Débloquer l'efficacité : Fraises à deux goujures pour un enlèvement de matière et un état de surface supérieurs
Deux flûtes fraises en bout sont des outils essentiels dans le monde de l'usinage, appréciés pour leur capacité à enlever rapidement de la matière et à produire une finition de surface lisse. Ces outils de coupe polyvalents se présentent sous différentes configurations, chacune adaptée à des tâches d'usinage spécifiques. Ce guide complet se concentre sur deux types principaux de fraises à deux goujures : fraises carrées à queue droite et fraises sphériques à queue droite. Nous examinerons leurs caractéristiques uniques, leurs applications, leurs avantages et la manière de choisir le bon outil pour vos besoins d'usinage.
Comprendre la puissance de deux : pourquoi des fraises à deux cannelures ?
Fraises à deux cannelures se caractérisent par leurs deux arêtes de coupe, une conception qui offre des avantages indéniables :
- Évacuation efficace des puces : Les goujures plus larges entre les arêtes de coupe facilitent l'évacuation efficace des copeaux, ce qui est particulièrement important lorsque l'on travaille avec des matériaux plus tendres comme l'aluminium ou les plastiques qui ont tendance à produire des copeaux longs et filandreux. Ce flux de copeaux efficace évite la recoupe des copeaux, améliore l'état de surface et prolonge la durée de vie de l'outil.
- Augmentation de la vitesse de coupe et de l'avance : La réduction du contact avec l'arête de coupe permet d'augmenter les vitesses de coupe et d'avance par rapport aux fraises à plusieurs goujures. Cela se traduit par des temps d'usinage plus courts et une productivité accrue.
- Forces de coupe inférieures : Avec moins d'arêtes de coupe engagées dans le matériau, les fraises à deux goujures génèrent des forces de coupe plus faibles, ce qui les rend adaptées à l'usinage de pièces plus fines ou plus délicates où une force excessive pourrait entraîner des déformations ou des ruptures.
Deux types, des applications distinctes : Fraises à bouts carrés ou à bouts sphériques
Fraises à queue carrée à queue droite : Les maîtres des surfaces planes et des angles vifs
- Caractéristique déterminante : Caractérisé par un fond plat avec deux arêtes de coupe tranchantes, idéal pour créer des surfaces planes, des épaulements, des fentes et des poches avec des angles vifs.
- Applications : Largement utilisé dans les opérations de fraisage qui nécessitent des angles précis à 90 degrés, comme par exemple :
- Création de voies d'accès : Usinage de fentes dans un arbre ou un moyeu pour recevoir une clavette, qui empêche la rotation entre les deux composants.
- Etapes de l'usinage : Création de caractéristiques en escalier sur une pièce, souvent utilisées pour créer différents niveaux ou plates-formes.
- Profilage des bords : Découpe de bords droits et de profils sur l'extérieur d'une pièce avec des angles vifs.
- Fraisage de face : Création d'une surface plane par fraisage sur le dessus d'une pièce.
- Fraisage en plongée : Couper en ligne droite dans une pièce pour créer une fente ou une poche profonde.
Fraises à billes à queue droite : Sculpter les contours et adoucir les transitions
- Caractéristique déterminante : Ils se distinguent par leur pointe de coupe hémisphérique, qui permet de créer des surfaces profilées, des congés, des rayons et des transitions douces entre différentes caractéristiques.
- Applications : Excellente dans les applications nécessitant des surfaces lisses et fluides, telles que.. :
- Fabrication de moules : Création de cavités complexes, de détails et de surfaces lisses dans les moules utilisés pour le moulage par injection, le moulage par soufflage et d'autres processus de moulage.
- Couler : Usinage de cavités et de détails dans les matrices utilisées pour l'emboutissage, le formage et d'autres opérations de façonnage des métaux.
- Fraisage des contours : Usinage de formes et de contours complexes en 3D en suivant une trajectoire prédéfinie.
- Création de filets et de rayons : L'usinage des coins et des arêtes arrondis permet de réduire les concentrations de contraintes et d'améliorer la résistance d'une pièce.
- Finition de surfaces complexes : Création d'une finition lisse et esthétique sur les surfaces courbes ou profilées.
