Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont les héros méconnus de l'usinage. Elles nous aident à façonner, sculpter et perfectionner le métal dans les formes précises dont nous avons besoin pour d'innombrables applications. Si vous travaillez dans le domaine de l'usinage ou de la fabrication, il est essentiel de comprendre les plaquettes de tournage en carbure. Ce guide se penche sur le monde des plaquettes de tournage en carbure, couvrant tous les aspects, des types et applications à la sélection de la plaquette la mieux adaptée à vos besoins.
Aperçu des plaquettes de tournage en carbure
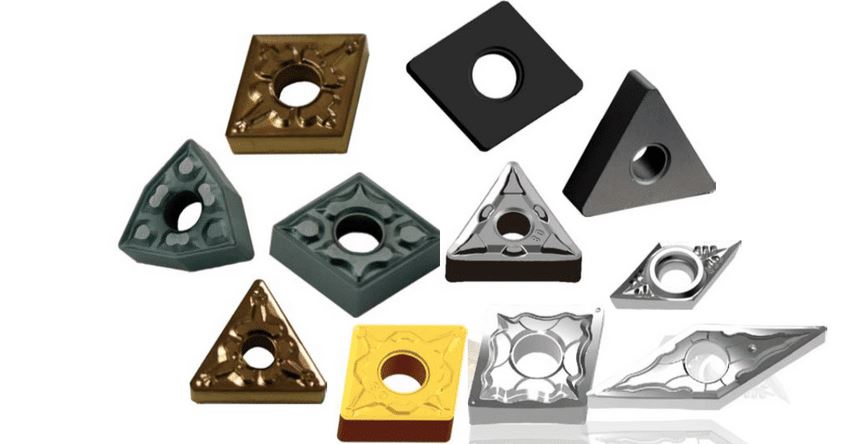
Plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont des outils de coupe utilisés dans les tours pour les opérations de tournage. Ils sont fabriqués en carbure, un composé de carbone et de tungstène, connu pour sa dureté et sa résistance à l'usure. Ces plaquettes sont conçues pour permettre la coupe à grande vitesse de matériaux résistants tels que l'acier, l'acier inoxydable, la fonte et les métaux non ferreux. Elles existent en différentes formes, tailles et qualités, chacune adaptée à des conditions de coupe et à des matériaux spécifiques.
Types de plaquettes de tournage en carbure
Il existe de nombreux types de plaquettes de tournage en carbure, chacun adapté à des tâches d'usinage différentes. Voici un tableau détaillé résumant les principaux types de plaquettes de tournage en carbure :
| Type d'insertion | Forme | Utilisation typique | Avantages | Inconvénients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type C (CNMG, CNMM) | Rhombique | Tournage général | Polyvalence et solidité des bords | Contrôle limité des puces |
| Type D (DNMG, DNMM) | 55° Rhombique | Opérations de finition | Bon pour les coupes légères | Bords fragiles |
| Type S (SNMG, SNMM) | Carré | Tournage robuste | Arêtes de coupe robustes | Moins de souplesse dans les formes |
| Type T (TNMG, TNMM) | Triangle | Ebauche et finition | Facilité d'utilisation multi-coins | Bords moins résistants |
| Type V (VNMG, VNMM) | 35° Rhombique | Finition soignée | Excellent pour les coupes précises | Fragile, moins durable |
| Type W (WNMG, WNMM) | Trigon | Dégrossissage à haut rendement | Très résistant, polyvalent | Formation complexe de copeaux |
| Type R (RNMG, RNMM) | Rond | Profilage, rainurage | L'insert le plus solide | Utilisation limitée des coins |
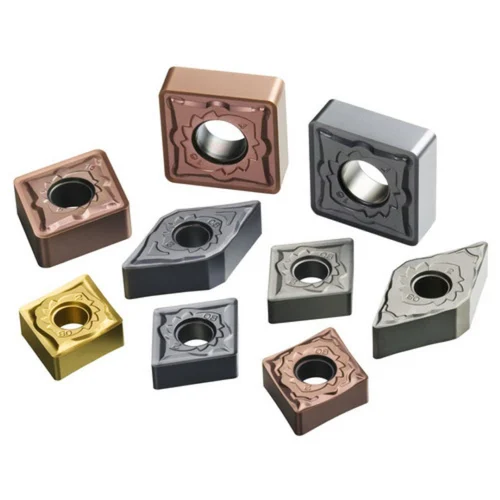

Applications des plaquettes de tournage en carbure
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont utilisées dans diverses industries en raison de leur polyvalence et de leur durabilité. Voici un tableau détaillant leurs applications :
| L'industrie | Application | Type d'insert recommandé |
|---|---|---|
| Automobile | Composants du moteur, arbres | Type C, Type S |
| Aérospatiale | Pièces de structure, pales de turbine | Type V, Type W |
| Dispositifs médicaux | Instruments chirurgicaux, implants | Type D, Type V |
| Pétrole et gaz | Raccords de tuyauterie, vannes | Type T, Type S |
| Ingénierie générale | Pièces de machines, outils | Type C, Type T |
| Électronique | Boîtiers, connecteurs | Type D, Type R |
| Matériel de construction | Composants hydrauliques, cadres | Type S, Type W |
Propriétés des matériaux des plaquettes de tournage en carbure
Comprendre les propriétés des matériaux plaquettes de tournage en carbure est essentiel pour choisir celui qui répondra le mieux à vos besoins spécifiques. Voici un tableau détaillé de ces propriétés :
| Propriété | Description |
|---|---|
| Dureté | Dureté élevée, typiquement 80-90 HRA |
| Solidité | Résistance à la rupture et à l'écaillage |
| Résistance à l'usure | Capacité à résister à l'usure des matériaux abrasifs |
| Conductivité thermique | Élevé, dissipe efficacement la chaleur |
| Stabilité chimique | Résistant à l'oxydation et aux réactions chimiques |
Composition et caractéristiques des plaquettes de tournage en carbure
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont composées de plusieurs éléments, chacun contribuant à leurs caractéristiques uniques :
