à maintenir l'efficacité de la coupe dans des conditions extrêmes. La combinaison d'une géométrie optimisée et d'une conception avancée permet à ces outils de réaliser des coupes précises et efficaces, ce qui les rend indispensables dans diverses industries.
FAQ
1. Comment l'angle de coupe affecte-t-il les performances de coupe ?
A : L'angle de coupe influence la formation des copeaux et les efforts de coupe. Un angle de coupe positif réduit les efforts de coupe et améliore l'efficacité, mais peut compromettre la résistance de l'outil.
2. Quelle est l'importance de l'angle de dépouille dans les pointes brasées au carbure ?
A : L'angle de dépouille empêche la friction et l'accumulation de chaleur entre l'outil et la pièce, ce qui améliore l'efficacité de la coupe et réduit l'usure de l'outil.
3. Comment les brise-copeaux améliorent-ils les performances de coupe ?
A : Les brise-copeaux contrôlent le flux de copeaux et empêchent le colmatage, ce qui maintient l'efficacité de la coupe et réduit le risque d'endommagement de l'outil.
4. Quels sont les facteurs à prendre en compte lors du choix d'un rayon d'angle ?
A : Le rayon de l'angle influe sur l'état de surface et l'usure de l'outil. Un rayon plus grand améliore la finition et réduit l'usure, mais nécessite des forces de coupe plus élevées.
5. Comment les revêtements améliorent-ils les performances des pointes brasées en carbure ?
A : Les revêtements réduisent le frottement, augmentent la résistance à l'usure et améliorent la dissipation de la chaleur, ce qui accroît les performances globales et la longévité des outils.
En comprenant l'impact de la géométrie et de la conception sur les performances de coupe des pointes brasées en carbure, vous pouvez prendre des décisions éclairées lors de la sélection et de l'utilisation de ces outils. Ces connaissances vous aideront à obtenir des résultats d'usinage optimaux, à améliorer l'efficacité et à prolonger la durée de vie de vos outils de coupe.