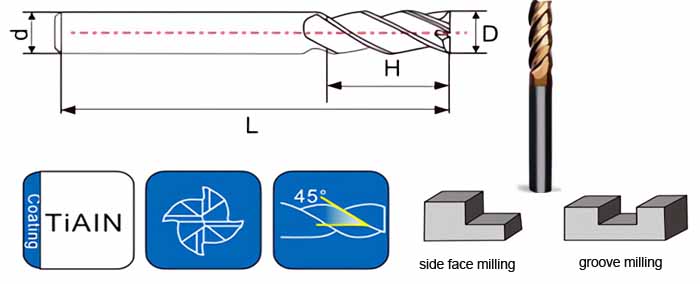
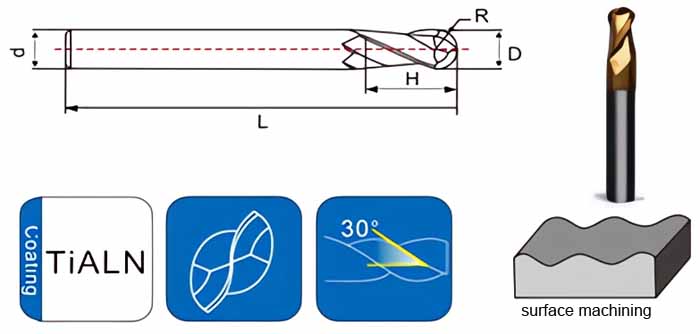
Disséquer la conception : Anatomie d'une fraise à deux cannelures
Les composants clés et leurs fonctions :
- Bords coupants : Deux arêtes rectifiées avec précision, responsables de l'enlèvement de matière, situées à la périphérie de la fraise. Leur géométrie et leur acuité ont un impact direct sur les performances de coupe et l'état de surface.
- Flûtes : Les rainures hélicoïdales qui courent le long du corps de la fraise offrent des voies d'évacuation des copeaux pendant l'usinage. Les fraises à deux goujures ont des goujures plus larges, ce qui améliore l'écoulement des copeaux.
- Tige : La partie cylindrique de la fraise qui est solidement maintenue dans le porte-outil de la fraiseuse. Les queues droites sont courantes pour les fraiseuses manuelles et certaines machines à commande numérique.
- Le corps : La section principale de la fraise, généralement fabriquée en carbure massif pour sa dureté, sa résistance à l'usure et sa capacité à maintenir des arêtes de coupe tranchantes.
- Longueur totale (OAL) : La longueur totale de la fraise, de la pointe du tranchant à l'extrémité de la tige.
- Diamètre de coupe : Le diamètre de la partie coupante de la fraise, qui détermine la largeur de coupe.
De la matière première à l'outil de précision : Le processus de fabrication
Un voyage de transformation :
- Préparation des ébauches en carbure : Le processus commence par une ébauche cylindrique en carbure, généralement produite par métallurgie des poudres. Les dimensions de l'ébauche sont légèrement supérieures à celles de la fraise finale.
- Opérations de broyage : Des machines de rectification de précision, utilisant souvent des meules diamantées, sont utilisées pour donner à l'ébauche en carbure la géométrie souhaitée pour la fraise. Il s'agit notamment de créer les arêtes de coupe, les goujures, la tige et les dimensions générales.
- Application du revêtement : Pour améliorer la durée de vie, la dureté et les performances de l'outil, divers revêtements, tels que TiN, TiCN ou AlTiN, peuvent être appliqués sur la fraise en utilisant des techniques telles que le dépôt chimique en phase vapeur (CVD) ou le dépôt physique en phase vapeur (PVD).
- Contrôle de la qualité et inspection : Des mesures rigoureuses de contrôle de la qualité sont appliquées tout au long du processus de fabrication afin de garantir que les fraises en bout respectent des tolérances dimensionnelles strictes, des exigences en matière d'état de surface et des normes de performance.
Les fraises à deux goujures en action : Un monde d'applications
De l'aérospatiale à l'automobile, et au-delà :
- Fabrication de moules : Création de cavités complexes, de détails et de surfaces lisses dans les moules utilisés pour le moulage par injection, le moulage par soufflage et d'autres processus de moulage. Les fraises à bout sphérique excellent dans la création de caractéristiques de moules profilés.