| Élément | Pourcentage (%) | Caractéristique |
|---|---|---|
| Tungstène (W) | 70-80 | Assure la dureté et la résistance |
| Carbone (C) | 6-10 | Forme le composé de carbure, ce qui augmente la dureté |
| Cobalt (Co) | 5-10 | Liaison des particules de carbure de tungstène entre elles |
| Titane (Ti) | 1-5 | Augmente la ténacité et la résistance à l'usure |
| Tantale (Ta) | 1-3 | Améliore la résistance à haute température |
| Niobium (Nb) | 0.5-2 | Améliore la résistance aux chocs thermiques |





Dureté, solidité et résistance à l'usure
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure doivent équilibrer la dureté, la solidité et la résistance à l'usure pour être efficaces. Voici un tableau comparatif :
| Propriété | Description |
|---|---|
| Dureté | Garantit que la plaquette peut couper des matériaux difficiles. |
| La force | Empêche la rupture de l'insert sous haute pression. |
| Résistance à l'usure | Prolonge la durée de vie de l'insert en résistant à l'usure. |
Spécifications, tailles, formes et normes
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont disponibles dans différentes spécifications afin de répondre aux différentes tâches d'usinage. Voici un tableau détaillant ces spécifications :
| Spécifications | Détails |
|---|---|
| Taille | Taille des arêtes de coupe allant de 1/8″ à 1″. |
| Forme | Rhombique, carré, triangle, rond, trigone |
| Normes | ISO, ANSI, DIN, JIS |
Fournisseurs et détails des prix
Voici une liste de fournisseurs importants et leurs tarifs pour les plaquettes de tournage en carbure :
| Fournisseur | Pays | Fourchette de prix (par encart) |
|---|---|---|
| Kennametal | ÉTATS-UNIS | $5 – $30 |
| Sandvik Coromant | Suède | $8 – $40 |
| Matériaux Mitsubishi | Japon | $7 – $35 |
| Outils Seco | Suède | $6 – $33 |
| Outils Walter | Allemagne | $9 – $37 |
| Iscar | Israël | $10 – $45 |
| Sumitomo Electric | Japon | $8 – $38 |
| Tungaloy | Japon | $7 – $34 |
| Kyocera | Japon | $6 – $32 |
| Taegutec | Corée du Sud | $5 – $30 |
Comment choisir les bonnes plaquettes de tournage en carbure
Le choix de la bonne plaquette de tournage en carbure peut avoir un impact significatif sur l'efficacité de l'usinage et la qualité du produit. Voici un tableau pour vous guider dans le processus de sélection :
| Critères | Considérations |
|---|---|
| Type de matériau | Choisissez des plaquettes adaptées au matériau à usiner. |
| Vitesse de coupe | Les vitesses plus élevées nécessitent des plaquettes plus robustes et plus résistantes à l'usure. |
| Vitesse d'alimentation | Adaptez l'insert à votre taux d'alimentation pour une performance optimale. |
| Profondeur de coupe | Assurez-vous que la plaquette peut supporter la profondeur de coupe requise. |
| Puissance de la machine | Choisissez des plaquettes compatibles avec la puissance de votre machine. |
| Exigences en matière de finition | Choisissez des inserts qui permettent d'obtenir la finition de surface souhaitée. |
Comparaison des avantages et des limites
Chaque type de plaquette de tournage en carbure présente ses propres avantages et limites. Voici un tableau comparatif pour vous aider à mieux les comprendre :
| Type d'insertion | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|
| Type C | Polyvalence et solidité des bords | Contrôle limité des puces |
| Type D | Bon pour les coupes légères | Bords fragiles |
| Type S | Arêtes de coupe robustes | Moins de souplesse dans les formes |
| Type T | Facilité d'utilisation multi-coins | Bords moins résistants |
| Type V | Excellent pour les coupes précises | Fragile, moins durable |
| Type W | Très résistant, polyvalent | Formation complexe de copeaux |
| Type R | L'insert le plus solide | Utilisation limitée des coins |
Modèles de poudres métalliques pour les plaquettes de tournage en carbure
Voici quelques modèles de poudres métalliques spécifiques utilisées dans la production de plaquettes de tournage en carbure, ainsi que leur description :
- WC-Co (carbure de tungstène-cobalt):
- Description: Matériau composite composé de particules de carbure de tungstène liées à du cobalt.
