Carbure Les bandes - ces petits bouts de matériau très dur - sont les moteurs silencieux d'innombrables processus industriels. Même si elles ne font pas les gros titres, leur capacité à couper, à façonner et à résister à des conditions extrêmes les rend indispensables dans un nombre surprenant d'applications. Rejoignez-nous pour un voyage dans le monde des bandes de carbure, en découvrant leurs secrets et en explorant leurs principales utilisations.
Que sont exactement les bandes de carbure ?
Imaginez un matériau si dur qu'il rivalise avec la résistance du diamant. C'est l'essence même des bandes de carbure. Ces pièces minces et plates sont fabriquées en carbure cémenté, un matériau composite réputé pour sa dureté et sa résistance à l'usure exceptionnelles. La magie réside dans leur composition :
- Carbure de tungstène : L'ingrédient vedette, connu pour sa dureté extrême (presque aussi dure que le diamant !), constitue l'épine dorsale du matériau.
- Cobalt Liant : Agissant comme une colle, le cobalt lie les particules de carbure de tungstène entre elles, ce qui leur confère résistance et robustesse.
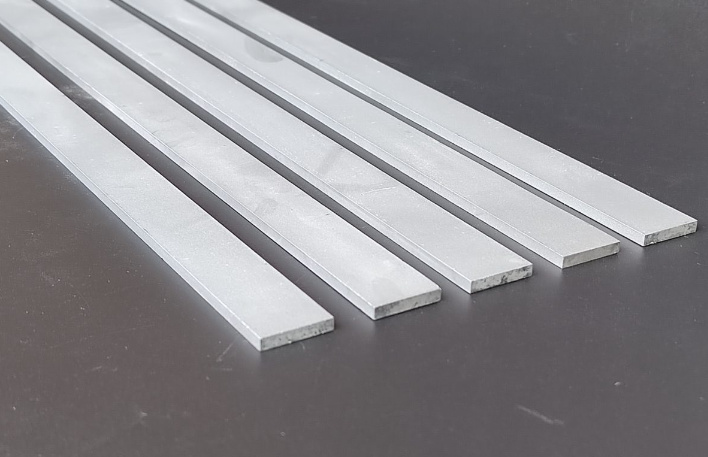
La fabrication d'un champion : comment naissent les bandes de carbure
La création de bandes de carbure est un témoignage de l'ingénierie de précision :
- Puissance de la poudre : Des poudres finement broyées de carbure de tungstène et de cobalt sont méticuleusement mélangées dans des proportions précises pour obtenir les propriétés souhaitées.
- Sous pression : Le mélange de poudres est ensuite soumis à une très forte pression dans des moules spécialisés, ce qui donne la forme initiale des bandes.
- Fusion ardente : Les bandes pressées subissent un processus de frittage à haute température dans une atmosphère contrôlée. Cette chaleur intense fusionne le liant de cobalt, solidifiant la bande en un matériau dense et incroyablement dur.
- Polir la perfection : Après le frittage, les bandes peuvent subir d'autres traitements, tels que le meulage, le polissage ou le revêtement, afin d'affiner leur finition de surface, leurs dimensions et d'améliorer leurs propriétés spécifiques.
Une bande pour chaque besoin : Types et propriétés
Les bandes de carbure ne sont pas uniques. Elles existent en différentes qualités, tailles et configurations, chacune adaptée à des applications spécifiques. Voici un aperçu de leur diversité :
Propriétés des bandes de carbure : Un aperçu
| Propriété | Description | Valeurs typiques |
|---|---|---|
| Dureté (HRA) | Résistance à la rayure et à l'indentation | 88-95 |
| Résistance à la rupture transversale (TRS) | Capacité à résister aux forces de flexion sans se rompre | 1500-3000 N/mm² |
| Densité | Masse par unité de volume | 13,5-15,0 g/cm³ |
| Taille des grains | Taille des particules de carbure de tungstène, influençant la dureté et la résistance à l'usure | 0,5-10 µm |
| Teneur en cobalt | Pourcentage de liant cobalt, ayant un impact sur la ténacité et la résistance à l'usure | 6-12% |
Tableau 1 : Principales propriétés des bandes de carbure
Principales applications des bandes de carbure
Les propriétés exceptionnelles des bandes de carbure les rendent idéales pour les applications exigeantes où la durabilité, la précision et la longévité sont primordiales. Examinons leurs principaux domaines de prédilection :
1. Le travail du bois : Apprivoiser le bois
- Conseils pour la scie : Les bandes de carbure forment les arêtes de coupe des lames de scies circulaires, de scies à onglets et de scies à table, permettant des coupes nettes et précises dans les bois durs, le contreplaqué et les matériaux composites.