- Aérospatiale : Usinage d'alliages légers et très résistants tels que l'aluminium et le titane pour les composants aérospatiaux, nécessitant souvent la précision et les finitions lisses offertes par les fraises à billes.
- Automobile : Production de composants de moteurs, de pièces de transmission et d'autres pièces automobiles nécessitant des tolérances précises et des finitions lisses, souvent à l'aide de fraises carrées et de fraises à billes.
- Fabrication de dispositifs médicaux : Création d'implants médicaux, d'instruments chirurgicaux et de dispositifs complexes exigeant une grande précision, des surfaces lisses et la biocompatibilité. Les fraises à billes sont souvent préférées pour leur capacité à créer des géométries complexes.
- Usinage général et prototypage : Utilisées dans diverses industries pour créer des prototypes, des montages, des gabarits et d'autres composants usinés, les fraises à bouts carrés et à bouts sphériques trouvent des applications en fonction de la géométrie souhaitée.
TRUER : Votre partenaire de confiance pour les fraises à deux goujures de qualité supérieure
Un engagement inébranlable en faveur de la qualité et de la performance :
- Ingénierie de précision : Les fraises à deux goujures TRUER sont méticuleusement conçues pour offrir une précision, une répétabilité et une durée de vie exceptionnelles, garantissant des coupes précises et des performances constantes.
- Grades de carbure de première qualité : Nous ne nous procurons que des matériaux en carbure de la plus haute qualité, soigneusement sélectionnés pour leur dureté, leur ténacité et leur résistance à l'usure, ce qui garantit une durée de vie prolongée de l'outil et des performances optimales.
- Expertise spécifique à l'application : Notre équipe d'ingénieurs expérimentés vous fournit des conseils d'experts pour vous aider à naviguer dans le processus de sélection et à trouver la fraise à deux goujures idéale pour vos besoins d'usinage spécifiques.
- Capacités de personnalisation : TRUER est spécialisé dans la conception de solutions sur mesure pour répondre aux besoins des applications les plus exigeantes et les plus spécialisées. Il s'agit notamment d'adapter les géométries, les revêtements et les dimensions à vos spécifications exactes.
TRUER contre la concurrence : Analyse comparative des fournisseurs de fraises à deux cannelures
Choisir le bon partenaire pour vos besoins d'usinage :
| Fournisseur | Localisation | Fourchette de prix (par pièce, approximatif) | Spécialités |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRUER | Chine | $15 – $150+ | Une qualité sans compromis, des conceptions spécifiques aux applications, des prix compétitifs, un support client exceptionnel |
| Coupeur Niagara | ÉTATS-UNIS | $18 – $180+ | Vaste sélection de fraises à haute performance, reconnues pour leur innovation et leur qualité |
| Outils de coupe Ingersoll | ÉTATS-UNIS | $16 – $160+ | Une large gamme d'outils de coupe, notamment des fraises, des forets et des alésoirs, axés sur la productivité et la fiabilité |
| Kennametal | ÉTATS-UNIS | $20 – $200+ | Leader mondial des solutions pour l'usinage des métaux, offrant une gamme complète d'outils de coupe et de systèmes d'outillage |
Remarque : Les prix des fraises à deux cannelures sont influencés par une multitude de facteurs, notamment la taille de la fraise, le type, le matériau, le revêtement, la quantité commandée, etc. Il est toujours recommandé de demander des devis à plusieurs fournisseurs à des fins de comparaison.Vous souhaitez acheter une fraise à deux cannelures de grande qualité au prix le plus bas ? Cliquez ici ici..