- Caractéristiques: Dureté, ténacité et résistance à l'usure élevées.
- TiC (carbure de titane):
- Description: Un composé de carbure de titane et de carbone.
- Caractéristiques: Excellente résistance à l'usure et stabilité chimique.
- TaC (carbure de tantale):
- Description: Carbure réfractaire de tantale et de carbone.
- Caractéristiques: Point de fusion, résistance et dureté élevés.
- NbC (carbure de niobium):
- Description: Carbure de métal dur et réfractaire.
- Caractéristiques: Dureté élevée, conductivité thermique et résistance chimique.
- VC (carbure de vanadium):
- Description: Carbure de vanadium et de carbone.
- Caractéristiques: Améliore la ténacité et la résistance à l'usure.
- CrC (carbure de chrome):
- Description: Composé de chrome et de carbone.
- Caractéristiques: Dureté élevée et résistance à la corrosion.
- Mo2C (carbure de molybdène):
- Description: Un composé de carbure de molybdène.
- Caractéristiques: Bonne dureté et stabilité thermique.
- WC-TiC-TaC (carbure composite):
- Description: Combinaison de carbure de tungstène, de carbure de titane et de carbure de tantale.
- Caractéristiques: Résistance à l'usure et ténacité supérieures.
- ZrC (carbure de zirconium):
- Description: Carbure de zirconium.
- Caractéristiques: Dureté et conductivité thermique élevées.
- HfC (carbure de hafnium):
- Description: Carbure réfractaire de hafnium.
- Caractéristiques: Dureté exceptionnelle et point de fusion élevé.
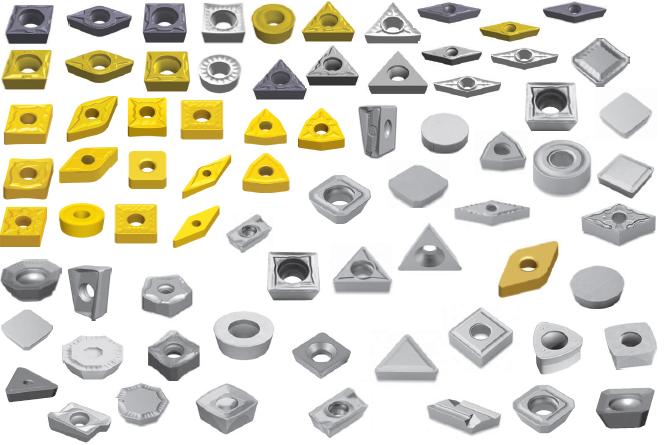

FAQ
De quoi sont faites les plaquettes de tournage en carbure ?
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont principalement composées de carbure de tungstène, de cobalt et d'autres éléments tels que le titane, le tantale et le niobium.
Pourquoi les plaquettes en carbure sont-elles privilégiées dans l'usinage ?
Ils sont préférés pour leur dureté, leur résistance à l'usure et leur capacité à supporter une coupe à grande vitesse.
Comment choisir la bonne plaquette de tournage en carbure ?
Tenez compte du type de matériau, de la vitesse de coupe, de la vitesse d'avance, de la profondeur de coupe, de la puissance de la machine et des exigences en matière de finition.
Quels sont les principaux types de plaquettes de tournage en carbure ?
Les principaux types sont les suivants : C-Type, D-Type, S-Type, T-Type, V-Type, W-Type et R-Type.
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure peuvent-elles être réutilisées ?
Oui, ils peuvent être indexés ou tournés pour utiliser plusieurs arêtes de coupe.
Quelle est la durée de vie d'une plaquette de tournage en carbure ?
Elle dépend du matériau usiné et des conditions de coupe, mais varie généralement de plusieurs heures à plusieurs jours d'utilisation continue.
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont-elles normalisées ?
Oui, ils respectent les normes internationales telles que ISO, ANSI, DIN et JIS.
Quelles sont les industries qui utilisent des plaquettes de tournage en carbure ?
Ils sont utilisés dans les secteurs de l'automobile, de l'aérospatiale, des appareils médicaux, du pétrole et du gaz, de l'ingénierie générale, de l'électronique et des équipements de construction.
Comment les plaquettes de tournage en carbure affectent-elles les performances d'usinage ?
Ils améliorent les performances d'usinage en fournissant des coupes précises, en réduisant les temps d'arrêt et en améliorant les finitions de surface.
Quelles sont les principales marques de plaquettes de tournage en carbure ?
Les marques les plus connues sont Kennametal, Sandvik Coromant, Mitsubishi Materials, Seco Tools, Walter Tools et Iscar.
Conclusion
Les plaquettes de tournage en carbure sont des outils indispensables à l'usinage moderne, offrant des performances inégalées en termes de dureté, de ténacité et de résistance à l'usure. Comprendre les différents types, applications et critères de sélection peut vous aider à choisir la plaquette adaptée à vos besoins spécifiques, à améliorer la productivité et à garantir des résultats de haute qualité dans vos opérations d'usinage.