- Mèches de routeur : Les plaquettes en carbure des mèches de toupie offrent des arêtes de coupe tranchantes et durables pour le façonnage, le profilage et l'assemblage dans les projets d'ébénisterie.
2. Travail des métaux : Façonner l'acier avec finesse
- Outils de coupe : Les plaquettes en carbure sont des composants essentiels des outils de tournage, des fraises et d'autres outils de coupe des métaux, permettant l'usinage de divers métaux avec une précision et une efficacité élevées.
- Pièces d'usure : Les bandes de carbure sont utilisées pour créer des composants résistants à l'usure dans les matrices de formage des métaux, les poinçons et d'autres outils, ce qui prolonge leur durée de vie et maintient la précision dimensionnelle.
3. La construction : A la conquête du béton et au-delà
- Sciage du béton : Des segments de bande de carbure forment les dents de coupe des lames de scie à béton, ce qui permet de couper le béton, l'asphalte et d'autres matériaux de construction durs.
- Forage et alésage : Les plaquettes en carbure sont utilisées dans les trépans, les carottes et autres outils de forage pour pénétrer dans le béton, la roche et d'autres matériaux difficiles.
4. Autres industries : Des horizons élargis
Les applications des bandes de carbure s'étendent bien au-delà de ces industries primaires. Leurs propriétés uniques les rendent précieuses dans :
- Fabrication : Guides, composants d'outillage et arêtes de coupe résistants à l'usure pour divers procédés de fabrication.
- L'agriculture : Outils de travail du sol, pièces d'usure pour machines agricoles et composants pour le traitement des récoltes.
- Impression et emballage : Lames de coupe, règles de rainage et autres pièces résistantes à l'usure pour les presses d'imprimerie et les équipements d'emballage.
FAQs : Percer les mystères des bandes de carbure
1. Qu'est-ce qui rend les bandes de carbure si dures ?
L'extrême dureté des bandes de carbure provient principalement des particules de carbure de tungstène qu'elles contiennent. Le carbure de tungstène est l'un des matériaux les plus durs connus, après le diamant.
2. Les bandes de carbure peuvent-elles être affûtées ?
Oui, les bandes de carbure peuvent être affûtées à l'aide de meules et d'équipements diamantés spécialisés. Toutefois, il est essentiel de maintenir des angles et des dégagements corrects pendant l'affûtage pour obtenir des performances optimales.
3. Quels sont les avantages de l'utilisation de bandes de carbure dans les outils de coupe ?
Les bandes de carbure offrent plusieurs avantages pour les outils de coupe, notamment
– Dureté et résistance à l'usure accrues : Il permet de prolonger la durée de vie des outils et de réduire les temps d'arrêt pour l'affûtage.
– Vitesses de coupe et avances plus élevées : Il permet des taux d'enlèvement de matière plus rapides et une productivité accrue.
– Amélioration de la qualité de coupe : Les coupes sont plus nettes et plus précises, avec moins d'éclats ou de déchirures.
4. Y a-t-il des problèmes de sécurité lorsque l'on travaille avec des bandes de carbure ?
En raison de leur extrême dureté, les bandes de carbure peuvent être fragiles et se briser en cas de chute ou de mauvaise manipulation. Portez toujours des lunettes de sécurité, des gants et des vêtements appropriés lorsque vous manipulez des bandes de carbure.
5. Comment choisir la bande de carbure adaptée à une application spécifique ?
Le choix de la bande de carbure appropriée implique la prise en compte de facteurs tels que
– Matière à découper : Différentes qualités de carbure sont optimisées pour la coupe de matériaux spécifiques (bois, métal, béton, etc.).
– Conditions de coupe : La vitesse de coupe, la vitesse d'avance et la profondeur de coupe influencent le choix de la nuance et de la géométrie du carbure.
– Durée de vie souhaitée de l'outil : Les applications nécessitant une durée de vie plus longue peuvent bénéficier d'une bande de carbure de qualité supérieure.
La consultation d'un fournisseur de carbure ou d'un expert en outillage peut fournir des conseils précieux pour sélectionner la bande de carbure la mieux adaptée à vos besoins.
Vous souhaitez acheter des bandes de carbure à un prix avantageux ? Cliquez sur ici.