Peser le pour et le contre : avantages et limites des fraises à deux goujures
Prendre des décisions éclairées en matière d'usinage : Une perspective équilibrée
| Fonctionnalité | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|
| Évacuation efficace des puces | - Les goujures plus larges permettent un excellent enlèvement des copeaux, en particulier dans les matériaux plus tendres.<br> - Réduction de la reprise des copeaux, d'où une amélioration de l'état de surface et une prolongation de la durée de vie de l'outil. | - Moins efficace dans les matériaux plus durs qui produisent des copeaux plus petits, où le conditionnement des copeaux peut devenir un problème. |
| Augmentation de la vitesse de coupe et de l'avance | - Le nombre réduit d'arêtes de coupe permet d'augmenter les vitesses de coupe et les vitesses d'avance, ce qui accroît la productivité.<br> - La réduction du temps de coupe peut se traduire par une diminution des coûts globaux d'usinage. | - Peut conduire à une finition de surface plus rugueuse que les fraises à plusieurs goujures, en particulier dans les matériaux plus durs. |
| Forces de coupe réduites | - Convient pour l'usinage de pièces plus fines ou plus délicates où une force excessive pourrait entraîner des déformations ou des ruptures.<br> - Peut réduire la déviation de l'outil, améliorant ainsi la précision | - Moins robustes que les fraises à plusieurs goujures, elles conviennent moins bien aux opérations d'ébauche lourdes. |
Approfondir : Des informations intéressantes sur les fraises à deux cannelures
Au-delà de l'essentiel :
- Coupe centrée et coupe non centrée : Les fraises à deux goujures peuvent être à coupe centrée ou non centrée. Les fraises à coupe centrale ont des arêtes de coupe qui s'étendent jusqu'au centre de l'outil, ce qui leur permet de plonger directement dans la pièce à usiner. Les fraises à coupe non centrée nécessitent un trou pré-percé ou une technique de rampe pour initier la coupe.
- Angle de l'hélice : L'angle d'hélice des goujures influence l'évacuation des copeaux et l'action de coupe. Un angle d'hélice plus élevé favorise une évacuation agressive des copeaux, tandis qu'un angle d'hélice plus faible permet une coupe plus douce, mais avec une évacuation des copeaux moins efficace.
- Fuite et équilibre : Le faux-rond et l'équilibre des fraises sont essentiels pour la précision, l'état de surface et la durée de vie de l'outil. Le faux-rond désigne toute excentricité ou oscillation dans la rotation de l'outil, tandis que le déséquilibre peut provoquer des vibrations et une usure prématurée. Les fraises de haute qualité sont fabriquées de manière à minimiser le faux-rond et à garantir un bon équilibre.
Foire aux questions : Répondre à vos questions sur les fraises à deux cannelures
1. Quels sont les principaux avantages de l'utilisation d'une fraise à deux goujures par rapport à une fraise à plusieurs goujures ?
Les fraises à deux goujures excellent dans l'évacuation efficace des copeaux, en particulier dans les matériaux plus tendres, et permettent des vitesses de coupe et des avances plus élevées grâce à la réduction du contact avec l'arête de coupe. Cela se traduit par des temps d'usinage plus courts et une productivité accrue.
2. Quand devrais-je choisir une fraise à queue carrée à queue droite plutôt qu'une fraise à queue sphérique à queue droite ?
Choisissez une fraise carrée à queue droite lorsque vous devez créer des surfaces planes, des épaulements, des fentes ou des poches avec des angles vifs à 90 degrés. Optez pour une fraise à queue sphérique lorsqu'il s'agit de créer des surfaces lisses et profilées, des congés, des rayons ou des transitions douces entre les caractéristiques.
3. Puis-je utiliser une fraise à deux goujures pour des opérations d'ébauche ?
Si les fraises à deux goujures peuvent être utilisées pour une légère ébauche, en particulier dans les matériaux plus tendres, elles sont généralement mieux adaptées aux opérations de finition ou aux coupes plus légères. Pour les gros travaux d'ébauche, il est recommandé d'utiliser des fraises à plusieurs goujures et de conception plus robuste.
4. Quels sont les signes courants d'usure d'une fraise à deux goujures et comment puis-je prolonger la durée de vie de l'outil ?
Les signes d'usure les plus courants sont l'augmentation des efforts de coupe, un mauvais état de surface, un échauffement excessif et l'écaillage ou la rupture des arêtes de coupe. Pour prolonger la durée de vie de l'outil, il convient d'utiliser les paramètres de coupe appropriés, d'appliquer efficacement le liquide de refroidissement, de maintenir un montage rigide et d'éviter une déviation excessive de l'outil.
5. Quelle est l'importance du revêtement d'une fraise à deux cannelures ?
Les revêtements améliorent la durée de vie, la dureté et les performances des outils. Le TiN est un revêtement polyvalent à usage général, le TiCN offre une dureté et une résistance à l'usure accrues, et l'AlTiN excelle dans les applications à haute température. Choisissez un revêtement en fonction du matériau usiné et de la durée de vie souhaitée de l'outil.




